Journal of Political Sciences & Public Affairs
Open Access
ISSN: 2332-0761
ISSN: 2332-0761
Research Article - (2017) Volume 5, Issue 2
National government’s key task and the most important aspect of human civilization that leads to greater prosperity and progress of human civilization in the world is to provide security inside the country and to deal with the potential influx of other governments to a territory and its citizens. The aim of this study was to investigate the components of political development on the national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran from the perspective of policy experts. This study used interview to collect information and the population consisted of professors and activists in politics. 15 people were interviewed as the sample. The results indicate that the effects of the components of political development on the national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran have been extracted in some spheres including military security, political security, social security, economic security and environmental security. In addition, strategies for the structural development of management, domestic and foreign accountability, planning to live in global networks, global responsibility, readiness for global assessments and liberalization of foreign trade have been provided as efforts to develop political and national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran.
Keywords: Political development; National security; the Islamic Republic of Iran
Power and security are fluid and complex social concepts that change in the course of time and by the evolution of events and change of attitudes and perceptions, and find new dimensions and different examples. Moreover, with the evolution of these concepts and their examples, the agents, the way they are understood, the way they are applied and provided undergo changes as well. In the traditional perspective specifically, public security is threatened from two sides. The threat of people against each other within the community and the threat of other communities and governments from outside. Governments are obliged to deal with the threat of individuals and organizations against each other within the territory of the country. External threats are caused by foreign actors that from the perspective of traditional approaches are governments [1].
In today’s globalized world, national security is related to individual, regional and international levels and cannot be achieved without them. A paradoxical agent in a political and cultural security is that the threats themselves often strengthen and support the invaded identity. If the degree of loyalty to some belief is increased in response to foreign pressures, to fulfill the security, the government needs a condition that the society achieves an acceptable level of reliability to secure and protect its national interests [2].
The main concept of national security for many countries implies the need to preserve territorial independence and integrity, to maintain national way of life and to prevent foreign interference in the domestic affairs of the country by increasing military power. Security and national security are of the concepts that have become common since the rise of nation-states. The use of this word has always been common in the political discourse, but with no specified definition. After the Second World War, political science researchers turned to it as an applied term and studied it in the form of various theories of the issue of national security [3].
Many researchers consider national security as “the ability of a country to maintain personal values against foreign threats” [4]. In a sense, national security is to achieve conditions that allow a country to remain safe against potential or actual foreign threats and foreign economic and political influence and to move toward the economic, social and humanitarian development and provide the integrity and existence of the country and public welfare without the interference of the foreigners. Protection of a nation against foreign aggressions, espionage, reconnaissance, sabotage, etc. is another definition of national security.
The main issue that this study sought was to respond the following question: what are the components of political development of national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran from the perspective of policy experts?
The concept of security
Search for security is of the most important human motivations and attractions. This attraction is inextricably linked with the essence of human existence. Self-preservation and protection is of the most basic human desires. Human beings enter various relations and form society in search of the satisfaction of their life requirements. The most important need of every society, whether a clan or tribe or a nation or a country is the security of the community and its people. At this time, smaller communities form large communities called countries and these countries have turned into the most important political units across the world. In previous societies and human history, security was indicative of a type of physical guarantee for the objective existence such as person, family, tribe and government. With the progress of human societies and more complex relations among individuals and communities, security gradually took a broad and complex concept that in addition to lack of threat and fear was indicative of a guarantee for the progress and development, education, flourishment of talents, development of human societies and a guarantee for the protection of material and spiritual life [5].
Countries are not on the same level in many ways including material and spiritual facilities such as strategic location, natural resources, population, economic growth, domestic cohesion and political stability. For this reason, their conceptions and expectations of the limits of their interests is not the same in the international society and their tools and facilities to progress those interests are not the same either. State interests are sometimes different and contradictory, causing disputes between them. For this reason, it could be stated that efforts to protect national security or to expand its scope, is of one of the most important objectives in the field of international relations [6].
In this way, since scattered feudal states and great empires were replaced by national governments or nation-states and these national governments became the basic unit of international relations, the term national security took over the language of statesmen and military leaders. Of course, the concept of human security included large and small societies. Small tribes of primitive societies, the great empires of the ancient world and the Greek city states were not unfamiliar with the concept of security, but the concept of “national security” as a term of two security words “security” (noun) and “national” (adjective) is naturally a new concept that has emerged with the emergence of the phenomenon of nation states in modern times.
