Journal of Tourism & Hospitality
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-0269
ISSN: 2167-0269
Review Article - (2024)Volume 13, Issue 3
Destination branding has been an extensively investigated idea as governments and corporations seek to reposition their respective destinations' images in the mainstream sphere. All areas of destination branding are being researched, not only for the purpose of branding or rebranding locations, but also to stimulate local economies. The purpose of this study is to obtain information about destination personality from the literature accessible in research sources. This review paper presents the findings of previous researches and the approaches used therein. Researchers, marketers, and government officials might benefit from an increased understanding of notions of destination personality and its implications in tourism, which could lead to adjustments and improvements in the branding of tourist, business and other kinds of destinations. It is essential to emphasise that this article is only a qualitative evaluation of the literature and is therefore confined to the results of prior research.
Destination; Researchers; Government officials; Implications; Tourism
Destination personality consider as brand personality in context of tourism literature. Though, the study of product/brand personality research had begun in the early 1960s in the domain of consumer goods. Conceivably, the identification and application of destination personality concept is quite new in tourism field. Destination personality contributes to encouraging tourists and in the marketing of destinations. According to Chen and Phou, destination personality has been widely used by marketers to competitively position their cities in the tourism market. This study aims to contextualise prior research results in terms of destination personality [1].
The aim of this study is to provide an overview of destination personality studies from 2006-2018. The purpose of this study is to create a better knowledge of the destination personality on the basis of the most recent findings, as well as to identify methodological concerns and the value of new information for future research in the destination.
Particularly, this paper offers a review and debate of the literature, concept, measurement and dimensions of destination personality. Additionally, the methodological methods for establishing destination personality are examined in an attempt to assist researchers in recording and determining the evolution of destination personality through years [2].
The scope of the most recent review was limited to the following issues:
• What are the latest findings of destination personality
research?
• What are the dimensions of the personality image?
• How to measure destination personality in tourism related
studies?
Conceptualization of personality
The word personality said to be derived from the Latin word “persona” which used in contras of “mask” meaning. “Persona” reflects the characteristics of an individual in any specific role rather than the original person behind the mask.
Over time, this concept comprehends with person attitude and behavioural characteristics.
Normally, it is very common to listen about people is that person has a good or bad personality. The actions are the reflection of the personality and it also defines it. Different behaviour distinguishes the uniqueness of every personality [3]. Personality of an individual is the composition of mental characteristics; thought patterns and sentiments all this stimulates one to behave in a certain way. It is also in saying that personality is “the characteristics or blend of characteristics that make a person unique.” Basically, temperaments or emotional tone also expressed the Personality. It is commonly said in personality psychology field that “some things change; some things stay the same. According to Stemmler and Wacker suggested that “personality is a dynamic organization, inside the person, of psychophysical systems that create the person’s characteristic patterns of thoughts, feelings and behaviours.”
In accordance with Mischel and Shoda demonstrated that personality gives the directions and coherence to an individual’s life with the dynamic organization of cognitions, affects and behaviours. Nature (genes) and nature experiences contains both personality structures and processes. Likewise, an individual personality also depicts its values, beliefs and expectations. Correspondingly, Personality development contains many potential factors. Following this an individual’s personality acquire values, beliefs and expectations from surrounding environment, socialization and with unique experiences which also enhance the self-concept/self-esteem/selfregulation/ self-efficacy/self-awarness and self-knowledge in personality. The distinctive pattern of behaviours, continuities, permanence of personality traits and dispositions over time defines personality development [4].
Types of personality
The individual behavioural differences personality traits such as Introversion/Extroversion (I/E) are always comprehensively explained by personality theorists in terms to used and understand them accordingly. Previous studies indicate that there is always a high emphasize on introversion-extroversion as the main traits of big-five personality model.
As well as Burruss and Kaenzig cited that Jung was the pioneer for the exploration of personality and development of its construct’s extroversion and introversion. Jung observed the human behaviour and habits as patterns and worked to recognize and rationalize these differences of personality according to uniqueness of human behaviour variable patterns. In early twentieth century, the concept of these two personality traits introvert/extravert were already existed, research had confirmed that introvert/extravert factors were very important dimensions of personality. Each dimension has its own characteristics, such as sociality, activity, expansiveness, etc [5].
Extroversion
Extroversion is "attitude-type characterized by concentration of interest on the external object". Extroverts found to be more “social-oriented”, “expressive”, “articulate”, “fun loving”, “easily caught the attention of other people”, much comfortable in group settings.
