Journal of Aeronautics & Aerospace Engineering
Open Access
ISSN: 2168-9792
ISSN: 2168-9792
Research Article - (2017) Volume 6, Issue 1
Flight dynamics - The science of the laws of motion of aircraft under the influence of wind, gravity, and reaction forces. It is a combination of mainly three classic disciplines: solid mechanics, fluid dynamics, and mathematics. Among the wide range of problems in the dynamics of flight of great practical importance are the problems connected with the study of the steady rectilinear motion of the aircraft. The solution allows them to determine the flight characteristics of the aircraft, characterized by the range of possible speeds and heights, rate of climb, range, flight time, and so on.
<Keywords: Calculation aerodynamic characteristics of the aircraft, AN-225; Thrust required and thrust available; Practical ceiling of aircraft; Building a polar flight; Flight dynamics
Building a polar flight, making level flight at various speeds (Mach number 0.4 to 0.9) and on the same altitude, the aircraft as it passes from one polar to another, it is the flight of the aircraft polar.
From the equilibrium conditions of the lift Ya gravity (weight) G (G = mg) in a horizontal flight:
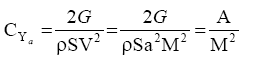
Where, 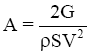 on the height and a constant weight of the aircraft,the value is constant.
on the height and a constant weight of the aircraft,the value is constant.
All calculations are carried out in SI.
From this formula, it follows that, in a steady horizontal flight, each Mach number M complies to
a specific lift coefficient CYa.
For the aircraft, AN-225 with turbojet engines must use the curves of required and available thrust. Calculation and construction of required thrust PReq by the formula:
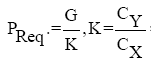 the aerodynamic quality of the aircraft.
the aerodynamic quality of the aircraft.
When determining the flight characteristics of the aircraft used by the equation of power in the projection on the axis of the trajectory of the coordinate system, considering at the same plane as the material point of variable mass. And when the aircraft stability and controllability of the calculations it is regarded as solid [1-4].
Initial data for the implementation of the research is of course work in aerodynamics,
"Calculation of aerodynamic characteristics of the aircraft AN-225", its geometrical parameters, the aerodynamic characteristics and polar cruising.
Research includes calculations, graphics and drawings, explanation and justification of the calculation of performance, the characteristics of longitudinal stability and controllability of the aircraft.
To calculate the flight characteristics of the aircraft AN-225, used the method of N.E. Zhukovsky,
A method based on the construction of curves thrust required and thrust available, which is determined by the parameters of steady flight modes.
Characteristics of the standard atmosphere are as follows:
Calculate thrust required and thrust available
Calculation of the algorithm:
Specifies flight height, Н, m.; H=0
Specifies the number of flight Mach; M=0.3
Determine the relative density of the air; Δ (Table 1); Δ=1
| Height, H, (km) |
Relative density, ∆ |
Relative speed of sound, Ka | Density, |
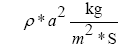 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1.225 | 141.8*103 |
| 2 | 0.822 | 0.977 | 1.0067 | 111.3*103 |
| 4 | 0.699 | 0.954 | 0.8194 | 86.3*103 |
| 6 | 0.538 | 0.930 | 0.6602 | 66, 08*103 |
| 8 | 0.429 | 0.905 | 0.5259 | 50*103 |
| 10 | 0.337 | 0.880 | 0.4136 | 37.06*103 |
| 11 | 0.298 | 0.867 | 0.3648 | 31.75*103 |
| 12 | 0.2536 | 0.867 | 0.3156 | 27.48*103 |
| 14 | 0.185 | 0.867 | 0.2306 | 20.08*103 |
| 16 | 0.135 | 0.867 | 0.1654 | 14.4*103 |
| 18 | 0.0983 | 0.867 | 0.1207 | 10.51*103 |
| 20 | 0.0718 | 0.867 | 0.0889 | 7.74*103 |
Table 1: Characteristics of the standard atmosphere.
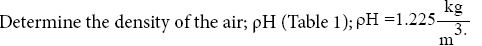
Determine the ratio; Ka (Table 1); Ka = 1
Determine the speed of sound at a given height with a given number M, (m/s).
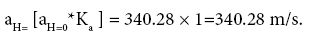
Where, aН=0=340.28 м/s - the speed of sound at sea level H=0
Determine the flight speed (m/s); V= [M×aН=0] =0.3×340.28=102.08 m/s.
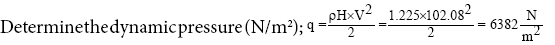
Determine the average gross weight of the aircraft, (N).
