Medicinal & Aromatic Plants
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-0412
ISSN: 2167-0412
Research Article - (2021)Volume 10, Issue 5
Striga hermonthica is an invasive and destructive weed which is usually infects crops as well as pasture and wild grasses. It is widely distributed in many African countries including Sudan and it is traditionally been used as abortifacient, for pneumonia, fungal infections, as contraceptive, mosquito repellent and anti-diabetic. This study was aimed to identify morphology of whole plant and microscopic characteristics of the root, stem, and leaf and powder microscopy to support its botanical pharmacognostical characterization. Morphological and microscopic study was carried out using fresh and dry whole plant, the root, stem and leaves. The results of present macroscopic and histomicroscopic features of root stem and leaves of S. hermonthica and powder microscopic were reported which may provide useful information for the regulatory aspects of the quality control measures of the crude drugs.
Striga hermonthica; Botanical pharmacognostical; Macroscopic; Microscopic
Striga hermonthica (Del.) Benth. is a weed belongs to the family Orobanchaceae which is considered invasive and destructive and nearly hard to exterminate and usually infect crops as sorghum, maize, millet, rice, and sugar cane, as well as pasture and wild grasses [1,2]. It attaches itself to the roots of the host plant and diverts essential nutrients, which render the host stunted and decrease the yield of the crops more than 50% [3]. S. hermonthica widely distributed in many African countries and its commonly known as Witchweed and locally in Sudan it is called Al-Booda. It is the most distributed among Striga species in Africa throughout the Nile Delta and have the most damage to crops. It has great within-species variation which is expected as it is an obligate out-breeder [4]. Also, S. hermonthica was collected from different geographical regions exhibits variability (Figure 1) [5]. Floral Striga hermonthica (Del.) Benth. is a weed belongs to the family Orobanchaceae which is considered invasive and destructive and nearly hard to exterminate and usually infect crops as sorghum, maize, millet, rice, and sugar cane, as well as pasture and wild grasses [1,2]. It attaches itself to the roots of the host plant and diverts essential nutrients, which render the host stunted and decrease the yield of the crops more than 50% [3]. S. hermonthica widely distributed in many African countries and its commonly known as Witchweed and locally in Sudan it is called Al-Booda. It is the most distributed among Striga species in Africa throughout the Nile Delta and have the most damage to crops. It has great within-species variation which is expected as it is an obligate out-breeder [4]. Also, S. hermonthica was collected from different geographical regions exhibits variability (Figure 1) [5]. Floral variations may discourage cross pollinations between these strains and further enhance the differentiation of populations in S. hermonthica as evidenced in recent molecular studies in which populations of S. hermonthica collected from sorghum, millet, and maize showed genetic differences, the maize strains were more closely related to the sorghum-strain than to the millet-strain. Despite its effects on crops and agriculture, it is traditionally been used orally as an abortifacient, for pneumonia, fungal infections, as contraceptive, mosquito repellent [6], anti-cancer [7], and anti-diabetic agent in western Sudan [8].
Figure 1: Geographical distribution map of S. hermonthica in Africa.
Some pharmacological investigations of S. hermonthica extracts were showed an in vitro effect against Trypanosoma congolense and Trypanosoma cruzi [9], antimicrobial activities against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli and Candida albicans [10]. The phytochemical studies of this plant showed the presence of terpenes, saponin, cardiac glycosides, alkaloids, anthrocenocides, coumarins, tannins and flavonoids [11]. However, few pharmacognostical studies were carried out for evaluation of plant material of S. hermonthica. Therefore, this study was aimed to study the morphology of whole plant and microscopic characteristics of the root, stem, leaf and powder microscopy, in order to identify botanical-pharmacognostical markers, which may be an important contribution regarding the aspects of quality control measures of S. hermonthica and related similar species.
The taxonomical position of S. hermonthica [12]
Domain: Eukaryota
Kingdom: Plantae
Phylum: Spermatophyta
Subphylum: Angiospermae
Class: Dicotyledonae
Order: Scrophulariales
Family: Orobanchaceae
Genus: Striga
Species: S. hermonthica.