Due to the fact that every individual differs from others in emotional reaction, this is referred to as "personality differences". Past studies stated extroverts generates more positive experience in comparison to introverts, so extroversion encounter positive affect. It also signifies extroversion to high active (arousal), assertiveness, impulsiveness, social behaviour and practicing positive emotions are its tendency. Extroverts have the ability to deal with life events by using problem-solving skills that provide them with a positive sense of self-worth [6].
At the other end of the spectrum from structural work in personality, extroversion interpersonal nature is not a monolithic characteristic, but rather is composed of two separate higher order qualities, namely, affiliation and agency. Affiliation is more about amusement, social interactions, being warm hearted, affable and loving. Agency reflects self-efficacy in terms of fulfilling goals in subjective sense, leadership roles, assertiveness and social power of control.
Additionally Hogan express extroversion is characterised by traits such as openness to new experiences, a desire to help others and a capacity for self-advocacy. Extroversion is divided into two subgroups: Sociability and ambition. In accordance to this some extroverts can be more sociable and like other group’s company and some extroverts can be self-confident, dominant and leaders. Furthermore, extroverts are highly competitive and focused regarding reward achievements [7].
Introversion
Morrone-Strupinsky and Lane defines introverts as self-oriented, self-responsible, persistent and intrinsically motivated towards their acts and results. According to studies, introversion does not prefer vast social life they are more intended towards rich inner life. Introverts are quiet, simple, prefer focused and closed relationship with small no of people. They are very anxious in nature but good in thinking while they are tranquil and follow internal directions preferably.
In invasion situation they isolate their self as they couldn’t manage to be themselves and strive to be extroverted, spontaneous or crazy. They are very inside-in regarding their best things and not actively participate or reluctant in a group situation just because they need time to fully develop their ideas and they think before speak. They have the skill to be appeared as extroverts when needed [8].
Seemingly they appeared as anti-social or shy but they are social but in a different way. They have a good capacity to listen, planning, focusing, one-on-one interactions and can perform independently. Interestingly they like to express themselves by writing, have ability to hold their self-back in any situation, be calm and get perspective. Thus, introverts are cooperative and facilitating in relationships. Introvert & extrovert personality traits chart shown in Figure 1.
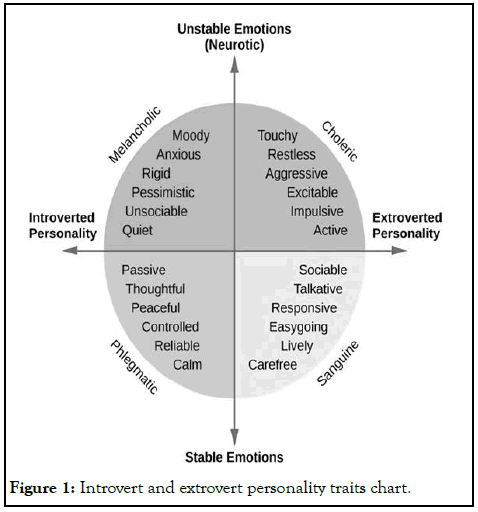
Figure 1: Introvert and extrovert personality traits chart.
Big-five personality traits
Initially the 16-item inventory of personality traits were developed by Raymond Cattel in 1940 with sixteen Personality Factor questionnaire (16PF) items to analyse these traits. Costa Jr and McCrae later established the FFM (Five Factor Model), which precisely describes the personality to measure in terms of five broad factors.
Among all the developed models for personality like Allport’s trait theory, Cattell’s 16FM, Eysenck’s Big Three and the Myers- Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), Costa Jr and McCrae model the Big Five Model (Five Factor Model) is commonly used for personality traits measurement in management and marketing literature.
This five factor model is being created after eliminating plenty of adjective to make it more precise with characterization of five dimensions. From the several years this model has been used by many researchers, has constantly used even today attracting attention and trust of the academicians due to its appropriate characteristics. This model involves the five main dimensions of personality that explain an individual.
In addition to the preceding research, the big five personality traits-a composite of five different categories are also explained in Figure 2 that are extraversion, neuroticism, openness, conscientiousness and agreeableness.
