Journal of Tourism & Hospitality
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-0269
ISSN: 2167-0269
Research Article - (2023)Volume 12, Issue 6
The consumer’s decision making process is influenced by the business and market environment. These factors play a significant role in strategic and business decision of organizations. The business and market environment factors are crucial for consumer’s satisfaction and increasing the profitability of organizations. The paper analyzed the consumers of hospitality services on the basis of the influence of business and market environment factors on their decision making while they availed the hospitality services. Business and market environment factors were categorized as qualitative and quantitative factors and then analyzed. Qualitative factors taken for study represents the qualitative variables of hospitality industry like quality of services, process handling, brand awareness, positioning, legal, social and political environment etc. on the other hand quantitative factors included the variables like price, distribution, packaging, people, infrastructure etc. The research paper contains a thorough review of studies related to hospitality sector, for which various books, websites and research papers were reviewed and consulted. The literature review led to the findings of significant gaps, on the basis of which researcher has formulated research problem and hypothesis. Researcher chalked out a suitable research and sampling design to carry the research. Research was carried out in Delhi and all the individuals above fifteen year of age were taken as the population. Sample size was calculated statistically and the study was carried out on the basis of gender. Researcher has used both primary and secondary data in this research. Questionnaires were used as sampling tools which were designed with the help of experts and were pretested. Data analysis was done with SPSS and appropriate statistical tool like measurement of internal consistence, skewness, kurtosis, mean, and chi-square statistics were used. The findings revealed that 95% of respondents are being influenced by these factors, but female respondents were found to be more influenced. Analysis of central tendency of both quantitative and qualitative factors revealed that both of them significantly influenced the consumer behavior of respondents, but a higher significant average mean value in case of qualitative factors revealed that they influenced the consumer behavior of respondents with a higher degree than quantitative factors. The study was further done on the basis of gender and analysis revealed that in both the categories i.e. qualitative as well as quantitative, female respondents (with a higher average mean) were more influenced than male respondents. The findings of study will help hospitality industry in formulating their strategies more efficiently and effectively, to satisfy consumers and increasing their revenues.
Business and market environment factors; Hospitality; Qualitative and quantitative factors; Brand; Positioning; Variables; Central tendency; Consumer behavior; Strategies; Revenues
Besides marketing mix and other marketing/operational strategies of hospitality industry, the consumer decision making process is being affected by the business and market environment. There is an important role of business and market environment factors in consumer satisfaction and increasing the profitability of organizations. The constituents of business and market environments are mentioned below.
Business environment factors
Business environment includes the factors those cannot be controlled by the management of organization. These factors includes customers, competitors, suppliers, government, social, political, economic, technology and legal environment. Some of these factors have a direct influence on the business enterprises while others influence the organizations indirectly. Therefore business environment may be defined as the total surrounding which directly or indirectly effect an organization. Some of these factors can be explained as follow.
Political environment: Is concerned with how government handles its economy. Political environment includes factors like laws related to environment, trade, tariffs and government stability. Political factors also includes goods/services which government want or don’t want to provide i.e. merit and demerit goods respectively. Political environment specifically involve health, education, infrastructure of a country basically.
Economic environment: Relates to the factors like growth of economy, exchange, interest and inflation rate these factors significantly affect organizations, their strategies and decision making process, for example rate of interest will effect a firms capital cost which further will affect its operational cost and this effect will adversely affect profitability of an organization. Similarly exchange rate will affect the supply and price of import and cost of exporting goods.
Social environment: Includes the factors related to consequences regarding health, growth rate of population, distribution of age, safety and carrer, preferences. Social trends affect demand of products and services. For example the aged population may be small and less willing to work which may increase the organizations labor cost. Therefore organization may adapt to various strategies regarding managing aged work force [1].
Technological, legal, and environmental factors: Technological environment influences the organizations in a big way and includes the factors like technology, research and development, automation and rate of change of technology. These factors help in determining the entry barriers, production level and outsourcing decisions. Changes in technology will definitely effect the innovation, cost and quality of products and services. The other aspect i.e. the legal environment which includes customer laws, antitrust law, laws related with health and safety directly makes an impact on organizations with respect to operational cost and demand of a product, if we talk about environment factors then it will includes the environmental and ecological sub factors like climate and weather which will effect industries like farming and hospitality.
Market environment factors
Market environment factors are elements those deals with the immediate area of operations of an organization that influences its performance and productivity. These factors are controllable and deal with the immediate markets. Some of these factors are product, price, promotion, distribution, physical evidences, process, infrastructure, quality, people, buyers, suppliers etc. As depicted in Figure 1 researcher identified and categorized above business and market environmental factors in qualitative and quantitative categories. The qualitative factors included the factors like quality of services, process handling, brand awareness etc. On the other hand the quantitative factors included, the factors like price of services, promotional strategies, distribution, infrastructure etc (Figure 1).
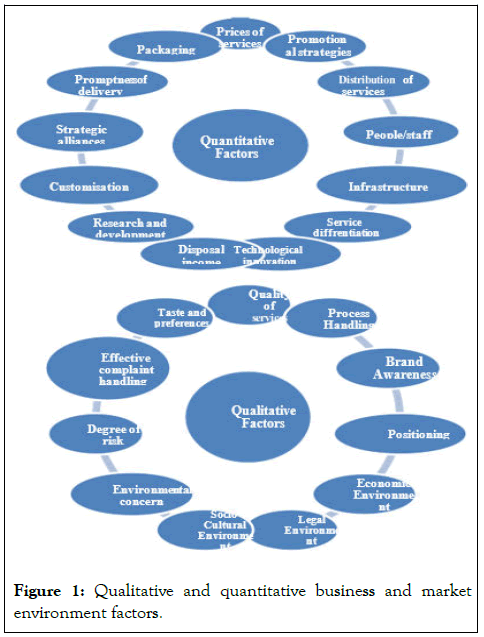
Figure 1: Qualitative and quantitative business and market environment factors.