S. hermonthica (whole plant) was collected from Shukaba province, South Gezira State, Sudan and identification and authentication were done at Department of Pharmacognosy University of Gezira. The used chemical materials and equipment include ethanol, distilled water, chloral hydrate 10%, safranin reagent 1%, glycerin, handheld magnifying lens (25x magnification), light microscope (OLYMPUS CH20i, Tokyo, Japan) connected to 16.0-Megapixel digital camera, razors and dissection sets.
Microscopical studies were carried out for whole plant parts using the handheld magnifying lens. Fine hand sections of the lamina, stem, root, using very harp razor were cut into very thin transverse sections, then mounted with chloral hydrate and heated using flame until bubbling occurs. The section were stained with aqueous safranin and mounted in glycerin. Microphotographs of sections and powder analysis were made by using microscope and photos were collected too.
Macroscopical study
S. hermonthica (Figures 2 and 3) is a herbaceous annual plant rang in height of 30-100 cm, where the most infectious forms occurring in Sudan and Ethiopia [12,13]. Larger plants show more branching. Stems and leaves are covered with specific trichomes rendering the plant with a harsh texture. Leaves mostly opposite on the lower half the stem but irregular above, narrowly lanceolate, or elliptic, 2-8 cm long, up to 1 cm wide. Inflorescence is a terminal nails of sessile flowers that branching from the axils of upper leaf. Flowers joined by bracts 1-2 cm long, up to 3 mm wide, with an edge of ciliate hairs. Calyx tubular reaching 1 cm long with 5 ribs and 5 teeth varying from 2-3 mm long. Flower asymmetrically campanulate, the tube 1-2 cm long, bent approximately halfway up in West African, Sudanese, and Ethiopian populations but usually well above halfway in East African populations [14]. Corolla lobes 4, one bi-lobed almost erect, the others spreading horizontally, up to 2 cm across, pink with some white markings within the throat. The stigma and stamens are concealed in the tube. The primary inflorescence spike may hold up to 100 flowers but only 6-10 are open at a time. The capsules are up to 1 cm long and each develops several hundred-minute seeds, approximately 0.3 mm long by 0.2 mm wide. The root system is delicate with little ability to uptake nutrients from the soil, but branches develop from lower nodes of the weed, ramifying and developing secondary haustoria and attachments on contact with other host roots, [15] which facilitate the loss of loses water, carbon, nitrogen and nutrients form the host plant to S. hermonthica [16].

Figure 2: Photo showing S. hermonthica in the wild.

Figure 3: Photo showing S. hermonthica (whole plant).
Microscopical study
Microscopic study of root: The root is elongated taproots, cylindrical, sharpened towards the ends with brownish-yellow color. Transverse section (T.S.) of the young root (Figure 4) appeared circular in shape with tissue organization as outer piliferous layer, followed by the middle cortex and inner stele. Most tissues cells were empty and appeared reddish to brown in color, but some cells contained the deposition of colored secretary substances. Cortex was well marked and contains the important section of the root where prenchymatous cells were found to contain air cavities that facilitate the gaseous exchange [17]. Starch grains were in the cortical parenchymatous cells (Figure 5), where carbohydrate storage [18]. Calcium oxalate crystals (Figure 6) were found in the outer cortical parenchyma cells with various functions regulation of calcium levels in plant tissues and organs, protection against herbivory, detoxification of heavy metals and/or strengthening of the tissues [19]. The central part or stele were highly reduced and represented largely by xylem vessels and phloem (Figure 7).