With the emergence of nation states, the term “national security” and under that the concept of “national security” also became common. The term “national security” was used for a long time in the catchwords of politicians and military leaders. Even social and political researchers and writers provided no definition of this concept while they explicitly and implicitly used it in their writings. Hence it can be said that the definition and analysis of the concept of national security has no long history and basically, social and political researchers studied this analytical concept and field of study. Studies related to the national security of the United States of America covered the evolution road before other countries. The emergence of nation-states, the formation of an international system in which the great, small and medium powers interacted with each other in proportion to their situation, the emergence of new technologies, the emergence of interdependence among nations, the emergence of new ideologies such as Fascism and Nazism and the development of nationalism are among the important factors influencing formation of the new concept of security in the present age [2].
Security has features that one can better understand and analyze the concept of security by understanding them.
Relative nature of security
Security is relative and the relativity of security means that it does not exist absolutely for any country, because no country operates in a vacuum and factors such as ideology, domestic circumstances and international situation of countries, perspective and insight of ruling leaders have a significant impact on the quantity and quality of security and the way it is secured, preserved and expanded. Security is the value and position that a country may enjoy it to a greater or lesser extent, but no country can ever benefit from total security [7]. To think about a secure (social, political, security) system can only be realized and become objective when it considers the features, capabilities and goals of potential threats. From this perspective, any kind of security analysis will necessarily be an extrovert analysis, depending directly on the diagnosis and assessment of the processing of the analyst of external threats. But on the other side, this analysis should also govern considerations and relationships inside a country. Since external threats are always rooted in the context of internal vulnerabilities. Due to such characteristics, the design of any “safe system” not only requires an understanding of the potential and actual (domestic and foreign) threats, but also it needs to measure its own degree and dimensions of strengths, weaknesses, limitations and capabilities as well.
Variable nature of sense of security or subjectivity of security
Security is a subjective issue. To define security and to delineate its field and scope on the one hand is directly and greatly linked with the mentality and understanding of the elite and the people of a community of vulnerabilities and threats, and on the other hand, it is influenced by their past experiences and presuppositions in issues such as core interests, national values, national interests, national power, etc.
The subjectivity of security can be due to four reasons:
• The credit that a country’s elites and decision makers consider for the threatening forces.
• The relationship that they can establish with the agent or agents of threat.
• The ability (limitations and capabilities) against the other (threat).
• Degree of credibility, urgency, priority and centrality of confirmed values and interests.
National Security is comprised of and influenced by some elements. These elements are military, political, economic, social and environmental and each of them is a focal point on security issues but all of them are completely intertwined. Generally, military security deals with the offensive and defensive capabilities of countries at one level, and what countries think of the intentions of each at the other level. Political security includes structural stability of the country, the government system and its ideology that gives it legitimacy. Economic security includes access to capital and market benefits that are necessary to maintain the level of prosperity and power of the country.
Social security means stability at the time of changing patterns of language, culture, religion, national identity and traditions. Environmental security includes maintaining the earth’s living conditions both regionally and globally because it means the preservation of human life on the planet.
Robert Mandel explains the concept of national security and mentions the military, economic, resources/environmental, political/ cultural spheres as four major dimensions of security. He also mentions two communication filters, which somewhat reduce the person’s ability to pursue these paths: one filter is the information that reflects the exact amount of information that anyone can successfully collect on the global situation (this reduces the intense and fundamental surprise to the least). Second, the perceptual or conceptual filter that reflects the success in conveying a feeling of safety to the people of a country (this maximizes public trust and legitimacy of the regime). These dimensions and filters ultimately rest on the fundamental elements of power that include domestic capacity or capabilities as well as foreign threats and alliances [8].
Despite differences in the emphasis on personal, state, regional or global security or on developed and developing societies, it seems that the elements of national security have general applicability.
The political/cultural dimension of national security is of dimensions classified less than the others. Political security is focused on the organizational and state stability. The intention of threat may vary from pressure on the government in a particular policy to the reversal of government, separatism and disrupting the political fabric of a government to weaken it before military invasion. The idea of the government, especially the national identity and the organizing ideology and institutions are common aspects of political threat. Because governments are basically political entities, the political threat may be as frightening as the military threat. The political threat is the result of ideas and traditions that are the main justification of international anarchy. Organizing ideologies of the twentieth century, liberal-democratic, fascist, communist and recently Islamic political opinions have been practically in conflict as were the political opinion in favor of monarchy and republicanism in the nineteenth century [2].
