Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry: Open Access
Open Access
ISSN: 2471-2698
ISSN: 2471-2698
Commentary - (2022)Volume 7, Issue 1
Auditing is a dynamic part of any pharmaceutical companies. Quality Audit is analysis and appraisal of all quality assurance program and quality control program to ensure its quality. It is one of the way to examine pharmacy program and make sure that procedures, compensation comply with regulatory and GMP requirements. Quality audit is usually operated by external experts or by a team selected by management of pharmaceutical companies. An audit will appraise strength and weakness of quality assurance processes, the result will help in improving the process and also build better system for company benefits. Pharmaceutical audits includes from design qualification upto performance qualification steps. It also included SOP, guildliness, validation policies.
Audit; Internal audit; SOP, Nonconformitites; Defects
An audit could be defined as, analysis of system or its process toensure that it meets requirements.[1] According to InternationalOrganization for Standardization (ISO) audits have defines as theSystematic, independent and documented process for obtainingaudit evidence and evaluating them objectively to determine the degree to which the verification criteria are met.[2,3] ( Figure 1).
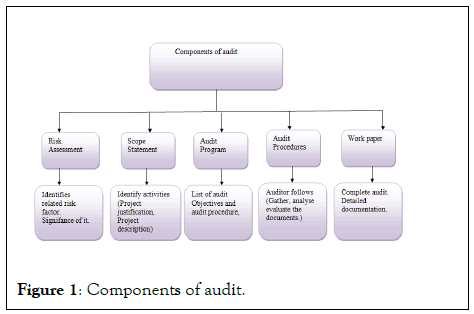
Figure 1: Components of audit.
Objectives of audit
• Establish effectiveness to assembles the quality requirements and quality objectives.
• Assembles the GMP and regulatory requirement.
• Providing an opportunity to audit team to improve quality management system [4].
• permitting list of audited registered companies in a register.
• Determining conformity or non-conformity to assembles specified quality system.
• Modifying potential of vendors.
• Assembles conformity of implementation of documents [5,6].
Internal audit
It is also known as self-audit or first party audit. Internal audit is a experienced authority that give advice to pharmaceutical companies or organization on how to achieve their goals in a better way [7,8] .The internal audit uses a systematic approach to evaluate organizational problems and solution on it. The objectives of internal audits are as follow.
• Regulate the internal system of pharmaceutical companies.
• Analysis of company policies and their operations.
• Analyse the accuracy and verify the errors and frauds.
• recognition and obstruction of errors and defects.
• Defend the assets.
• Advice in smooth functioning of internal control system.
External audit
External audit is also known as Second-Party audit. They assign customer for conducting an audit on a supplier or contractor basis. Example a second party audit may conducted by a medical device company that contracted laboratory to do sterility testing. to regulate that labs meet its QSR (Quality System Regulation) requirement. It is always desirable to analyse the ability of contra -ctors to check activities are according to GMP.
Advantages are as follow:
• Expand knowledge and assurance in the partnership agreement.
• Ensures that requirements are assumed and detected.
• Decrease the risk of failure.
Regulatory audit
A regulatory agency or an independent body performs this type of audit for compliance or registration purpose. It is not conducted by individual customer or suppliers. For Example, a team of American Pathologist auditing a blood bank for accreditation purpose (Figure 2).
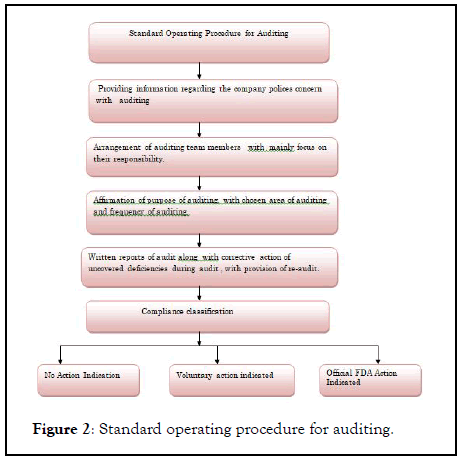
Figure 2: Standard operating procedure for auditing.
This type of audit is unannounced and conducted by regulatory agencies as MCA,USFDA .after regulatory audit, formal report will be delivered to
For MCA: Verbal feedback report is given at exit meeting.
For USFDA: Provides feedback in form no 483 at exit meeting.
Notification
It is the first step of audit. This process notify the party about date and time of the audit. It also notify the the list documents that check, in order to understand policies of company.
Planning
This is pre- step of audit. Auditor takes this step to identify the risk area and area of interest.
Opening meeting
Meeting between auditing staff and senior management as well as administrative staff .auditor will explain the process they will undertake. Management will explain the area of risk and interest to them.
Field work
Field work start after the results of meeting to adjust final audit plan. employee are notify about audit, schedules are drawn up regarding the activities of audit. Investigation begun after learning business procedure, interviewing of staff , testing current business practices by sampling.