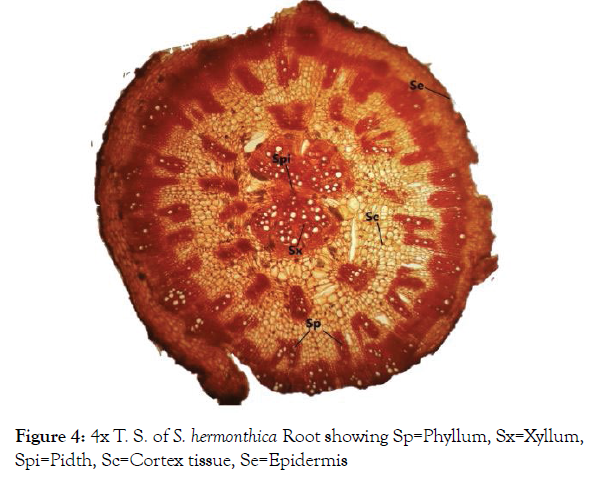
Figure 4: 4x T. S. of S. hermonthica Root showing Sp=Phyllum, Sx=Xyllum, Spi=Pidth, Sc=Cortex tissue, Se=Epidermis
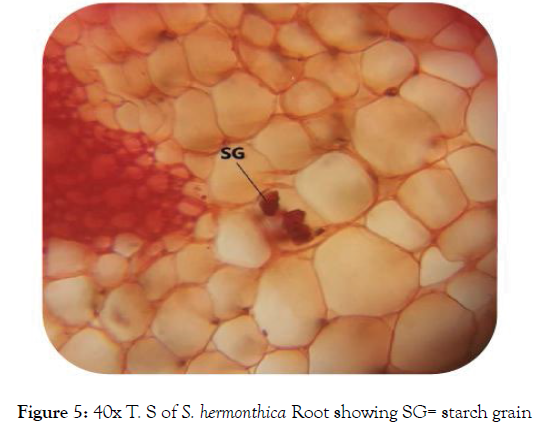
Figure 5: 40x T. S of S. hermonthica Root showing SG= starch grain
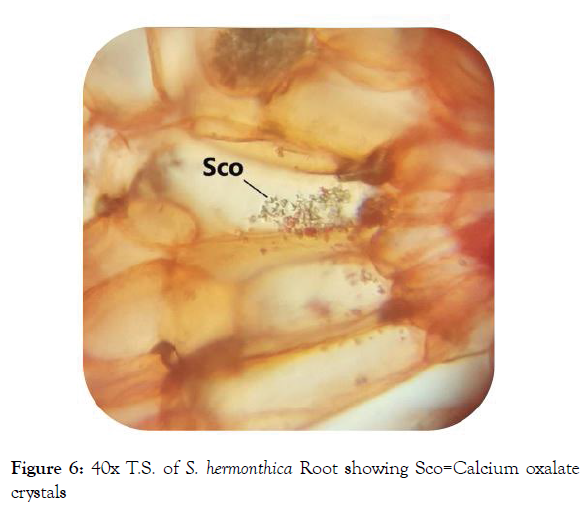
Figure 6: 40x T.S. of S. hermonthica Root showing Sco=Calcium oxalate crystals
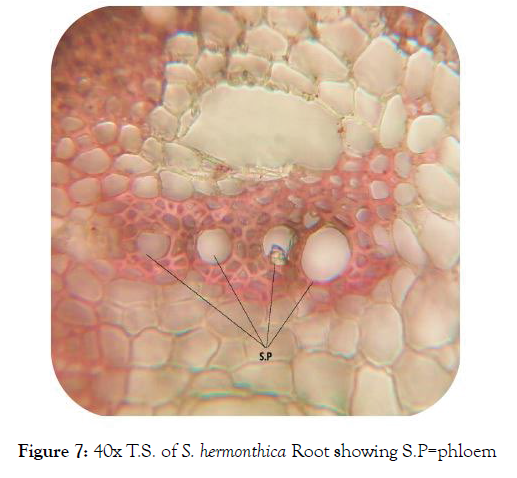
Figure 7: 40x T.S. of S. hermonthica Root showing S.P=phloem
Microscopic study of stem: T.S. of S. hermonthica stem was appeared with semi-regularly circular outline (Figure 8) with tissue organization as outer layer of epidermis, followed by the cortex and vascular bundle. Epidermis consisted of single cellular layer with thick cuticle. The Cortex was appeared in rows of cells contained chlorophyll and calcium oxalate crystals. Vascular bundles were mostly secluded with polygonal to ovoid shapes.