Vavra TG in his book” improving your measurement of customer satisfaction” revealed some strategies those helped in measuring the customer satisfaction in a better way in hospitality organizations. The author emphasized that there are five precautions that any researcher should keep in mind if he/she want to measure the customer satisfaction. Smith AK, et al. in their paper “a model of customer satisfaction with service encounters involving failure and recovery” conducted a research with the help of a mix design model. The research was carried away on the belief that customers strongly showed their displeasure if there is a service failure, so it was suggested by the authors that organizations must reacts with better service recovery strategies to counter check the customer’s dissatisfaction. Jay Kandampully and Dwi Suhartanto in their research paper “consumers loyalty in the hotel industry” stated that the objectives of the study was to find the elements those influenced the positioning of hotel industry and affected the satisfaction level of consumers. The study helped researchers to understand the level of satisfaction of consumers towards hotel industry and the relation of the satisfaction with loyalty of consumers. Holjevac IA, et al. in their paper “customer satisfaction measurement in hotel industry: Content analysis study.” Found that to provide and maintain customers satisfaction in hotel industry was the biggest challenge for managers. The study was conducted in 25 hotels in opatija, in which researcher analyzed the guests comments cards of hotels and customers satisfaction management schemes run by hotels.
Willard Hom in his research paper “an overview of customer satisfaction models” classified and studied two models of customer’s satisfaction. These models considered customer satisfaction variables, as the construct of models and in this way author has theorized the elements of customer’s satisfaction. Author has provided these models of customer satisfactions from the point of view of marketing research. Roger J. Challanand Gabrielle Kyndt in their research paper business travelers’ perception of service quality: “A prefatory study of two european city centre hotels” had studied the level of satisfaction of customers for different attributes of hotel industry. The study was made with respect to the different categories of customers of hotel industry. Silvia Figiniand Paolo Giudici in their research paper “statistical model for customer satisfaction data measuring risks with ordinal variables” analyzed the various ways to collect the data which could be used to measure the satisfaction of consumers. Author discussed and proposed the various methodologies those were based on graphical model and data related with customers and its statistical analysis.
Namasivayam Karthik and Hinkin Timothy R in their research paper “the customer’s role in the service encounter: The effects of control and fairness” studied the real customer and service encounters in hotels. It was also observed that if customer loses a control while there was a service encounter then service quality is going to be highly deteriorated. The study further revealed that four characteristics of service provider have affected the perception of hotel consumers. Thanika Devi Juwaheer and Darren Lee Ross in their research paper. “A study of hotel guest perceptions in Mauritius” assessed consumer’s perception and expectation regarding services quality delivered by Mauritius hotels. Author identified the gaps between customer’s expectations and perceptions; besides this the other objective of this paper was to compare the perceptions of hotel managers regarding quality of services they delivered to their customers. Malthouse EC, et al. in their research paper “customer satisfaction across organizational units” analyzed the satisfaction level of consumers throughout all the units of organization [2].
The authors analyzed and described the models of customer satisfaction for investigating the relations of satisfaction with particular attributes of products and services. Karnikeya Budhwar in his research paper “an analysis of the gap between management perceptions and customer expectations” did the research to assess and measure the important factors that will influence the failure or success of any restaurant. The study found out the gaps in between managers perception and consumers perception in hospitality industry. Chand Mohinder and Kamra Krishan K in their book “basics of tourism theory, operation and practices” explored many interrelated parameters of hospitality and tourism industry. The book explained the origin and development of hospitality and tourism industry and also discussed the future prospects of it. It has also highlighted the factors those affected the psychology of tourists. The author further examined various qualitative characteristics required for the tourist’s products. Fyall Alan and Wanhill Stephen in their research paper “tourism-principals and practices” advocated that the main responsibility of a travel agent is to provide the hospitality and tourism services to the people. Travel Agents make a tie-up with suppliers and organizations and do the business on behalf of them. It was suggested that the agent’s main concern should be the choice of location to ensure ready availability of the principal’s products in the market place Biju MR in his book “sustainable dimensions of tourism management” highlighted tourism and hospitality industry aspects. The opening chapters of book analyzed and studied the evolution of tourism sector in Kerala (India) from regional, national and global perspective. The second part studied the recent issues in tourism like strategic management, service quality, personalization, natural environment and impact of terrorism in tourism industry.
The concluding part presented a few micro level studies from experimental perspectives. Feickert Julie, et al. in their research paper “safeguarding your customers: The guest’s view of hotel security” investigated the acceptance of increased tariffs for these security measures in hotels by the guests. The sample size of research was 930 respondents of different strata’s, and was proportionately divided on the basis of gender. Rizaldi and Vijay in their research paper “analysis of five SERVQUAL dimensions through disconfirmation theory” studied the dimensions of SERVQUAL scales. The dimensions were analyzed with the help of disconfirmation theory. Authors used this theory to elaborate the quality of services and satisfaction which has been perceived by the consumers. Gupta Sachin, et al. in their research paper “guest satisfaction and restaurant performance” collected the data from a restaurant chain which has a national presence and constructed a series of mathematical models. These models could predict how the customers satisfaction level will bring them back to the restaurants. Rooma in her research paper “developing a service quality questionnaire for the hotel industry in Mauritius” advocated that evaluation of customer satisfaction is very important for all organization in service sector so that they can show the better performance in cut throat competitive world. Ball Stephen, et al. in their book titled “contemporary hospitality and tourism”, mentioned about the growth and development of Indian hotel sector. The book identified and studied the main sectors of hospitality industry.