Communication
The audit team contact with corporate auditor to simplify the processes ,gain the access to documents.
Draft audit
After completion of audit, next step is preparation of draft audit. It is detail about what was done and what has found, a distribution list of parties to receive preliminary results and list of concern.
Response of management
The draft futher given to management to review,edit, suggest changes, and correct errors. By making final corrections reports are given to management for management response. Management is requested to answer the report by stating whether they agree with problems cited, and expected date by which all issues have been corrected.
Final meeting
The final meeting is planned to discuss the management response and approach the opportunity of audit.
Report distribution
It is ninth step of audit, where the final report of audit is send to arrogate officials inside an outside of audit area.
Feedback
The last step of audit is feedback, where the audited company implements the recommended changes .this continues until all issues are take up and next audit cycle starts.
Master controls pharmaceutical audit management software is automating managing an process of audit with the effective cost. This software is directly coordinate with cGMP ,FDA, ISO regulations. the software approach to cGMP regulation of pharmaceutical industry for internal audit at systematic intervals to evaluate ,implement and maintain quality system. Master control software provides a unique transfer OQ (TOQ) test which provides complete validation documents. This documents attend manifestation that software is performing properly according to regulatory specification (Figure 3).
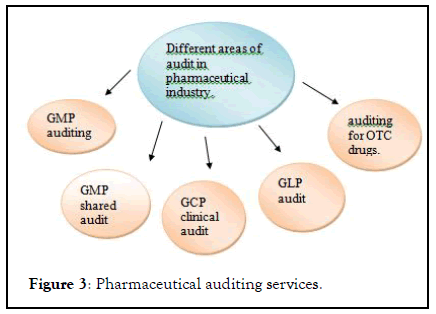
Figure 3: Pharmaceutical auditing services.
Key features of software
• Gather information such as audit agenda, audit team members, checklist.
• Efficient audit Tracking through master control audit solution.
• Scheduling of audit.
• Follow up by emails notification.
• Analysis of audit.
• Compliance of audit.
• Corrective action and preventative action.
As audit starts, there might some situation arise that indicates the failure of partially or wholly quality management system, such situation called conformities or deficiencies.
Reasons of nonconformities
The defined process does not conform to the GMP and regulatory requirements.
The define process has not been put in use in describe way.
Planned results are not achieve.
Classification of deficiencies
Following types of nonconformities are identified during internal audit as well as regulatory audit.
Critical defects : Critical defects shows adverse physiological response by consumer. It shows effects on strength, purity, safety, efficiency in product. Cross contamination, inadequate labeling, active ingredients out of specification this are some sources of critical defects.
Major defects : It reduces the stability of product, without causing harm to consumers. Sources of major defects are Equipments are not calibrated, Lack of equipment cleaning, operator are not familiar with standard operating procedure.
Minor defects : It has low probability of affecting quality, stability of product. Cracks in wall surface, warehouse not clean as per schedule, review of standard operating procedure is over. This might some sources of minor defects (Figure 4).
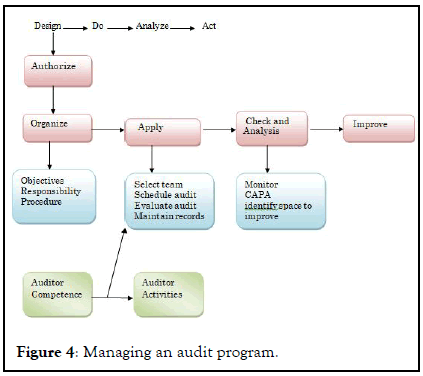
Figure 4: Managing an audit program.
Audits are observed as important tool for management for achieving continues improvement. It is necessary business process that advices for improvement. Audits are essential to appraise how successfully process have been implemented. It achieve the effectiveness of any defined target levels. When employees and managers start to observe audits as opportunities to improve, they start to see auditors as productive member of organization not as police officers. Improvement of any organization reflects on staff, program as well as on profession.
[Cross ref ], [google scholar]
[Cross ref ],[ google scholar]
[Cross ref ], [google scholar ]
[Cross ref ] , [google scholar]
[Cross ref ] ,[google scholar]
[Cross ref ] ,[google scholar ]
[Cross ref], [google scholar ]
[Cross ref ], [google scholar ]
Citation: Jain AA, Babar VB, Kulkarni AA (2022) . Review on Audit in pharmaceutical industry. Pharm Anal Chem. 7: 142.
Received: 04-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. PACO-20-5366; Editor assigned: 07-Jan-2022, Pre QC No. PACO-20-5366 (PQ); Reviewed: 21-Jan-2022, QC No. PACO-20-5366; Revised: 25-Jan-2022, Manuscript No. PACO-20-5366 (R); Published: 01-Feb-2022 , DOI: 10.35248/ 2471-2698.22.142
Copyright: © 2022 AA Jain. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.