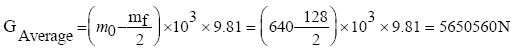
where,W0= 640 ton-takeoff weight of the aircraft;
Wf =128 ton-mass of the fuel
The coefficient of aerodynamic lift in a horizontal flight.
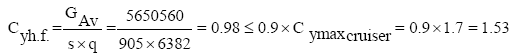
where,
Cymax cruiser is the maximum lift coefficient of the wing when stowed mechanization (Tables 2-4).
| Changing the ratio of the polar blade, Ka(M) |
Mach number (M) |
Change parasitic drag coefficient, KCX0(M) |
Changing the maximum lift coefficient, Kcymax(M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0.2 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0.4 | 1 | 1 |
| 1.09 | 0.6 | 1.03 | 0.94 |
| 1.16 | 0.7 | 1.2 | 0.89 |
| 1.27 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 0.81 |
| 1.4 | 0.9 | 1.9 | 0.73 |
| 1.6 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 0.65 |
Table 2: Odd changes in the number of M.
| Take-off weight, m0 | Fuel weight, mf |
Wing area, S, m2 | Take-off thrust, P0, k N | Parasitic drag coefficient, Cx0 | Wingspan, Lwing, m |
Specific fuel consumption, 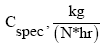 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 640 | 128 | 905 | 6*234 | 0.021 | 88.4 | 0.057 |
Table 3: Personal data on the aircraft AN-225.
| Cymax cruiser |
Mmax | Qmax, 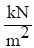 |
Cmax, T.off | KT.off | Cymax const | Kconst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.7 | 0.88 | 22 | 2.5 | 8.5 | 3.1 | 5.0 |
Table 4: Personal data on the aircraft AN-225.
Determine the effective extension of the wing:
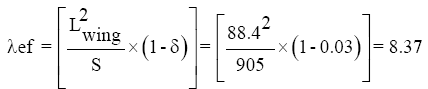
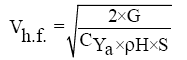
Where, δ =0.02….0.04;
S=905 m2- wing area;
Lwing = 88.4 - wingspan
Determine the ratio of the blade of the polar;
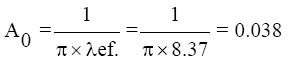
Determine the rate of change of blade polar depending on the number of M, KA (Table 2); KA=1
Determine the rate of change of parasitic drag coefficient as a function of the number of M, KCX0 (Table 2).
KCX0 =1
Determine the drag coefficient in horizontal flight;
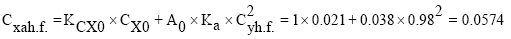
where,Cx0=0.021- parasitic drag coefficient (Table 3).
Define flight aerodynamic efficiency;
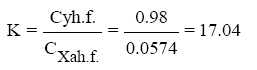
Identify thrust required for level flight, N.
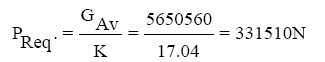
Determine the ratio of thrust change the number of M.
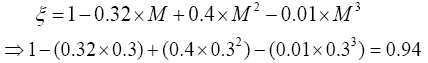
Determine the takeoff thrust engines (N) (Table 3).
P0 =6*234000=1404000N
Identify the thrust available in horizontal flight.
When,
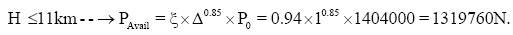
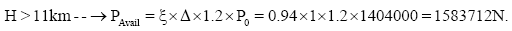
By algorithm, using a program in Excel.
The calculation results are shown in Tables 5 - 13 and in Figures 1 - 13.