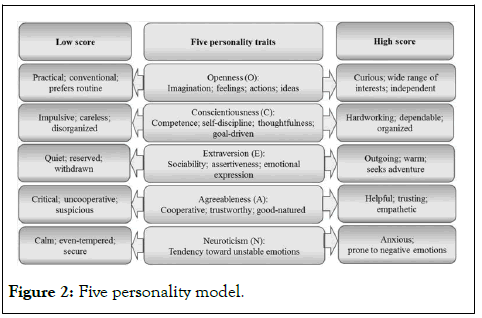
Figure 2: Five personality model.
Extraversion
Individuals with an extravagant personality include being talkative, gregarious, socially poised, assertive, leading, outgoing, energetic and cheerful. The individual with high level of extraversion has obtained stable and positive affect and behaviours. They are very positive regarding future, less vulnerable and very open towards competition, not like low level of extraversion who prefer to be alone, less participated in activity, calm and staying at the back with avoidance of stimulation [9].
Neuroticism
Individuals with features of calm, relaxed, satisfied with self, clear cut personality, stress-tolerant, pride self on objectivity are highly emotionally stable personality. Traits opposite of this emotional stability behaviour involve negativity for their-self, being worried, anxious, insecure, shy, tense, depressed and always worry about other opinions present neurotic personality traits. Individual with low level of emotional stability always tends to unsuccessful to have healthy interactions with people around them.
Openness
Traits used to describe openness to experience personality type include creative, intellectual, analytic, imaginative, open to other people’s perspective, adventurous, narrow and have a broad level of intellectual curiosity at the end of continuum. Openness personality always value intellectual stimulus. Comparatively, lees open to experience personalities are associated with conservative, simplicity, indifferent, behaviourally rigid and conformist in their cognition.
Conscientiousness
This personality trait commonly categorized as careful, responsible, systematic, self-disciplined, determined, detailed, highly success ambitious. High conscientiousness personality is eager to achieve their goals. In contrast with this individual who are irresponsible, unplanned, disorganized, poor decision making, easily distracted have lower conscientiousness dimension level.
Agreeableness
Personality involved in this dimension are eager, collaborative, behaves in a given way, sympathetic, warm, straightforward and compassionate. They avoid conflicts and have cooperative manners. Critical, skeptical, behave condescend, hard headed, express hostility directly, tries to push limits and aggressive to others have lesser agreeableness level. When it comes to assessing the quality of one's interpersonal attitude, agreeableness is a personality attribute (e.g. disbelieving vs. believing).
Destination personality
However, for many decades, tourism research has mostly focused on the destination image, academics have paid less attention to destination personality due to the concept's relative novelty in the tourist sector. Distinguishing and substituting destinations based on their functional features reduces their uniqueness and makes them less identifiable. Thus, including extra characteristics for destination personality such as value propositions may aid in distinguishing destinations and attracting travellers. When marketing their branded cities and destinations in a highly competitive tourist sector, destination marketers employ destination personality to distinguish and position their brands. Indeed, destination personality is increasingly being used as a metaphor for marketing and positioning in the tourism industry. Many researchers defined destination personality in different way as shown in Table 1 [10].
| Author/s | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Keller | The symbolic function of a brand whereas brand image refers to both symbolic and functional benefits of a brand |
| Aaker | The set of human characteristics associated with a brand |
| Ekinci and Hosany | The set of human characteristics associated with a destination as perceived from a tourist view- point |
Table 1: Destination personality definitions.
For the study of personality traits, the Big Five model (BFF) is very known. Its five measures are Openness to experience (curious, adventurous), extraversion (emotional, submissive) conscientiousness (self-indulgent, productive), agreeableness (skeptical, critical) and neuroticism (thin-skinned, anxious, irritable). With reference to human personality model Aaker, developed the Brand Personality Scale (BPS) for the analyzation of product/brand personality attributes. Since then, this scale Aaker has been widely used to examining the product/brand personality. Aaker defines brand personality as “the set of human characteristics associated with a brand”.
Following this, it can view that consumer perceives the brands as similar to humanlike traits, which is valuable sense to respond a brand emotionally that stimulate their opinions, purchase intension and consumer decision making. Consequently, Consumer feel more intended and supportive towards a brand regarding which they feel personally more relevant and this build positive relationship and leads in customer’s trust towards the brand and increases his/her loyalty.