To disrupt the political security of a state, threats to national identity appear more considerably. Such threats fuel the ethnic-cultural differences among the groups in the country and the result would be secessionist tendencies. Structural political threats to the political security are created when the constituent principles of two countries are at odds with each other and countries cannot ignore each other.
Theoretically, Iran’s domestic and foreign security are linked. Historically, Iran has been attacked repeatedly from North, South, East and West. In addition to foreign threats over the past two hundred years, revolutions, uprisings and coups occurred in Iran. It is noteworthy that proportionality between national goals and national power in providing national security is vital. If the objectives of a political system are beyond its national capacity, it will lead to the destruction of the country’s resources.
There is disagreement about the answer to the question that providing national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran depends on pursuing what kind of objectives. There are at least five types of views in this area, each considering the pursue of specific a objective as the major factor in maintaining national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran and consider it the most strategic objective of the Islamic Republic of Iran. Each of these are referred to in the following:
The first opinion believes that the present problem of the Islamic Republic of Iran and its most strategic issue is the economic conditions. Their argument is that economic problems can cause public discontent and finally eliminate tolerance to inflation and class differences. According to this group, if the situation continues this way, the system will be faced with an economic boom. The followers of this theory consider economic development as the most important strategic goal of the Islamic Republic of Iran [6].
The second theory emphasizes the development of political and civil liberties. According to this theory, political freedoms and activities of the factions in cultural, social and political fields is of strategic importance. This freedom provides an opportunity for the people to overcome their complex and eliminate the chance of violent opposition against the system. Those who favor this theory, think that dictatorship provokes rebellion against the system much faster than economic oppression.
The third theory considers maintaining the principles of the revolution as the most strategic goal and believes that adherence to principles is important to the extent that even the system must be sacrificed for it. In other words, the idea separates the revolution and the system and considers revolution as the principle. According to this group, maintaining the principles of the revolution is essential at any cost [9].
The three theories mentioned above can be called introvert or introspective comments. Of course, the third theory has many external consequences. However, the first two theories can mobilize and employ the external environment with an emphasis on internal enabling in order to achieve internal purposes. Unlike these three theories, there are two other theories that can be called outward or extrovert. The fourth theory is centered on foreign policy issues. According to this theory, maintaining the national security of Islamic Republic of Iran in military terms, is the most important issue for the system and it claims that to provide it, all the resources and programs shall be directed toward that direction. This view which is based on the Iraqi regime invasion of Iran, believes that there is always the danger of war and the need to high military readiness to repel any foreign aggression [2].
The fifth theory believes that the greatest enemy of the Islamic Republic of Iran is America and its various agents in the region and globally. So, the system should try to get involved with America not only in Iran and in Islamic countries, but in the whole world and take any opportunity anywhere to hit that country. It is obvious that this theory also fits the traditional definition of security but compared to the fourth theory, the circle is tighter and the consequences are more dangerous [9].
In proportion to the change in political systems, the importance of people and their major influence in choosing their rulers has become the dominant form of government in modern societies and in proportion to these developments, attention to their rights has been considered seriously. Although this topic formed the basis of political systems in the West after World War II and the expansion of democracy, but it was delayed in third world countries. Few research has been done in this area in Iran and the existing research has mostly dealt with the topic regarding the global dimension of national security. Mousavi has discussed “policy and its impact on the concept of national security” in a study [10]. In this thesis, the main debate over national sovereignty is in the sphere of politics. In order to explain the views, some debates are raised about globalization of economy and culture. The final conclusion is that as a result of economic globalization, the rise of multinational corporations, strengthening transnational media, the emergence of NGOs and similar issues, the nation-state model does not have sufficient capability for the analysis of international relations. These discussions will cover the first three chapters. In subsequent chapters, the second axis of research that deals with the issue of security. Economic and cultural security is discussed and then realism theory on international relations and its security model is explained. Following the explanation of realism security, the disadvantages of this view in the era of globalization are mentioned. In the end, the need for the change and modernization of the realism theory on security is emphasized and it is concluded that due to the reduced power of national governments in the era of globalization and the emergence of new issues, traditional theories such as realism must adapt to new conditions. Mahdavi conducted a study on “globalization and its impact on the change of the supply of components of the national security of Iran (case study on ethnicity)” [2]. The findings suggest that the world has entered a new phase of developments in the 21st century which is different from the past and no doubt in such circumstances, no country can avoid and be indifferent to the developments and the effects of globalization (with a process view). In fact, globalization has practically changed the components of national security from hardware dimension (militarism) to software dimension (knowledge-based) as the reduced role of national governments and the change in the nature of the threat and in this context; the ethnic groups have increased their cultural demand. Moreover, this issue will be followed by opportunities and challenges in various political, economic, social and particularly cultural aspects. Cheraghi conducted a study entitled “evaluating the effect of cultural globalization on national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran” [5]. The findings suggest that cultural globalization is one of the processes which are happening that sweeps all human borders and leaves its effects that can harm the national security of the country or strengthen it. This subject was tested by examining the case study of the Islamic Republic of Iran.