The book included the studies of hotels of India and China. Grigoroudis E and Siskos Y in their book “customer satisfaction evaluation” elaborated the problems, related with evaluation of customer satisfaction. Authors classified the customers in three categories.
Self-unit customers: This category consisted of people those have an attitude of discipline and a passion to excel.
Internal customers: These are the individuals those are employees of the organization.
External customers: This category contained the individuals those are the users or buyers of the organizations product or services.
Petermann Thomas and Christoph Revermann in their research paper “future trends in tourism” elaborated that in hospitality industry a shift in demographics and particularly a rise in senior citizens number will affect the industry trends in future. Data analysis revealed that in the year 2050 about 16.3% population of world will be below 20 and 36.9% will be of age 60 year or above Singh Mahesh Chandra in his study “medical tourism” stated that health care and medical tourism in India is growing with an annual rate of 30.7%. This industry is catering the patients of West Asia, Africa, US and Europe. India has become the most preferred destination for health care services because it is providing the high quality medical services at very low prices Mary Beth MC Enen in her article “The game has changed” stressed that customers were willing to develop relations with hospitality organizations. The author believed that old beliefs regarding customers satisfaction those brought success for organization may not be successful in future. Besides goods and services, the environment now is expecting more from hospitality organizations [3].
People are going to be very important for hospitality industry, these may be customers, employees and sales partners and they all are expecting long term strong relations with hospitality organizations. Simons Tony in his book “the integrity dividend” described about his study which was conducted on 6800 employees in 76 holiday inns. He found a significant positive relation in between the profits of hotels and behavioral integrity of each hotel. The findings revealed that managers those scored highest integrity from their employees also were found to earn the higher profits, which positively affected the quality of services and enhanced the retention of customers. Maria- Cristina, Sidonia Ravar, et al. in their research paper “developing creativity and innovation in hospitality industry” stated the impact of creativity and innovation in hospitality industry and concluded that it’s just the beginning stage. The objective of paper was to investigate the role of creativity and innovation on the decision making process of consumers while they availed hospitality services. Pavia Nadia, Grzini Jasmine in their research paper “specialization as a trend in modern hotel industry” determined changes in hotel competitiveness levels, which hotels achieved by implementation specialized label standards. The methodology of the study included the primary data collection and use of appropriate statistical tools. Kyrlakids Alex in his article “hospitality 2015, game changer or spectators” advocated that India and China both the countries will attain the same growth in tourism and hospitality sector by the year 2015, both the countries will be the top tourism and hospitality countries and will leave France, UK and Japan behind. Besides developing their domestic tourism market both the countries will emerge as top tourism brands all over the world. Anawade PA, Dr. Shilpak Bendale in their research paper “recent trends in hotel industry and its impact on individual spending”. The researcher reviewed the impact of the spending on hoteling by the individual. The rural area was considered for review and researcher tried to focus on the changes in spending pattern due to the recent trends in the hotel industry in rural areas.
The extensive literature review led to the findings of following gaps: Literature review revealed that most of the researches have been made in foreign countries like China, Malaysia, Cyprus, Darwin and very few in India. Therefore researcher carried the study in Delhi. Literature review also revealed that very few researches were made which specifically researched on the influence of business and market environmental factors on consumer behavior of people; therefore this was formulated as the objective of research.
Objective of research paper: An analysis of influence of business and environmental factors on consumer behavior in hospitality industry.
Hypothesis formulated: H1-business and market environment factors significantly influence consumer behavior in hospitality industry.
Benefit of study: By identifying and understanding the business and market environmental factors those influences the consumers behavior and affect the consumer’s choices to avail the hospitality services, organizations have an opportunity to develop marketing and operational strategies, which can fulfill the needs and desires of their customers and thus increasing their revenues and profitability. Studies done by researchers has identified various, market and environmental factors those influence the process of decision making of consumers during consuming hospitality services.
Consumer’s behavior is affected by cultural, psychological, social, personal, organizational and market and business environmental factors. These factors influence consumers to develop brand and product preferences. Understanding of the impact of these factors helps hospitality organizations to develop the marketing mix strategies to appeal to the preferences of the target market. A consumer may not take a decision in isolation, but may be influenced by other people those exist in various roles. Therefore consumer’s buying behavior is influenced by social, cultural, psychological and personal characteristics. An understanding of the affect of these factors is important for marketers to develop appropriate Marketing mix to the needs of target customers.
Research design used: Exploratory and descriptive
Area of study: Because of nearness and approachability for researcher, Delhi is taken as the city to carry out the research.
The other reason besides it is the presence of knowledgeable and qualified consumers in Delhi. Sample was collected proportionately from all the zones of Delhi.
Population: Population consists of all the individuals of Delhi those are 15 yrs and are availing hospitality services. The age slot was taken because individual of this age and above, are aware and understand hospitality services well.
Sample size: The sample size was calculated statistically. The total population of hospitality consumers above 15 yrs is 10250000 (Approx), at 95% confidence level and at a confidence interval of 4 the sample size came out to be 1067.