Aaker defined brand personality is the combination of characteristics which are similar to human but associated with product/brand cited in. Youthful, sporty, energetic, outdoorsy or sophisticated can be traits characteristics. This is why, brands are often explained by intangible characteristics. For instance, humanistic characteristic is utilized to describe some brands and products such as “masculine” for Malborow, “cool” for Coca- Cola and “young” for Pepsi, “sophistication” for BMW, “unique” in the case of Dr. Pepper, “intelligent” to describe IBM computers and “feminine” to describe channel perfumes.
Since Aaker describes five dimensions and fifteen aspects that characterise a brand's personality as traits that are exclusive to humans and are thus attributable to a brand, as seen in Figure 3.This five-factor scale (BPS) includes dimension of “excitement (which means the characters of full-spirit, trendy, courage and high imagination, as well as up-to-date in making difference and innovation)”; “sincerity (which means the characters of honest, humble, down- to-earth, family-oriented, small- town, friendly, sincere, real, original and simple)”; “ruggedness (which is the brand characteristic that is associated with the ability, that is the brand characteristic in supporting outdoor activities and the strength or durability of product)”; “competence (which means security, intelligence, tenacity, skill convenience, ability to be reliable and trusted by consumers) and sophistication (which means characters related to exclusivity that is formed by excellence of prestige, brand image and attraction offered to customers)” [11].
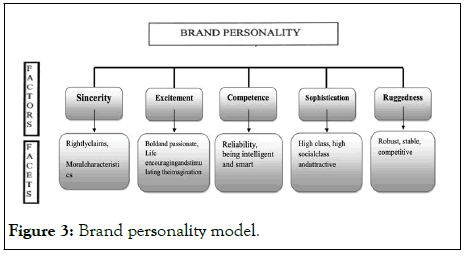
Figure 3: Brand personality model.
Aaker, BPS is based on three foundations: Firstly, personality measurement scale from psychology, secondly personality scales derived from marketing, lastly unique qualitative research on personality characteristics related with a number of well-known businesses. Along with 42-item BPS, Aaker recommend that theoretical brand personality framework with five dimension is generic and this can apply throughout product categories. It has also been stated by Aaker that BPS might not accurately fit across cultures and more research is required to get the stability of these personality dimensions across culture. Above all, research and literature get increased on brand personality and numerous studies are conducted by researchers on a variety of product categories and across a variety of cultures using a brand personality framework.
This Aaker contribution in this domain of brand personality influence the researchers to study. Hence, brand personality influences the development of favorable brand evaluations, brand preferences, brand trust, brand affect and brand loyalty, as well as the development of brand loyalty. Murphy, et al., suggested that in background of brand personality, destination personality also enhances the specification of destinations and make them different, unique and outstanding in comparison with its competitors. According to Hosany, et al., stated that destination personality signifies with the characteristic of human which is being associated with the touristic destination. In correspondence to this fact products hold customers emotional attachments through having reciprocated characteristics of customers [12].
For the first time, researchers Ekinci and Hosany, examined the validity and application of the brand personality framework for tourism destinations and they found that the model of BPS could be apply to tourism destination as the tourist relates their personality traits to the destinations. They found that three dimension of brand personality including sincerity, excitement, and conviviality are salient dimensions of the human qualities that are assigned to the destination are referred to as the destination's personality. Sincerity and excitement were revealed to be the two most important elements of destination personality, while conviviality is a newly discovered destinationspecific feature. Since that date till now, the tourism literature getting deep with empirical study of destination personality.
Furthermore, destinations are comprehended with destination personalities and characteristics in two ways i.e., direct and indirect. In direct way, characteristics allocation means the perception and assumptions of the visitor based on their experience of destination visit. These characteristic falls in symbolic values and personality traits, which consist of tangible factors (e.g., hotel staff, destination attractions and citizen) connected with specific values, memories, events. Likewise, indirect way contains personality features which include intangible factors of marketing strategies (e.g., promotion, intellectual properties, value-based pricing to customers, celebrities from the country and mass media).
For making tourist destinations highly positioned and more distinct, functional attributes must be instigated with additional traits and selling propositions like destination personality to make tourist destinations less substitutable with high spirit of encouraging tourists. In contrast, making destinations highly competitive in tourism market when it comes to marketing and branding of destinations, destination personality is becoming a very useful metaphor. For example, Western Australia brand which symbolizes freshness, natural, spirited and free. Scotland brand reflects personality traits such as straight, open, honest, ethical, educated, competent, warm, welcoming, friendly, accessible, with distinctive voices, names and attitudes. Henderson found that New Asia-Singapore brand is composed of personality characteristics such as cosmopolitan, youthful, vibrant, modern, reliability and comfort. Portugal found with personality traits of traditional, contemporary, modern, sophisticated in the U.S. travel media. London known as openminded, unorthodox, vibrant and creative, Paris as romantic and Spain as friendly and family oriented [13].