| Flight altitude, км | 0 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The number of flight Mach | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 |
| Relative density of the air, D | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| The air density, rH, kg/m3 | 1.225 | 1.225 | 1.225 | 1.225 | 1.225 | 1.225 | 1.225 | 1.225 | 1.225 | 1.225 |
| Coefficient Ka | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| The speed of sound a, m/S | 340.28 | 340.28 | 340.28 | 340.28 | 340.28 | 340.28 | 340.28 | 340.28 | 340.28 | 340.28 |
| Flight speed , V, m/s | 34.03 | 68.06 | 102.08 | 136.11 | 204.17 | 238.20 | 272.22 | 289.24 | 306.25 | 323.27 |
| Dynamic pressure, N/m2 | 709 | 2837 | 6383 | 11347 | 25532 | 34752 | 45390 | 51241 | 57447 | 64007 |
| The average gross weight of the aircraft, Gav. N | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamiclift in horizontal flight, Cyh.f. | 8.80 | 2.20 | 0.98 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.10 |
| Effective of wing extension , λ | 8, 38 | 8.38 | 8, 38 | 8, 38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 |
| Factor Blade of the polar, A0 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 |
| Coefficient Ka | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.27 | 1.33 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Coefficient KCX0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1, 03 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.95 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic drag in horizontal flight, Cxa h.f. | 2.9664 | 0.2051 | 0.0574 | 0.0325 | 0.0241 | 0.0266 | 0.0324 | 0.0365 | 0.0405 | 0.0415 |
| Flight aerodynamic quality, K | 2.97 | 10.73 | 17.05 | 16.93 | 10.14 | 6.75 | 4.24 | 3.34 | 2.68 | 2.35 |
| Thrust required Prequired, N |
1903984 | 526541 | 331364 | 333815 | 557029 | 837300 | 1331466 | 1690318 | 2107042 | 2403497 |
| The Rate of changes in the thrust of the number of flight Mach , ξ | 0.972 | 0.952 | 0.940 | 0, 935 | 0, 950 | 0.969 | 0.995 | 1.011 | 1.029 | 1.048 |
| Take-off thrust engines, P0, N, | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 |
| Thrust available, Pavail, N | 1364674 | 1336496 | 1319381 | 1313245 | 1333575 | 1359872 | 1396812 | 1419246 | 1444309 | 1471990 |
| Vertical speed, Vy, m/S | -3.25 | 9.76 | 17.85 | 23.59 | 28.06 | 22.03 | 3.15 | -13.88 | -35.92 | -53.29 |
Table 5: The calculation of thrust required and thrust available, H = 0 km.
| Flight altitude, км | 2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The number of flight Mach | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 |
| Relative density of the air, D | 0.822 | 0.822 | 0.822 | 0.822 | 0, 822 | 0.822 | 0.822 | 0.822 | 0.822 | 0.822 |
The air density, 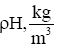 |
1.0067 | 1.0067 | 1.0067 | 1.0067 | 1.0067 | 1.0067 | 1.0067 | 1.0067 | 1.0067 | 1.0067 |
| Coefficient Ka | 0.977 | 0.977 | 0.977 | 0.977 | 0.977 | 0.977 | 0.977 | 0.977 | 0.977 | 0.977 |
| The speed of sound a, m/S | 332.454 | 332.454 | 332.454 | 332.454 | 332.454 | 332.454 | 332.454 | 332.454 | 332.454 | 332.454 |
| Flight speed , V, m/s | 33.25 | 66.49 | 99.74 | 132.98 | 199.47 | 232.72 | 265.96 | 282.59 | 299.21 | 315.83 |
| Dynamic pressure, N/m2 | 556 | 2225 | 5007 | 8901 | 20028 | 27260 | 35605 | 40195 | 45063 | 50209 |
| The average gross weight of the aircraft, GAv, N | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic lift in horizontal flight, Cyh.f. |
11.22 | 2.81 | 1.25 | 0.70 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| Effective of wing extension , λ | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 |
| Factor Blade of the polar, A0 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0, 038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0, 038 | 0.038 |
| Coefficient Ka | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.27 | 1.33 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Coefficient KCX0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.03 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1, 95 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic drag in horizontal flight, Cxa h.f. | 4.8078 | 0.3202 | 0.0801 | 0, 0397 | 0.0257 | 0.0275 | 0.0330 | 0.0369 | 0.0409 | 0.0418 |
| Flight aerodynamic quality, K | 2.33 | 8.76 | 15.57 | 17.67 | 12.15 | 8.32 | 5.32 | 4.21 | 3.39 | 2.97 |
| Thrust required Prequired, N | 2420616 | 644803 | 362940 | 319796 | 465019 | 678749 | 1062836 | 1342999 | 1668846 | 1900779 |
| The Rate of changes in the thrust of the number of flight Mach , ξ | 0.972 | 0.952 | 0, 940 | 0.935 | 0.950 | 0.969 | 0.995 | 1.011 | 1.029 | 1.048 |
| Take-off thrust engines, P0, N | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 |
| Thrust available, Pavail, N |
1155234 | 1131380 | 1116892 | 1111698 | 1128908 | 1151169 | 1182439 | 1201430 | 1222647 | 1246080 |
| Vertical speed, Vy, m/S | -7.44 | 5.73 | 13.31 | 18.64 | 23.44 | 19.46 | 5.63 | -7.08 | -23.63 | -36.59 |
Table 6: The calculation of thrust required and thrust available, H = 2 km.