Considering that the aim of this study is the examination of the components of political developments on the national security the Islamic Republic of Iran from the perspective of experts, the present study used the qualitative method to answer the main research question. For data collection, the interview method was used. For analyzing the data from the interviews, theme analysis was used.
In this study, interviews were used to collect information. The interview is without doubt one of the most frequently used techniques to conduct systematic research. In this study, available sampling procedure was used. In this regard, for selecting the sample, a pre study was performed. In this study 15 policy experts including university professors and political activists were interviewed. The sample size in qualitative research is theoretical saturation that in the present study, the researcher observed theoretical adequacy in the twelfth interview but to ensure the adequacy, the work was kept up to the fifteenth interview.
To calculate the retest reliability, some interviews were chosen as the sample from among the conducted interviews and each of them were coded twice in a short specified time interval. Then, the codes specified in the two intervals for each of the interviews were compared with each other. Re-test method was used to assess the stability of the coding by the researcher, but it was faced with the problem that the results of re-test can be influenced by exercise (experience) and the coders’ memory and so, it can lead to changes in the reliability of the coding. In each of these interviews, codes that were similar in the two intervals were specified with the term “agreement” and dissimilar codes were termed “disagreement”. The method of calculating the reliability of the coding performed by the researchers at two intervals was as follows1.
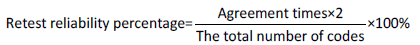
To calculate the retest reliability of the interviews conducted in the present study, three interviews were selected and each of them was coded twice by the researcher in a period of 30 days. The results of this coding are presented in Table 1.
| Row | Number of disagreements | Number of agreements | Total number codes | Title of interview | Retest reliability (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S2 | 109 | 48 | 19 | 88% |
| 2 | S4 | 81 | 35 | 12 | 86% |
| 3 | S1 | 60 | 27 | 6 | 90% |
| Total | 250 | 110 | 37 | 88% |
Table 1: Calculation of retest reliability.
As can be seen from Table 1, the total number of codes in two 30 day intervals is 250, the total number of agreements between codes in these two times is 110, and the total number of disagreements in the two times is 37. Retest reliability of the interviews conducted in this study using the above formula is 88 percent. Given that the reliability is above 60% (Wall, 1996: 237), the reliability of coding is confirmed.
To perform data analysis for the information obtained from the interviews in the present research, thematic analysis method was used. So, according to what was discussed, first the review texts were investigated and coded and by doing so, various concepts used in this study were extracted. These concepts are divided according to the content appearing in the form of conceptual categories that actually represent an independent concept. These categories are also offered in the form of different themes. The elements that work as the components of political development influencing the national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran, include military security, political security, social security, economic security and environmental security. The theme was divided in the form of conceptual categories that actually represent an independent concept.
As seen in Figure 1, the theme “component of political development” has been presented in five conceptual categories (military security, political security, social security, economic security and environmental security) and the conceptual categories include items that the interviewees stated the outcome of conceptual categories above were formed as a separate theme called “the political components of political development on the national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran”.
The dimensions of political development for the national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran have been extracted in the following Table 2. The conceptual categories related to the dimensions of political development are presented in Table 2.
| Examination of political developments on the national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran | Military Security (1A) | Non-violence, strengthening the military power through deterrence policy, cross-regional interventions, trade of military weapons |
| Political Security (1B) | Belief in the right of public participation, political confidence, culture of tolerance and non-removal and non-democratic destruction, political engagement and competition, reducing political dominance, the full realization of republicanism and pluralism, development and support of the press, public participation in the governance of the society as a right, increased public oversight of the trend of political power | |
| Social Security (1C) | The increased bonding of multiple cultures, the ability to raise the cultures of minorities, the existence of multiple sources of creating identity, government support of civil rights | |
| Economic Security (1D) | Entering global markets, globalization of the strategy of companies in a competitive market, technology publishing along with global research and development, increasing the role of nation-state in the design of rules for global policy. | |
| Environmental Security (1E) | Development of tourism, disposal of toxic waste, deforestation and destruction of biodiversity |
Table 2: The conceptual categories of the dimensions of political development.