A large number of research have been carried out to determine the use of brand personality in the tourist industry and Aaker’s BP scale was widely used to measure the destination personality representation. Originally, big five factor model and Aaker brand personality scale developed for product/brand attributes measurement not for destination personality that is why some personality traits that apply on product brand or person resulted irrelevant for destinations (country). Subsequently, the application of five factors, their significance and stability were not conclusive when applied to cities, countries or destinations in general (Table 2).
| Author (s) | Destination type | sample size | Sample type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ekinci and Hosany | A number of destinations by recalling the last destination visited | 250 | Visitors |
| Hosany, et al. | Three different cities in the United Kingdom. | 148 | Visitors |
| Murphy, et al. | Two destinations in Queensland, Australia: Cairns and Whitsunday Islands | 464 | Visitors |
| d'Astous and Boujbel | A number of countries representing five continents | French speaking Canadians | - |
| Prayag | South Africa-Cape Town | 85 | Visitors |
| Pitt, et al. | 10 African countries | Official tourism websites of 10 African countries | - |
| Murphy, et al. | Queensland, Australia | 277 | Visitors |
| Hosany, et al. | A number of destinations by recalling the last destination visited | 148 | Visitors |
| Ekinci, et al. | Mediterranean region of Turkey | 365 | Visitors |
| Sahin | Istanbul, Turkey | 272 | Visitors |
| Lee, et al. | France, USA, China | 429 | Visitors |
| Stokburger-Sauer | Ireland | 421 | Visitors |
| Usakli and Baloglu | Las Vegas. | 368 | Visitors |
| Kilic and Sop | Turkey | 226 | Visitors |
| Chen and Phou | Cambodia | 428 | Visitors |
| Lin | Taiwan | 315 | Visitors |
| Kim and Lehto | South Korea | 480 | Visitors |
| Xie and Lee | Beijing | 497 | Visitors |
| Baloglu, et al. | Jamaica's | 312 | Visitors |
| Kumar and Nayak | India | 152 | Visitors |
| Kim and Lee | South Korea | 302 | Visitors |
| Hultman, et al. | Taiwan | 490 | Visitors |
| Zeugner-Roth and Zabkar | Austria, Italy, Germany | 411 | Visitors |
| Gomez Aguilar, et al. | Spain destinations: Granada, Torremolinos | 329 | Visitors |
| Souiden, et al. | Dubai | 173 | Visitors |
| Pan, et al. | Chine | 515 | Visitors |
| Kim, et al. | South Korea | 316 | Visitors |
| Chi, et al. | Italy: Sardinia | 1266 | Visitors |
Table 2: Summary of survey methods of destination personality studies 2006-2018.
Apart from all this still more study and research is required to understand the destination personality role and its importance for destination branding. In spite of the growing body of work on destination branding in general, particularly at a national or country level, little research has been done to determine whether or not tourists attribute tourism destinations with brand personality characteristics and if so, whether or not this influences their travel behavior.
Destination personality consider as brand personality in context of tourism literature. This study accomplished a comprehensive evaluation of the literature of destination personality from 2006-2018, synthesizing literature with regards to the concepts, dimensions and measurements. The review of the more recent destination personality literature reveals that 42-item BPS of Aaker was used to measure destination personality.
But the most noticeable dimensions of destination personality based on which human characteristics are attributed to the destination are sincerity, excitement and conviviality and researchers used these dimensions are most commonly to measure destination personality. And these noticeable dimensions of destination personality sincerity and excitement were found to be two main dimensions and conviviality is newly specific to destination.
Citation: Zulfiqar U (2024) An Overview of Destination Personality and its Measurement Issue in Tourism: A Literature Review. J Tourism Hospit. 13:551.
Received: 15-Dec-2021, Manuscript No. JTH-21-15010; Editor assigned: 20-Dec-2021, Pre QC No. JTH-21-15010 (PQ); Reviewed: 03-Jan-2022, QC No. JTH-21-15010; Revised: 22-May-2024, Manuscript No. JTH-21-15010 (R); Published: 19-Jun-2024 , DOI: 10.35248/2167-0269.24.13.551
Copyright: © 2024 Zulfiqar U. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.