| Flight altitude, км | 4 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The number of flight Mach | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 |
| Relative density of the air, D | 0.699 | 0.699 | 0.699 | 0.699 | 0.699 | 0.699 | 0.699 | 0.699 | 0.699 | 0.699 |
The air density, 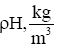 |
0.8194 | 0.8194 | 0.8194 | 0.8194 | 0.8194 | 0.8194 | 0.8194 | 0.8194 | 0.8194 | 0.8194 |
| Coefficient Ka | 0.954 | 0.954 | 0.954 | 0.954 | 0.954 | 0.954 | 0.954 | 0.954 | 0.954 | 0.954 |
| The speed of sound a, m/S | 324.627 | 324.627 | 324.627 | 324.627 | 324.627 | 324.627 | 324.627 | 324.627 | 324.627 | 324.627 |
| Flight speed , V, m/s | 32.46 | 64.93 | 97.39 | 129.85 | 194.78 | 227.24 | 259.70 | 275.93 | 292.16 | 308.40 |
| Dynamic pressure, N/m2 |
432 | 1727 | 3886 | 6908 | 15543 | 21156 | 27632 | 31194 | 34972 | 38966 |
| The average gross weight of the aircraft, GAv, N | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic lift in horizontal flight, Cyh.f. |
14.46 | 3.62 | 1.61 | 0.90 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.16 |
| Effective of wing extension , λ | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 |
| Factor Blade of the polar, A0 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 |
| Coefficient Ka | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.27 | 1.33 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Coefficient KCX0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.03 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.95 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic drag in horizontal flight, Cxa .h.f. | 7.9686 | 0.5177 | 0.1191 | 0.0520 | 0.0283 | 0.0290 | 0.0340 | 0.0377 | 0.0416 | 0.0424 |
| Flight aerodynamic quality, K | 1.81 | 6.98 | 13.49 | 17.37 | 14.19 | 10.16 | 6.65 | 5.31 | 4.29 | 3.78 |
| Thrust required Prequired, N | 3113632 | 809179 | 418897 | 325377 | 398284 | 555998 | 849348 | 1065002 | 1316496 | 1495674 |
| The Rate of changes in the thrust of the number of flight Mach , ξ | 0.972 | 0.952 | 0.940 | 0.935 | 0.950 | 0.969 | 0.995 | 1.011 | 1.029 | 1.048 |
| Take-off thrust engines P0, N | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 |
| Thrust available, Pavail, N | 1006548 | 985764 | 973141 | 968616 | 983611 | 1003006 | 1030252 | 1046799 | 1065285 | 1085702 |
| Vertical speed, Vy, m/S | -12.11 | 2.03 | 9.55 | 14.78 | 20.18 | 17.98 | 8.31 | -0.89 | -12.99 | -22.38 |
Table 7: The calculation of thrust required and thrust available, H = 4 km.
| Flight altitude, км | 6 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The number of flight Mach | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 |
| Relative density of the air, D | 0.538 | 0.538 | 0.538 | 0.538 | 0.538 | 0.538 | 0.538 | 0.538 | 0.538 | 0.538 |
The air density, 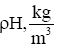 |
0.6602 | 0.6602 | 0.6602 | 0.6602 | 0.6602 | 0.6602 | 0.6602 | 0.6602 | 0.6602 | 0.6602 |
| Coefficient Ka | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| The speed of sound a, m/S | 316.46 | 316.46 | 316.46 | 316.46 | 316.46 | 316.46 | 316.46 | 316.46 | 316.46 | 316.46 |
| Flight speed , V, m/s | 31.65 | 63.29 | 94.94 | 126.58 | 189.88 | 221.52 | 253.17 | 268.99 | 284.81 | 300.64 |
| Dynamic pressure, N/m2 |
331 | 1322 | 2975 | 5289 | 11901 | 16199 | 21157 | 23885 | 26777 | 29835 |
| The average gross weight of the aircraft, GAv, N | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic lift in horizontal flight, Cyh.f. |
18.89 | 4.72 | 2.10 | 1.18 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.21 |
| Effective of wing extension , λ | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 |
| Factor Blade of the polar, A0 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 |
| Coefficient Ka | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.27 | 1.33 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Coefficient KCX0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.03 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.95 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic drag in horizontal flight, Cxa .h.f. | 13.5773 | 0.8683 | 0.1884 | 0.0740 | 0.0330 | 0.0317 | 0.0357 | 0.0392 | 0.0428 | 0.0434 |
| Flight aerodynamic quality, K | 1.39 | 5.44 | 11.14 | 15.96 | 15.88 | 12.14 | 8.27 | 6.68 | 5.45 | 4.82 |
| Thrust required Prequired, N | 4062046 | 1039072 | 507185 | 354010 | 355765 | 465442 | 683629 | 846343 | 1037020 | 1173100 |
| The Rate of changes in the thrust of the number of flight Mach , ξ | 0.972 | 0.952 | 0.940 | 0.935 | 0.950 | 0.969 | 0.995 | 1.011 | 1.029 | 1.048 |
| Take-off thrust engines P0, N | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 |
| Thrust available, Pavail, N | 805738 | 789101 | 778996 | 775373 | 787377 | 802903 | 824713 | 837959 | 852756 | 869100 |
| Vertical speed, Vy, m/S | -18.24 | -2.80 | 4.57 | 9.44 | 14.50 | 13.23 | 6.32 | -0.40 | -9.29 | -16.17 |
Table 8: The calculation of thrust required and thrust available, H = 6 km.