The first conceptual category that forms the theme of the foreign policy sphere of national security in the view of experts is military security (2A). Some of the statements made in this area were:
The most important problem that can be pre-military security from the perspective of foreign policy is trans-regional interventions in countries under various pretexts (2s1).
The second conceptual category mentioned in the context of the theme globalization that influences foreign policy of national security is political security (2B). The participants in this study report the importance of this conceptual category as the following:
Public participation in society governance shall be considered as a right (4 s2)
Or:
Republicanism and pluralism must be realized in order to be able to take steps toward political development (2s14).
The third conceptual category that plays an important role in the national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran’s foreign policy is social security (2C). One of the interviewees raised the issue this way:
Given that there are various subcultures in the country, they should be linked so as to use them as an opportunity (3s8).
The fourth conceptual category that that plays an important role in the foreign policy of the Islamic Republic of Iran’s foreign policy is economic security (2C). One of the interviewees raised the issue this way:
It should be tried to publish the technology along with the process of research and development at the global level and not to remain consumer (6s9).
The last conceptual category referred to in the context of the theme of examination of the components of political development on the national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran is environmental security (2D); participants in this study mentioned the importance of this concept as the following:
To achieve the political development and national security, we should pay attention to the tourism industry (2s9).
In this study, an examination of the components of political development in the view of experts was performed on national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran. The results of interviews with experts indicate that in the field of military security, non-violence, strengthening the military power through deterrence policy, crossregional interventions and trade of military weapons lead to political development and national security of the country.
In addition, in the area of political security, the components of belief in the right of public participation, political confidence, culture of tolerance and non-removal and non-democratic destruction, political engagement and competition, reducing political dominance, the full realization of republicanism and pluralism, development and support of the press, public participation in the governance of the society as a right and increased public oversight of the trend of political power were extracted as the components of political development.
The results also showed that the components of increased bonding of multiple cultures, the ability to raise the cultures of minorities, the existence of multiple sources of creating identity, government support of civil rights in the area of social security lead to political development and national security. The findings also indicate that in the area of economic security, entering global markets, globalization of the strategy of companies in a competitive market, technology publishing along with global research and development, increasing the role of the nation-state in the design of rules for global policy leads to political development and national security.
The results showed that environmental security is another dimension of political development with the components of development of tourism, disposal of toxic waste, deforestation and destruction of biodiversity that lead to political development and national security.
The results of research in the field of political development and national security in this research are consistent with the findings of the previous research work [2,5,10,11]. The above researches have emphasized on the role of political development in the areas of national security and domestic and foreign policy which confirm the research findings in this field. Also, according to the view of policy experts, the following strategies were proposed as the strategies for the political development of the Islamic Republic of Iran.
These strategies include conceptual categories (structural change of management, domestic and foreign accountability, planning to live in global networks, global responsibility, readiness for global assessment and liberalization of foreign trade (Figure 2). Based on this theme, the above strategies influence political and national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran. The following shows the conceptual category related to these strategies:
According to research findings, effective strategies increase political development and efficiency of national security in Iran and have a direct relationship with its efficiency. It means that with more adherences to these guidelines, the political development and efficiency of national security of the Islamic Republic of Iran both in domestic and foreign politics would become higher.
1If the number of members of sample space (here the total number of codes) are shown with n (S), the number of members of the event A (here the number of agreements between the two stages of coding) are shown with n (A), and the number of members of the event B (here the number of disagreement between the two stages of coding) are shown with a n (B), then the probability of A (here retest reliability) that is P (A) will be as follows:
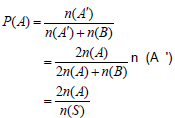 represents the number of codes related to the agreements. Regarding that the agreements are identified by reference to two codes and disagreements are identified by reference to one code, to consider this effect, the number of agreements should be multiplied by 2:n(A′) = 2n(A)
represents the number of codes related to the agreements. Regarding that the agreements are identified by reference to two codes and disagreements are identified by reference to one code, to consider this effect, the number of agreements should be multiplied by 2:n(A′) = 2n(A)