Sampling technique
The study was carried out with the help of multistage sampling which is followed by convenience sampling. 1st stage of sampling involved dividing the population as per the zones followed by 2nd stage which includes dividing the population further on the basis of gender.
Questionnaire development
Data was collected through structured questionnaires. Questions were carefully drafted after going through the research objectives, all the essentials of questionnaire constructions are taken care of. Questionnaire was consulted with experts and was pretested before being induced to the population.
Data analysis tools
The data was analyzed on SPSS and the tools like, measurement of internal consistency, frequency analysis, measurement of central tendency and chi square statistics were used.
Analysis of business and market environment factors
The Table 1 and Figure 2 respectively, depicted that almost all the respondents (95.32%) agreed that business environment and market factors played a significant role in decision making while they availed the hospitality services. It is pertinent to mention that 46.77% male and 48.55% female respondents considered these factors as an important aspect in decision making while they availed hospitality services. Data analysis further revealed that female gender was more influenced by these factors.
| Gender | Male | Female | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | 499 (46.77 ) | 518 (48.55) | 1017 (95.32) |
| No | 34 (3.19) | 16 (1.50) | 50 (4.69) |
| Total | 533 (49.95) | 534 (50.05) | 1067 |
Table 1: Analysis of respondents on the basis of influence of business environment and market factors.
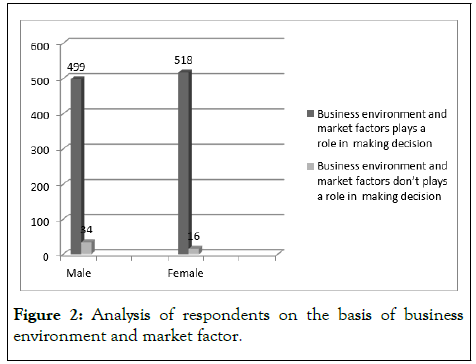
Figure 2: Analysis of respondents on the basis of business environment and market factor.
Analysis of business and market environmental factors (qualitative)
Business and market environment factors can be divided in two categories qualitative and quantitative. The factors those cannot be quantified are put in qualitative factors category like service quality, process handling, brand awareness, position of services, economic, legal, social environment and degree of risk etc [3].
Influence of quality of services: As depicted in Table 2 a mean of 4.16 in case of male respondents concluded that quality of services influenced their decision significantly, to avail the hospitality services. The conclusion is supported by the Chi-square value which comes at 370.18, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed and is leptokurtic. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 4.22 revealed that female respondents too agreed that quality of services significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, but the level of influence was more than male gender, which further is supported by Chi square value which comes out to be 492.56, at a significance level of 0.000. In female gender distribution is again negatively skewed and is leptokurtic.
Influence of effective process handling: As depicted in Table 2 a mean of 3.82 in case of male respondents revealed that effective process handling of hospitality industry influenced their decision significantly to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes out to be 700.98, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.747 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of 2.670. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 4.02 shows that female respondents strongly agreed that effective process handling of hospitality industry influenced their decision to avail hospitality services significantly, but degree of influence was more than male gender, which is further is supported by Chi square value of 695.25, and significance level of 0.000. In female gender distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -2.250 and is leptokurtic with kurtosis value of 6.503.
Influence of brand awareness: As depicted in Table 2 a mean of 3.55 in case of male respondents revealed that, brand awareness of hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality Services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 435.07 and significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.176 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.821. On the other hand in case of female population a mean of 3.77 shows that female respondent too agreed that brand awareness of hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services but the degree of influence was higher than male gender, which is further, is supported by Chi square value of 678.70, at a significance level of 0.000. In female gender distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.568 and is almost mesokurtic with kurtosis value of 2.958 [4].
Influence of positioning of hospitality services: As depicted in Table 2 a mean of 3.38 in case of male respondents revealed that, positioning of hospitality services significantly influenced their decision to avail them. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 399.56, and significance level of 0.000, the distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -0.866 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of -0.831. On the other hand in case of female population a Mean of 3.50 showed that female respondents too agreed that positioning of hospitality services influenced their decision to avail them, but the degree of influence was higher than male gender, which further is supported by Chi square value of 454.42 and significance level of 0.000. In female gender distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -0.831 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of -0.831.
Influence of economic environment: As depicted in Table 2 a mean of 3.49 in case of male respondents revealed that, economic environment significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 247.78, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -0.965 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.451. On the other hand in case of female gender a mean of 3.67 shows that female respondent too agreed that economic environment significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, but the degree of influence was more than male gender which further is supported by Chi square value of 485.93 and significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis, distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.255 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.906 [5].
Influence of legal environment: As depicted in Table 2 a mean of 3.43 in case of male respondents revealed that, legal environment significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 318.35 and significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -0.924 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.146 on the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.62 shows that female respondents too agreed that legal environment influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, which further is supported by Chi square value of 601.05 and significance level of 0.000. In female gender distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.231 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.280.
Influence of socio-cultural environment: As depicted in Table 2 a mean of 3.43 in case of male respondents revealed that, cultural environment significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 296.40 and significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -0.924 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.214. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.66 shows that female respondents too agreed that socio-cultural environment significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services but the degree of influence was higher than male respondents, which further is supported by Chi square value of 571.12 and significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.300 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.634.
Influence of environmental concern of hospitality industry: As depicted in Table 2 a mean of 3.61 in case of male respondents revealed that, environmental concern shown by hospitality industry, significantly influenced their decision to avail them. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 483.56, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.287 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.010. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.79 shows that female respondents too agreed that environmental concerns shown by hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail these services, what the degree of influences was more than male respondents, which further is supported by Chi square value of 809.23 and significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.300 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.634 [6].