| Flight altitude, км | 8 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The number of flight Mach | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 |
| Relative density of the air, D | 0.429 | 0.429 | 0.429 | 0.429 | 0.429 | 0.429 | 0.429 | 0.429 | 0.429 | 0.429 |
The air density, 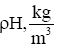 |
0.5259 | 0.5259 | 0.5259 | 0.5259 | 0.5259 | 0.5259 | 0.5259 | 0.5259 | 0.5259 | 0.5259 |
| Coefficient Ka | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.905 |
| The speed of sound a, m/S | 307.953 | 307.953 | 307.953 | 307.953 | 307.953 | 307.953 | 307.953 | 307.953 | 307.953 | 307.953 |
| Flight speed , V, m/s | 30.80 | 61.59 | 92.39 | 123.18 | 184.77 | 215.57 | 246.36 | 261.76 | 277.16 | 292.56 |
| Dynamic pressure, N/m2 |
249 | 997 | 2244 | 3990 | 8977 | 12219 | 15960 | 18017 | 20199 | 22506 |
| The average gross weight of the aircraft, GAv, N | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic lift in horizontal flight, Cyh.f. |
25.04 | 6.26 | 2.78 | 1.56 | 0.70 | 0.51 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0, .1 | 0.28 |
| Effective of wing extension , λ | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 |
| Factor Blade of the polar, A0 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 |
| Coefficient Ka | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.27 | 1.33 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Coefficient KCX0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.03 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.95 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic drag in horizontal flight, Cxa .h.f. | 23.8454 | 1.5100 | 0.3151 | 0.1141 | 0.0417 | 0.0367 | 0.0389 | 0.0418 | 0.0450 | 0.0453 |
| Flight aerodynamic quality, K | 1.05 | 4.15 | 8.83 | 13.72 | 16.69 | 13.92 | 10.06 | 8.30 | 6.87 | 6.12 |
| Thrust required Prequired, N | 5381413 | 1363125 | 640062 | 411870 | 338526 | 405953 | 561663 | 681076 | 822303 | 923415 |
| The Rate of changes in the thrust of the number of flight Mach , ξ | 0.972 | 0.952 | 0.940 | 0.935 | 0.950 | 0.969 | 0.995 | 1.011 | 1.029 | 1.048 |
| Take-off thrust engines P0, N | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 |
| Thrust available, Pavail, N | 664688 | 650963 | 642627 | 639639 | 649541 | 662349 | 680341 | 691268 | 703475 | 716958 |
| Vertical speed, Vy, m/S | -25.71 | -7.76 | 0.04 | 4.97 | 10.17 | 9.78 | 5.17 | 0.47 | -5.83 | -10.69 |
Table 9: The calculation of thrust required and thrust available, H = 8 km.
| Flight altitude, км | 10 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The number of flight Mach | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 |
| Relative density of the air, D | 0.337 | 0.337 | 0.337 | 0.337 | 0.337 | 0.337 | 0.337 | 0.337 | 0.337 | 0.337 |
The air density, 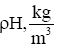 |
0.4136 | 0.4136 | 0, 4136 | 0.4136 | 0.4136 | 0.4136 | 0.4136 | 0.4136 | 0.4136 | 0.4136 |
| Coefficient Ka | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| The speed of sound a, m/S | 299.446 | 299.446 | 299.446 | 299.446 | 299.446 | 299.446 | 299.446 | 299.446 | 299.446 | 299.446 |
| Flight speed , V, m/s | 29.94 | 59.89 | 89.83 | 119.78 | 179.67 | 209.61 | 239.56 | 254.53 | 269.50 | 284.47 |
| Dynamic pressure, N/m2 |
185 | 742 | 1669 | 2967 | 6676 | 9086 | 11868 | 13398 | 15020 | 16735 |
| The average gross weight of the aircraft, GAv, N |
5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic lift in horizontal flight, Cyh.f. |
33.67 | 8.42 | 3.74 | 2.10 | 0.94 | 0.69 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.37 |
| Effective of wing extension , λ | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 |
| Factor Blade of the polar, A0 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 |
| Coefficient Ka | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1, 09 | 1, 16 | 1, 27 | 1, 33 | 1, 4 | 1, 5 |
| Coefficient KCX0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.03 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.95 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic drag in horizontal flight, Cxa h.f. | 43.1065 | 2.7138 | 0.5529 | 0.1893 | 0.0579 | 0.0460 | 0.0449 | 0.0467 | 0.0491 | 0.0489 |
| Flight aerodynamic quality, K | 0.78 | 3.10 | 6.77 | 11.12 | 16.16 | 14.93 | 11.73 | 9.98 | 8.47 | 7.63 |
| Thrust required Prequired, N | 7234021 | 1821721 | 835106 | 508293 | 349600 | 378392 | 481800 | 565957 | 667341 | 740384 |
| The Rate of changes in the thrust of the number of flight Mach , ξ | 0.972 | 0.952 | 0.940 | 0.935 | 0.950 | 0.969 | 0.995 | 1.011 | 1.029 | 1.048 |
| Take-off thrust engines, P0, N | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 |
| Thrust available, Pavail, N |
541395 | 530216 | 523426 | 520992 | 529058 | 539490 | 554145 | 563045 | 572988 | 583970 |
| Vertical speed, Vy, m/S | -35.47 | -13.69 | -4.96 | 0.27 | 5.71 | 5.98 | 3.07 | -0.13 | -4.50 | -7.87 |
Table 10: The calculation of thrust required and thrust available, H = 10 km.