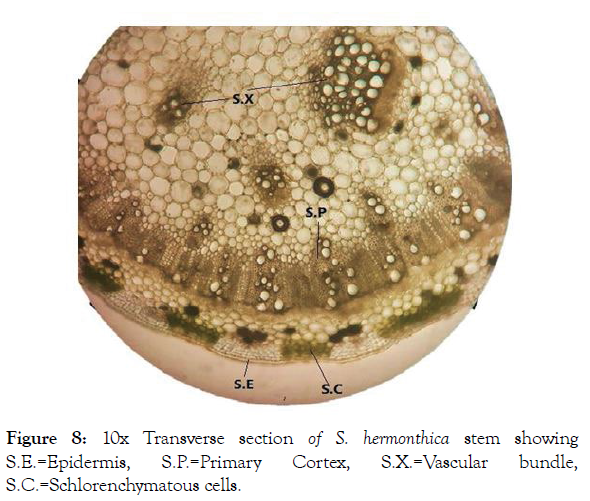
Figure 8: 10x Transverse section of S. hermonthica stem showing S.E.=Epidermis, S.P.=Primary Cortex, S.X.=Vascular bundle, S.C.=Schlorenchymatous cells.
Microscopic study of leaf: T.S. of S. hermonthica leaf indicated that the lamina was differentiated into epidermis, mesophyll and vascular tissues (Figure 9). Upper and lower epidermises were a single layer composed of tightly arranged rectangular cells with striated outer walls covered by cuticle to reduce epidermal water loss [3] and presence of few trichomes. Below the both epidermis there was a layer of sclerenchymatous tissues. The mid rib area was appeared to have an acute depression on the adaxial side with broadly ovoid abaxial side. Midrib was composed of epidemics, sclerenchyma, collenchyma and vascular bundle (Figure 10). Lamina was differentiated upper elongated mesophyll having a compact palisade cells contain chloroplasts and lower spongy parenchymatous tissue (Figure 11) which allows efficient nutrient remobilization [20].
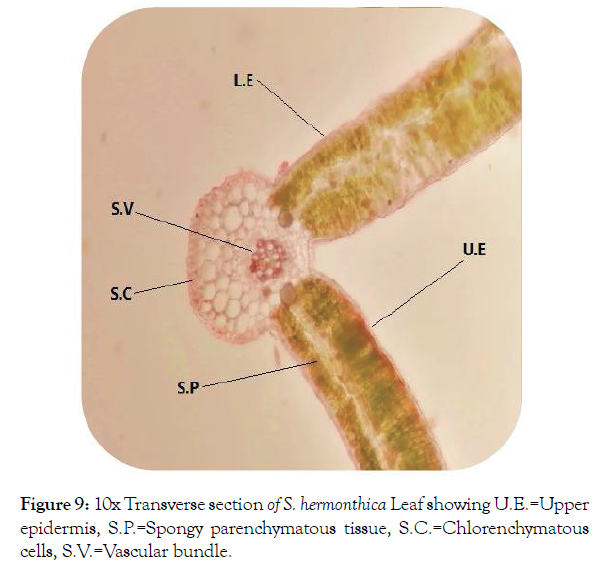
Figure 9: 10x Transverse section of S. hermonthica Leaf showing U.E.=Upper epidermis, S.P.=Spongy parenchymatous tissue, S.C.=Chlorenchymatous cells, S.V.=Vascular bundle.
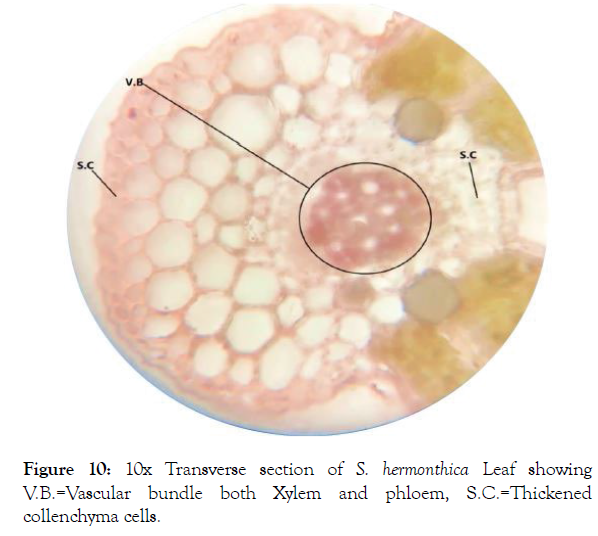
Figure 10: 10x Transverse section of S. hermonthica Leaf showing V.B.=Vascular bundle both Xylem and phloem, S.C.=Thickened collenchyma cells.