Influence of degree of risk: As depicted in Table 2 a mean of 3.51 in case of male respondents revealed that, degree of risk significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 364.78, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.012 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of .320. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.50 shows that female respondent too agreed that degree of risk significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, which further is supported by Chi square value of 573.23, at a significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -0.934 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.373.
Influence of effective complaint handling: As depicted in Table 2 a mean of 3.93 in case of male respondents revealed that, effective complaint handling by hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail these services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 528.68 and significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.616 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.991. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 4.00 shows that female respondents strongly agreed that effective complaint handling by hospitality industry, significantly influenced their decision to avail these services, but the degree of influence was found more than male gender which further is supported by Chi square value of 622.54 and significance level of 0.000. In female gender distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.629 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 2.588.
Influence of taste and preferences: As depicted in Table 2 a Mean of 3.95 in case of male respondents revealed that taste and preferences significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services.
This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 627.59, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.871 and is leptokurtic with kurtosis value of 3.168 On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 4.10 shows that female respondents strongly agreed that taste and preferences, significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, but the degree of influence was more than the male respondents, which further is supported by Chi square value of 892.13 and significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -2.340 and is leptokurtic with kurtosis value of 6.967 [6].
| Qualitative factors | Gender | To a very large extent | To large extent | Not at all | To some extent | To a very small extent | N | Mean | S.D | Sk. | Kt. | Ch. sq. | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality of services influenced the choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 244 (45.8) | 244 (45.8) | 0 (0) | 11 (2.1) | 0 (0) | 533 | 4.16 | 1.24 | -2.393 | 5.469 | 370.18 | 0 |
| Female | 200 (37.5) | 311 (58.2) | 0 (0) | 6 (1.1) | 0 (0) | 534 | 4.22 | 0.938 | -2.871 | 10.791 | 492.56 | 0 | |
| Effective process handling influenced the choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 149 (28.0) | 290 (54.4) | 15 (2.8) | 44 (8.3) | 1 (0.2) | 533 | 3.82 | 1.2837 | -1.747 | 2.67 | 700.98 | 0 |
| Female | 148 (27.7) | 329 (61.6) | 15 (2.8) | 25 (4.7) | 0 (0.0) | 534 | 4.02 | 1.0014 | -2.25 | 6.503 | 695.25 | 0 | |
| Brand awareness influenced choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 119 (22.7) | 248 (46.5) | 46 (8.6) | 84 (15.8) | 2 (0.4) | 533 | 3.55 | 1.3416 | -1.176 | 0.821 | 435.07 | 0 |
| Female | 110 (20.6) | 300 (56.2) | 56 (10.5) | 49 (9.2) | 2 (0.4) | 534 | 3.77 | 1.0836 | -1.568 | 2.958 | 678.7 | 0 | |
| Positioning of hospitality services influenced choice to avail them | Male | 105 (19.7) | 233 (43.7) | 31 (5.8) | 124 (23.3) | 6 (1.1) | 533 | 3.38 | 1.3901 | -0.866 | -0.034 | 399.56 | 0 |
| Female | 108 (20.2) | 244 (45.7) | 32 (6.0) | 124 (23.2) | 9 (1.7) | 534 | 3.5 | 1.2669 | -0.831 | -0.001 | 454.42 | 0 | |
| Economic environment influenced choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 133 (25.0) | 186 (34.9) | 95 (17.8) | 83 (15.6) | 2 (0.4) | 533 | 3.49 | 1.36 | -0.965 | 0.451 | 247.78 | 0 |
| Female | 106 (19.9) | 260 (48.7) | 91 (17) | 58 (10.9) | 2 (0.4) | 534 | 3.67 | 1.11 | -1.255 | 1.906 | 485.93 | 0 | |
| Legal environment influenced choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 116 (21.8) | 21 (40.9) | 55 (10.3) | 102 (19.1) | 8 (1.5) | 533 | 3.43 | 1.38 | -0.924 | 0.146 | 318.35 | 0 |
| Female | 94 (17.6) | 289 (54.1) | 47 (8.8) | 78 (14.6) | 9 (1.7) | 534 | 3.62 | 1.16 | -1.231 | 1.28 | 601.05 | 0 | |
| Socio-cultural environment influences choices for availing these services | Male | 131 (24.6) | 206 (38.6) | 59 (11.1) | 97 (18.2) | 6 (1.1) | 533 | 3.43 | 1.38 | -0.924 | 1.214 | 296.4 | 0 |
| Female | 101 (18.9) | 283 (53) | 60 (11.2) | 64 (12.0) | 9 (1.7) | 534 | 3.66 | 1.15 | -1.3 | 1.634 | 571.12 | 0 | |
| Environmental concern of services providers influences choice for availing these services | Male | 127 (23.8) | 259 (48.6) | 37 (6.9) | 67 (12.6) | 9 (1.7) | 533 | 3.61 | 1.35 | -1.287 | 1.01 | 483.56 | 0 |
| Female | 108 (20.2) | 323 (60.5) | 28 (5.2) | 49 (9.2) | 9 (1.7) | 534 | 3.79 | 1.11 | -1.661 | 2.892 | 809.23 | 0 | |
| Degree of risk associated with Hospitality services, influenced choice | Male | 129 (24.2) | 224 (42.0) | 42 (7.9) | 100 (18.8) | 4 (0.8) | 533 | 3.51 | 1.38 | -1.012 | 0.32 | 364.78 | 0 |
| Female | 87 (16.3) | 273 (51.1) | 32 (6.0) | 123 (23) | 2 (0.4) | 534 | 3.5 | 1.2 | -0.934 | 0.373 | 573.23 | 0 | |
| Effective process handling influenced choices for availing hospitality service | Male | 224 (42.0) | 200 (37.5) | 26 (4.9) | 48 (9.0) | 1 (0.2) | 533 | 3.93 | 1.36 | -1.616 | 1.991 | 528.68 | 0 |
| Female | 201 (37.6) | 242 (45.3) | 14 (2.6) | 59 (11.0) | 1 (0.2) | 534 | 4 | 1.17 | -1.629 | 2.588 | 622.54 | 0 | |
| Consumers taste and preferences influenced choices for availing hospitality services | Male | 195 (36.6) | 250 (46.9) | 24 (4.5) | 29 (5.4) | 1 (0.2) | 533 | 3.95 | 1.291 | -1.871 | 3.168 | 627.59 | 0 |
| Female | 175 (32.8) | 309 (57.9) | 13 (2.4) | 19 (3.6) | 1 (0.2) | 534 | 4.1 | 1 | -2.34 | 6.967 | 892.13 | 0 |
Table 2: Descriptive analysis of qualitative factors influencing consumer behavior.