| Flight altitude, км | 11 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The number of flight Mach | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 |
| Relative density of the air, D | 0.298 | 0.298 | 0.298 | 0.298 | 0.298 | 0.298 | 0.298 | 0.298 | 0.298 | 0.298 |
The air density, 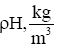 |
0.3648 | 0.3648 | 0.3648 | 0.3648 | 0.3648 | 0.3648 | 0.3648 | 0.3648 | 0.3648 | 0.3648 |
| Coefficient Ka | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 |
| The speed of sound a, m/S | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 |
| Flight speed , V, m/s | 29.50 | 59.00 | 88.51 | 118.01 | 177.01 | 206.52 | 236.02 | 250.77 | 265.52 | 280.27 |
| Dynamic pressure, N/m2 | 159 | 635 | 1429 | 2540 | 5715 | 7779 | 10161 | 11470 | 12859 | 14328 |
| The average gross weight of the aircraft, GAv, N |
5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic lift in horizontal flight, Cyh.f. |
39.33 | 9.83 | 4.37 | 2.46 | 1.09 | 0.80 | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.49 | 0.44 |
| Effective of wing extension , λ | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 |
| Factor Blade of the polar, A0 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 |
| Coefficient Ka | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.27 | 1.33 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Coefficient KCX0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.03 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.95 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic drag in horizontal flight, Cxah.f. | 58.8019 | 3.6948 | 0.7467 | 0.2506 | 0.0711 | 0.0536 | 0.0497 | 0.0507 | 0.0524 | 0.0518 |
| Flight aerodynamic quality, K | 0.67 | 2.66 | 5.85 | 9.81 | 15.37 | 14.97 | 12.36 | 10.74 | 9.26 | 8.42 |
| Thrust required Prequired, N | 8448432 | 2123422 | 965534 | 576114 | 367586 | 377343 | 457240 | 526053 | 610317 | 671356 |
| The Rate of changes in the thrust of the number of flight Mach , ξ | 0.972 | 0.952 | 0.940 | 0.935 | 0.950 | 0.969 | 0.995 | 1.011 | 1.029 | 1.048 |
| Take-off thrust engines, P0, N | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 |
| Thrust available, Pavail, N |
487655 | 477586 | 471470 | 469277 | 476542 | 485939 | 499139 | 507156 | 516112 | 526004 |
| Vertical speed, Vy, m/S | -41.56 | -17.19 | -7.74 | -2.23 | 3.41 | 3.97 | 1.75 | -0.84 | -4.43 | -7.21 |
Table 11: The calculation of thrust required and thrust available, H = 11 km.