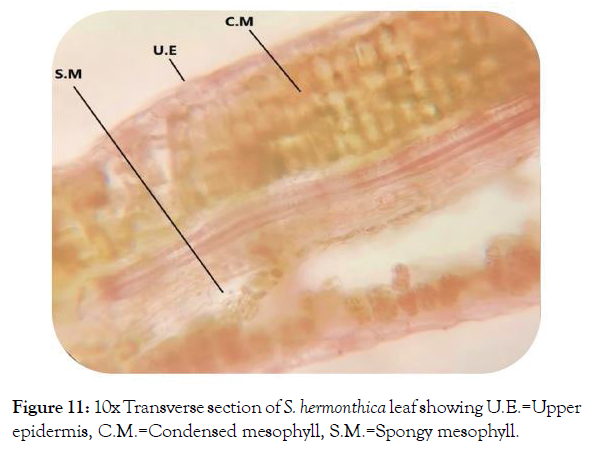
Figure 11: 10x Transverse section of S. hermonthica leaf showing U.E.=Upper epidermis, C.M.=Condensed mesophyll, S.M.=Spongy mesophyll.
Microscopic study of powder: The shade dried S. hermonthica whole plant was milled into powder that subjected to microscopic examination which showed fragments of leaf epidermis with venations, flower stalk fragments, calcium oxalate crystals, sclerenchyma and parenchyma fragments and starch grains (Figure 12).
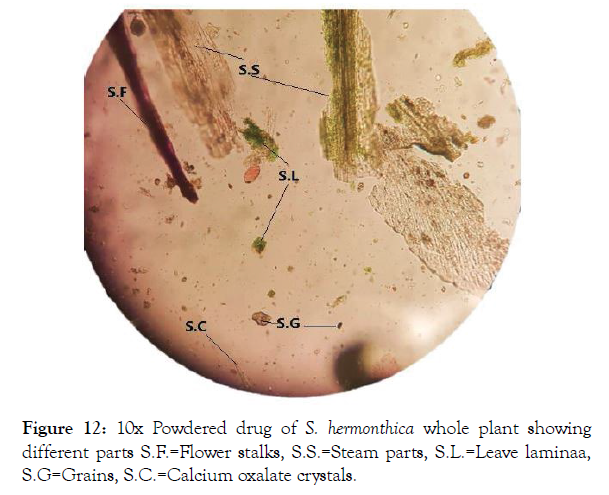
Figure 12: 10x Powdered drug of S. hermonthica whole plant showing different parts S.F.=Flower stalks, S.S.=Steam parts, S.L.=Leave laminaa, S.G=Grains, S.C.=Calcium oxalate crystals.
This study reported the morphological and anatomical features of S. hermonthica (Del.) Benth distributed in Sudan, including general macroscopical characters and microscopical study of root, stem, leaf and whole powdered plant materials. These findings could be remarkable anatomical markers useful for identifying this species that are useful for Botanical Pharmacognostic standards or markers for identification of crude drug materials which found scant for S. hermonthica.
None.
The authors would like to extend their sincere gratitude to Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Gezira, Sudan for support.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Citation: Abdelgadir AA, Bushra BE (2021) Botanical Pharmacognostical Study of Al-Booda (Striga hermonthica) Distributed in Gezira State, Sudan. Med Aromat Plants (Los Angeles) 10: 388.
Received: 10-May-2021 Accepted: 24-May-2021 Published: 31-May-2021 , DOI: 10.35248/2167-0412.21.10.388
Copyright: © 2021 Abdelgadir AA, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.