Analysis of business and market environmental factors (quantitative)
The other categories of factors those influenced the consumer behavior of respondents while they availed hospitality services are quantitative factors e.g. price, distribution, promotional strategies, people, infrastructure etc. These factors play an important role in decision making process while consumers availed hospitality services [7].
Influence of prices of services: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.71 in case of male respondents revealed that prices of services significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 569.32 and significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed and is leptokurtic.
On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.77 revealed that female respondents too agreed that prices of services significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, but the degree of influence was more than male gender, which further is supported by Chi square value which comes out to be 735.21, and significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed and is leptokurtic.
Influence of distribution of services: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.39 in case of male respondents revealed that distribution of services significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 792, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.184 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.679.
On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.62 shows that female respondents too agreed that distribution of services significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, but the degree of influence was more than male gender, which further is supported by Chi square value of 813.07 and significance level of 0.000.
In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.526 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 2.139.
Influence of promotional strategies: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.53 in case of male respondents revealed that, promotional strategies of hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 778.38 and significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.431 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.449.
On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.54 shows that female respondents too agreed that promotional strategies of services significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, which further is supported by Chi square value of 786.20 and significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.304 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 2.139 [8].
Influence of people/staff: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.54 in case of male respondents revealed that people/staff of hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail the services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 316.80, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -.898 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.077.
On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.66 showed that female respondents too agreed that people/staff of hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail the services, but the degree of influence was found to be more than male gender, which further is supported by Chi square value of 414.38, at a significance level of 0.000. In female respondents analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -0.849 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of -0.849.
Influence of infrastructure and layout: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.79 in case of male respondents revealed that infrastructure and layout of hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail the services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 263.09, at a significance level of 0.000.
The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.338 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.109. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 4.04 revealed that female respondents strongly agreed that infrastructure and layout of hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail these services, but the degree of influence was higher than the male respondents, which further is supported by Chi square value of 483.75 and significance level of 0.000.
In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.795 and is leptokurtic with kurtosis value of 3.406.
Influence of differentiation of services: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.60 in case of male respondents revealed that differentiation significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 468.17, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.219 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.783.
On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.72 revealed that female respondents strongly agreed that taste and service differentiation, significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, but the degree of influence was more than male respondents, which further is supported by Chi square value of 552.83, at a significance level of 0.000.
In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.212 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.031 [9].
Influence of technological innovation: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.57 in case of male respondents revealed that, technological innovations in hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail these services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 614.69, at a significance level of 0.000.
The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.351 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.451. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.70 revealed that they too agreed that technological innovations in hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, but the degree of influence was higher than male respondents, which further is supported by Chi-value of 660.36, at a significance level of 0.000.
In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.292 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.464.
Influence of disposable income: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.54 in case of male respondents revealed that, disposable income significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 496.24, at a significance level of . 000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.087 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.424.
On the other hand in case of female population a mean of 3.56 revealed that female respondents too agreed that disposable income significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality Services, which further is supported by Chi square value of 641.73, and significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.043 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.557.
Influence of R and D of hospitality industry: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.34 in case of male respondents revealed that, R and D of hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail the services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 451.86, at a significance level of 0.000.
The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.074 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of -0.446. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.40 showed that female respondents too agreed that R and D of hospitality industry significantly influenced their decision to avail the services, which further is supported by Chi square value of 637.32, and significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.135 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of -0.573 [10].
Influence of in-house animation: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.30 in case of male respondents revealed, that in-house animation significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 428.27, and significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -0.963 and is platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.138.
On the other hand in case of female population a mean of 3.39 revealed that female respondents too agreed that in-house animation significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, but the degree of influence was more than male gender, which further is supported by Chi square value of 403.55, and significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis, distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -0.805 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of -0.273.
Influence of customization of hospitality services: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.58 in case of male respondents revealed that hospitality industry products significantly influenced their decision to avail these services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 622.63, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.392 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.485. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.73 revealed that female respondents too agreed that customization of hospitality products significantly influenced their decision to avail them, but the degree of influence was more than male gender, which further is supported by Chi square value of 622.49, and significance level of 0.000. In female analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.411 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 2.182.