| Flight altitude, км | 12 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The number of flight Mach | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 |
| Relative density of the air, D | 0.2536 | 0.2536 | 0.2536 | 0.2536 | 0.2536 | 0.2536 | 0.2536 | 0.2536 | 0.2536 | 0.2536 |
The air density, 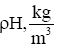 |
0.3156 | 0.3156 | 0.3156 | 0.3156 | 0.3156 | 0.3156 | 0.3156 | 0.3156 | 0.3156 | 0.3156 |
| Coefficient Ka | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 |
| The speed of sound a, m/S | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 |
| Flight speed , V, m/s | 29.50 | 59.00 | 88.51 | 118.01 | 177.01 | 206.52 | 236.02 | 250.77 | 265.52 | 280.27 |
| Dynamic pressure, N/m2 |
137 | 549 | 1236 | 2198 | 4944 | 6730 | 8790 | 9923 | 11125 | 12396 |
| The average gross weight of the aircraft, GAv, N |
5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic lift in horizontal flight, Cyh.f. |
45.46 | 11.36 | 5.05 | 2.84 | 1.26 | 0.93 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.56 | 0.50 |
| Effective of wing extension , λ | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 |
| Factor Blade of the polar, A0 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 |
| Coefficient Ka | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.27 | 1.33 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Coefficient KCX0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.03 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.95 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic drag in horizontal flight, Cxa h.f. | 78.5576 | 4.9295 | 0.9906 | 0.3278 | 0.0877 | 0.0631 | 0.0559 | 0.0557 | 0.0567 | 0.0554 |
| Flight aerodynamic quality, K | 0.58 | 2.31 | 5.10 | 8, 67 | 14.40 | 14.69 | 12.72 | 11.29 | 9.91 | 9.09 |
| Thrust required Prequired, N | 9764610 | 2450941 | 1108159 | 651889 | 392361 | 384584 | 444301 | 500309 | 570447 | 621625 |
| The Rate of changes in the thrust of the number of flight Mach , ξ | 0.972 | 0.952 | 0.940 | 0.935 | 0.950 | 0.969 | 0.995 | 1.011 | 1.029 | 1.048 |
| Take-off thrust engines, P0, N | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 |
| Thrust available, Pavail, N |
425163 | 416384 | 411052 | 409141 | 415475 | 423667 | 435176 | 442165 | 449973 | 458598 |
| Vertical speed, Vy, m/S | -48.76 | -21.25 | -10.92 | -5.07 | 0.72 | 1.43 | -0.38 | -2.58 | -5.66 | -8.09 |
Table 12: The calculation of thrust required and thrust available, H = 12 km.
| Flight altitude, км | 12.4 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The number of flight Mach | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.95 |
| Relative density of the air, D | 0.2399 | 0.2399 | 0.2399 | 0.2399 | 0.2399 | 0.2399 | 0.2399 | 0.2399 | 0.2399 | 0.2399 |
The air density, 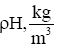 |
0.2986 | 0.2986 | 0.2986 | 0.2986 | 0.2986 | 0.2986 | 0.2986 | 0.2986 | 0.2986 | 0.2986 |
| Coefficient Ka | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 |
| The speed of sound a, m/S | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 | 295.023 |
| Flight speed , V, m/s | 29.50 | 59.00 | 88.51 | 118.01 | 177.01 | 206.52 | 236.02 | 250.77 | 265.52 | 280.27 |
| Dynamic pressure, N/m2 | 130 | 520 | 1170 | 2079 | 4678 | 6367 | 8317 | 9389 | 10526 | 11728 |
| The average gross weight of the aircraft, GAv, N | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 | 5650560 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic lift in horizontal flight, Cyh.f. |
48.05 | 12.01 | 5.34 | 3.00 | 1.33 | 0.98 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.59 | 0.53 |
| Effective of wing extension , λ | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 |
| Factor Blade of the polar, A0 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 |
| Coefficient Ka | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.09 | 1.16 | 1.27 | 1.33 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| Coefficient KCX0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.03 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.95 |
| The coefficient of aerodynamic drag in horizontal flight, Cxah.f. | 87.7547 | 5.5044 | 1.1041 | 0.3637 | 0.0954 | 0.0676 | 0.0587 | 0.0581 | 0.0586 | 0.0571 |
| Flight aerodynamic quality, K | 0.55 | 2.18 | 4.84 | 8.26 | 13.99 | 14.51 | 12.79 | 11.46 | 10.12 | 9.32 |
| Thrust required Prequired, N | 1E+07 | 2589322 | 1168646 | 684376 | 403975 | 389474 | 441832 | 493270 | 558414 | 606117 |
| The Rate of changes in the thrust of the number of flight Mach , ξ | 0.972 | 0.952 | 0.940 | 0.935 | 0.950 | 0.969 | 0.995 | 1.011 | 1.029 | 1.048 |
| Take-off thrust engines, P0, N | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 | 1404000 |
| Thrust available, Pavail, N |
405560 | 397185 | 392099 | 390276 | 396318 | 404133 | 415110 | 421777 | 429226 | 437452 |
| Vertical speed, Vy, m/S |
-51.77 | -22.89 | -12.16 | -6.14 | -0.24 | 0.54 | -1.12 | -3.17 | -6.07 | -8.37 |
Table 13: The calculation of thrust required and thrust available, H = 12.4 km.
Area velocity values, at which horizontal flight is possible at a fixed weight of the aircraft and the altitude, it called horizontal flight speed range.
At this altitude:

At this altitude, the curve of Thrust available (or power) not intersects the curve of thrust required, but only touches it.”
At the intersection point of the curve Thrust Required and Thrust Available, we define the boundaries of the possible limits of the aircraft (Table 14).
| Height Flight, Н, km | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 12.4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum speed, vmin, m/s (left) | 46 | 55 | 60 | 70 | 94 | 118 | 140 | 170 | 200 |
| Maximum(Full) speed, vmax, m/s (right) | 277 | 275 | 275 | 267 | 264 | 255 | 248 | 230 | 200 |
Table 14: Calculation of a possible aircraft flight boundaries
Drawing a schedule of possible aircraft flight boundaries under the conditions of thrust required and thrust available (Figures 11-13).
On the left side, should be restrictions on the minimum flight speed of the conditions for safe values of the coefficient of lift of the aircraft.
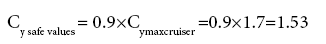
The significance of this factor determines the minimum speed of horizontal flight of the conditions of a possible lift of an aircraft wing.
The minimum flight speed by the formula:
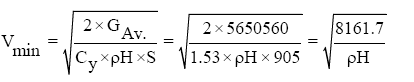
On the right side, should be limits on the N/m2 maximum velocity head from the condition of strength qmax,max = 22000 .
Defining this condition maximum speed flight according to the formula (Tables 15 and 16):
| Height, Н, km | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 12.4 |
| Density of air, ρH, kg/m3 | 1.225 | 1.0067 | 0.8194 | 0.6602 | 0.5259 | 0.4136 | 0.3648 | 0.3156 | 0.2986 |
| Minimum speed, Vmin,m/s | 81.6 | 90 | 99.8 | 111.2 | 124.6 | 140.5 | 149.6 | 160.8 | 165.3 |
Table 15: Calculation of the minimum flight speed.
| Height, Н, km | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 12.4 |
| Density of air, ρH, kg/m3 | 1.225 | 1.0067 | 0.8194 | 0.6602 | 0.5259 | 0.4136 | 0.3648 | 0.3156 | 0.2986 |
| Minimum speed, Vmin,m/s | 189.5 | 209.1 | 231.7 | 258.2 | 289.3 | 326.2 | 347.3 | 373.4 | 383.9 |
Table 16: The calculation of the maximum flight speed of conditions limitations on the maximun velocity head.
1. By, considering level flight at various altitudes with the same weight of flight and angle of attack, when performing level flight at any altitude is necessary to ensure equality of lifting forces and gravity of the aircraft, as Ya =G. To fulfill this condition for constant weight and angle of attack at high altitudes where the air density is less true speed horizontal flight should be more, but the airspeed remains constant.
2. In carrying out flight on a modern passenger airplane Flight weight is significantly reduced due to fuel production. Such a change of flight mass causes a significant change in the aircraft flight characteristics. To perform horizontal flight of flight with less weight requires less lifting force, hence for the same attack and altitude angle requires less speed and less traction.
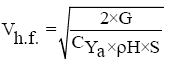
3. As can be seen from the graphs of Thrust Required and Thrust Available (power), the speed range is reduced by raising at height, So all the speed characteristics increases by raising at height, with the exception of the Vmax, because its value is determined by the characteristics of the engine.
4. With increasing altitude, the air density decreases, which leads to an increase in required speed and reduction of vertical speed(climb). Characteristics of climb is getting worse due to the fall of the engine thrust. At a certain height excess thrust is reduced to zero, so a further climb is not possible.
5. With increasing altitude, the excess thrust is reduced and at some certain height becomes zero. This means that the vertical velocity of the steady rise is also reduced to zero. At this altitude and above the aircraft is not able to make a steady recovery.
6. Flight altitude at which the vertical velocity of the steady rise equal zero is called a theoretical (or static), the ceiling of the aircraft.
7. There’s not an excess thrust On a theoretical ceiling therefore the only possible is horizontal flight, and only the most advantageous angle of attack (and only in the most advantageous rate) at which the lowest Required thrust power. Speed range at this moment equal zero.
8. With the steady rise of the plane, almost cannot reach the theoretical ceiling, because as you get closer to it excess thrust becomes so small, that in order to set the height of the rest needs to spend too much time and fuel. Due to the lack of excess flying thrust on a theoretical ceiling is almost impossible, because any violation of the flight mode cannot be eliminated without excessive traction. For example, when randomly formed even small roll plane loses a considerable height (falls). Therefore, in addition to theoretical concepts (static) Ceiling introduced the concept of practical ceiling.