Influence of strategic alliances: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.44 in case of male respondents revealed that, strategic alliances of hospitality organizations with reputed brands significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 474.13, and significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.121 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of .534. On the other hand in case of female population a mean of 3.67 revealed that female gender too agreed that strategic alliances of hospitality organizations significantly influenced their decision to avail the services, but the degree of influence was more than male gender, which further is supported by Chi square value of 676.47, and significance level of 0.000. In female analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.450 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 2.187 [11].
Influence of promptness of delivering the services: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.82 in case of male respondents revealed that male respondents agreed that, promptness of service delivery Chi square value which comes at 598.56, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.645 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 2.215. on the other hand in case of female population a mean of 3.93 shows that female respondents strongly agreed that promptness in service delivery shown by hospitality industry, significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, but the level of influence was more than male gender, which further is supported by Chi square value of 817.23, at a significance level of 0.000. In female analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.300 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.634.
Influence of service packaging: As depicted in Table 3 a mean of 3.61 in case of male respondents revealed that, service packaging significantly influenced their decision to avail the hospitality services. This conclusion is supported by the Chi square value which comes at 447.90, at a significance level of 0.000. The distribution is negatively skewed with a value of -1.189 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 0.553. On the other hand in case of female respondents a mean of 3.80 revealed that female respondents strongly agreed that service packaging, significantly influenced their decision to avail hospitality services, but the degree of influence was greater than male gender, which further is supported by Chi square value of 642.99, at a significance level of 0.000. In female gender analysis distribution is again negatively skewed with a value of -1.441 and is Platykurtic with kurtosis value of 1.0602 [12].
| Factors | Gender | To a very large extent | To large extent | Not at all | To some extent | To a very small extent | N | Mean | S.D | Sk. | Kt. | Ch. sq. | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prices of services influenced choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 149 (28) | 265 (49.7) | 14 (2.6) | 64 (12) | 7 (13) | 533 | 3.71 | 1.3598 | -1.425 | 1.346 | 569.32 | 0 |
| Female | 124 (23.2) | 303 (56.7) | 11 (2.1) | 73 (13.7) | 6 (1.1) | 534 | 3.77 | 1.1674 | -1.455 | 1.913 | 735.21 | 0 | |
| Distribution of services influenced choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 124 (23.2) | 303 (56.7) | 11 (2.1) | 73(13.7) | 6 (1.1) | 533 | 3.39 | 1.2896 | -1.184 | 0.679 | 792 | 0 |
| Female | 56 (10.5) | 363 (68) | 5 (0.9) | 73 (17.4) | 0 (0) | 534 | 3.62 | 1.0853 | -1.526 | 2.139 | 813.07 | 0 | |
| Promotional strategies influenced choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 74 (13.9) | 322 (60.4) | 23 ( 4.3) | 75 (14.1) | 5 (0.9) | 533 | 3.53 | 1.2778 | -1.431 | 1.449 | 778.38 | 0 |
| Female | 70 (13.1) | 326 (610) | 25 (4.7) | 68 (12.7) | 28 (5.2) | 534 | 3.54 | 1.21 | -1.304 | 1.033 | 786.2 | 0 | |
| Staff/People influenced choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 170 (31.9) | 176 (33) | 35 (6.6) | 115 (21.6) | 3 (0.6) | 533 | 3.54 | 1.456 | -0.898 | 0.077 | 316.8 | 0 |
| Female | 175 (32.8) | 191 (35.8) | 19 (3.6) | 129 (24.2) | 3 (0.6) | 534 | 3.66 | 1.3343 | -0.849 | 0.161 | 414.38 | 0 | |
| Infrastructure and layout of services influenced choices for availing hospitality services | Male | 201 (37.7) | 193 (36.2) | 36 (6.8) | 69 (12.9) | 3 (0.6) | 533 | 3.79 | 1.3946 | -1.338 | 1.109 | 263.09 | 0 |
| Female | 203 (38) | 254 (47.6) | 9 (1.7) | 51 (9.6) | 0 (0) | 534 | 4.04 | 1.1352 | -1.795 | 3.406 | 483.75 | 0 | |
| Services differentiation influenced choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 128 (24) | 254 (47.7) | 32 (6) | 76 (14.3) | 9 (1.7) | 533 | 3.6 | 1.37 | -1.219 | 0.783 | 468.17 | 0 |
| Female | 137 (25.7) | 264 (49.4) | 23(4.3) | 86 (16.1) | 7 (1.3) | 534 | 3.72 | 1.22 | -1.212 | 1.031 | 552.83 | 0 | |
| Technological innovations influenced choice to avail hospitality services | Male | 99 (18.6) | 291 (56.6) | 31(5.8) | 73 (13.7) | 5 (0.9) | 533 | 3.57 | 1.3 | -1.351 | 1.256 | 614.69 | 0 |
| Female | 113 (21.2) | 292 (54.7) | 24 (4.5) | 86 (16.1) | 2 (0.4) | 534 | 3.7 | 1.16 | -1.292 | 1.464 | 660.36 | 0 | |
| My disposable income influenced choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 125 (23.5) | 251 (47.1) | 14 (2.6) | 107 (20.1) | 2 (0.4) | 533 | 3.54 | 1.38 | -1.087 | 0.424 | 496.24 | 0 |
| Female | 95 (17.8) | 286 (53.6) | 17 (3.2) | 115 (21.5) | 4 (0.7) | 534 | 3.56 | 1.2 | -1.043 | 0.557 | 641.73 | 0 | |
| Research and development activities, influenced choice | Male | 68 (12.8) | 266 (12.8) | 68 (12.8) | 77 (14.4) | 20 (3.8) | 533 | 3.34 | 1.3279 | -1.074 | 0.446 | 451.86 | 0 |
| Female | 52 (9.7) | 303 (56.7) | 57 (10.7) | 71 (13.3) | 34 (6.4) | 534 | 3.4 | 1.2119 | -1.135 | 0.573 | 637.32 | 0 | |
| In-house animations and outdoor events influenced choice to avail these services | Male | 71 (13.3) | 259 (48.6) | 55 (10.3) | 93 (17.4) | 21 (3.9) | 533 | 3.3 | 1.3541 | -0.968 | 0.138 | 428.27 | 0 |
| Female | 94 (17.6) | 248 (46.4) | 38 (7.1) | 100 (18.7) | 37 (6.9) | 534 | 3.39 | 1.32 | -0.805 | 0.273 | 403.55 | 0 | |
| Customization of services influenced decision to avail these services | Male | 95 (17.8) | 293 (55) | 38 (7.1) | 72 (13.5) | 1 (0.2) | 533 | 3.58 | 1.28 | -1.392 | 1.485 | 622.63 | 0 |
| Female | 112 (21) | 289 (54.1) | 51 (9.6) | 63 (11.8) | 2 (0.4) | 534 | 3.73 | 1.12 | -1.411 | 2.182 | 622.49 | 0 | |
| Strategic alliance of services providers with reputed brands influenced decision to avail these services | Male | 91 (17.1) | 267 (50.1) | 46 (8.6) | 80 (15) | 15 (2.8) | 533 | 3.44 | 1.35 | -1.121 | 0.534 | 474.13 | |
| Female | 89 (16.7) | 305 (57.1) | 59 (11) | 54 (10.1) | 10 (1.9) | 534 | 3.67 | 1.11 | -1.45 | 2.187 | 676.47 | 0 | |
| Promptness of delivering the services influenced choice for availing hospitality services | Male | 162 (30.4) | 266 (49.9) | 24 (4.5) | 42 (7.9) | 5 (0.9) | 533 | 3.82 | 1.31 | -1.645 | 2.215 | 598.56 | 0 |
| Female | 143 (26.8) | 313 (58.6) | 20 (3.7) | 33 (6.2) | 8 (1.5) | 534 | 3.93 | 1.09 | -1.903 | 4.068 | 817.23 | 0 | |
| Services Packaging influenced choices for availing hospitality services | Male | 147 (27.6) | 241 (45.2) | 21 (3.9) | 75 (14.1) | 15 (2.8) | 533 | 3.61 | 1.41 | -1.189 | 0.553 | 447.9 | 0 |
| Female | 149 (27.9) | 277 (51.9) | 16 (3) | 56 (10.5) | 19 (3.6) | 534 | 3.8 | 1.23 | -1.441 | 1.602 | 642.99 | 0 |
Table 3: Descriptive analysis of quantitative factors influencing consumer behavior [12].
Analysis of respondents on the basis of the influence of business and market environmental factors revealed that majority of respondents (95%) were being influenced by these factors, But female respondents were found to be more influenced. Business and market environment factors were categorized as qualitative and quantitative factors. Qualitative factors represents the qualitative variables of hospitality industry like quality of services, process handling, brand awareness, positioning, legal, social and political environment etc. On the other hand quantitative factors included the variables like price, distribution, packaging, people, infrastructure etc. Analysis of central tendency of both the categories revealed that both of them significantly influenced the consumer behavior of respondents, but a higher average mean value in case of qualitative factors revealed that they influenced the consumer behavior of respondents with a higher degree than quantitative factors. “Sharma Sunil” in his book “planning and development of tourism and hospitality” too identified these market and environmental factors those influenced the buying process of consumers while they availed these services. Gender based analysis revealed that in both the categories i.e. qualitative as well as quantitative, female respondents (with a higher average mean) are more influenced than male respondents.
Hospitality industry should try to take care of every factor, but should focus more on above extracted components and factors they contain. This will lead to better influences on the consumer behavior and will positively affect the profitability of hospitality organizations. It was also found that qualitative factors influenced the consumers behavior to a greater extent than quantitative factors and female respondents were more influenced by these factors therefore keeping in mind these findings hospitality industry should chalk out appropriate strategies in this regard.
The researcher has conducted the study with respect to consumer’s perspective. These objectives can be investigated with respect to hospitality industry. The present research analyzes the influence of business and market environment factors on decision making process of consumers. The studies can be carried to investigate the following problems:
• To study the role of digital marketing in hospitality industry.
• To study the influence of technology on consumer behavior in
hospitality industry.
• To study the impact of changing demographics and
globalization in hospitality.
• To investigate the influence of operations management on
consumer behavior in hospitality industry.
• To study the significance of E-commerce in hospitality
industry.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Citation: Kalotra A (2023) An Analysis of Business and Environmental Factors on Consumer Behavior in Hospitality Industry. J Tourism Hospit. 12:536.
Received: 26-Aug-2019, Manuscript No. jth-23-1651; Editor assigned: 30-Aug-2019, Pre QC No. jth-23-1651 (PQ); Reviewed: 14-Sep-2019, QC No. jth-23-1651; Revised: 10-Nov-2023, Manuscript No. jth-23-1651 (R); Published: 08-Dec-2023 , DOI: 10.35248/2167-0269.23.12.536
Copyright: © 2023 Kalotra A. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.