
Anesthesia & Clinical Research
Open Access
ISSN: 2155-6148

ISSN: 2155-6148
Research - (2023)Volume 14, Issue 2
Introduction: Awareness in anaesthesia is an unpleasant complication which may even lead to Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and for that monitoring of depth of anaesthesia is a major concern now-a-days. Now days Bispectral Index Score (BIS) is widely used to monitor the depth of anaesthesia. Change in patient position during surgery under general anaesthesia can cause change in BIS score and hence changes the depth of anaesthesia. Here we have studied the change in anaesthetic depth during different position of patient who is undergoing open cholecystectomy under general anaesthesia by using BIS monitoring system.
Methodology: It is a cross sectional observational study conducted in surgery OT of AGMC and GBP Hospital. Total 40 numbers of patients were included in the study that has given consent for the study and fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Induction and maintenance of anaesthesia were done as per institutional protocol and changes in Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, RR, BIS Score were measured in regular time interval and time of Sweating or tearing of the patient was noted if any during supine, trendelenberg and reverse trendelenberg position. Data were recorded in Microsoft excel and analyzed in SPSS 15.0 version and t-test applied for testing significance of different variables between two groups.
Results: Changes in patient position during surgery under general anaesthesia significantly changes BIS score and thereby depth of anaesthesia. Trendelenurg position increases MAP, HR, sweating and increase BIS value.
BIS (Bispectral Index Score); Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP); HR (Heart Rate); Sweating; Anaesthesia
General Anaesthesia is defined as drug induced loss of consciousness during which patients are not arousable even by painful stimulus. During general anaesthesia patients often require positive pressure ventilation to maintain airway due to drug induced depression of neuromuscular function. Awareness in anaesthesia is a unpleasant complication which may lead to PTSD or Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (incidence 0.1-0.2%) and for that monitoring of depth of anaesthesia is a major concern now a days [1]. Various methods are being used to monitor the depth of anaesthesia like patients movement, autonomic changes (Evans score), EEG, AER, HR and others. In October 1996, the US FDA had approved BIS monitoring as an accepted measure of the hypnotics and sedative drugs. BIS is based on processing of different amplitude and frequency waves of EEG; derived through cortical surface electrodes. BIS value scaled from 0-100 where 0 is isoelectric and 100 is fully awake. Since its inception BIS monitoring has gained popularity in daily practice. Different positioning done after induction of anaesthesia for better accessibility and ease of surgery according to site and nature of surgical field which can change the hemodynamic parameter of the patient and few researcher found that those changes can change the BIS parameter too. Present study is designed to demonstrate the variation of BIS score and patients hemodynamic vitals and PRST score in relation to change in patient position during elective cholecystectomy surgery under GA in our hospital setting.
Awareness is the post-operative recall of sensory perception during general anaesthesia and this can be extremely distressing for the patients [2]. Sebel also found that Awareness after general anaesthesia is infrequent phenomenon that may lead to Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). BIS is very important tool to monitor depth of anaesthesia. Since its introduction in 1996, BIS has gained increasing popularity in daily anaesthesia practice [3].
The relation between change in BP with change in the patient position from supine to trendelenburg or Reverse Trendelenberg position [4,5].
Conducted a study in 2009 & found that several factor affects depth of anaesthesia & among them patient positioning is one of the important factors [6]. Positioning of the patient is one among other factors which changes the depth of anaesthesia and subsequently BIS value [7].
It is a cross sectional observational study conducted in Surgery OT of AGMC and GBP Hospital for two years. All the patients of both sexes admitted for elective open cholecystectomy under general anaesthesia, who gave consent to participate in the study and who are more than 18 years ago with ASA grade I and II were included in this study. Those who did not give consent for study , who are ASA III,IV and V and who has history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorder, recent history of head injury, neuro deficiency, allergy with propofol and atracurium, hepatic or renal insufficiency, were excluded from the study. COVIDEN BIS Monitor (Complete monitoring system) PIN 185-0151(VT40899) and Skanray star 90 multipara monitor were used in our study.
After getting approval from institutional ethical committee and after taking proper informed consent patients were included in our study. Pre-operative fasting guideline maintained strictly. All the patients were pre-medicated with tab Alprazolam 0.5 mg, tab Ranitidine 150 mg. Routine monitoring includes NIBP, Pulse oximetry, ECG, RR, urine output and four electrodes of BIS monitoring attached to the forehead of the patient. All the patients were induced with inj propofol 2 mg/kg and intubated with inj succinyl choline 2 mg/kg. All of them received premedication with inj glycopyrrolate, inj nalbuphine, and inj ondansetron. Muscle relaxation maintained with inj atracurium. After intubation ventilation is maintained with 33% oxygen, 67% nitrous oxide, 1% sevoflurane and paracetamol 1 gm infusion used for analgesia. After five minutes of induction keeping the patients in neutral position BIS value recorded in 5 minutes interval at 5, 10 and 15 minutes, followed by change in position to head down three BIS value recorded at 20, 25 and 30 min. The position of patient again reset to neutral position and BIS value recorded at 35, 40 and 45 minutes. Lastly patient tilted to head up position (Reverse Trendelenberg) and again values recorded at 50, 55 and 60 minutes.
After completion of surgery reversal done with inj Neostigmine (0.05 mg/kg) and Glycolpyrrolate (0.01 mg/kg) and shifted to post-operative ward after extubation with close monitoring. They were interviewed after 24 hours for recall. Data were collected in Microsoft excel and analyzed using SPSS software version 15.0. Mean, Median, Mode and standard deviation calculated and t-test applied for testing of significance of mean between two groups.
The difference in demographic profile like age, sex and ASA status is not significant (p<0.05). Most of our patients were ASA I. These are similar to study conducted and they also found no significant relation between age, sex and ASA status (Tables 1 and 2).
| Age in Group | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| ≤30 | 12 | 30.00% |
| 31-40 | 14 | 35.00% |
| 41-50 | 11 | 27.50% |
| 51-60 | 3 | 7.50% |
| Total | 40 | 100.00% |
Table 1: Frequency of distribution of age in two groups.
| ASA | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| I | 30 | 75.00% |
| II | 10 | 25.00% |
| Total | 40 | 100.00% |
Table 2: Percentage of ASA status in two groups.
We observed that 2.5% patient has sweating at 5 min, 2.5% had sweating at 25 min, 10% had sweating at 30 min and 2.5% had sweating at 35min Figure 1. All of these were statistically significant into two groups (Figure 2).
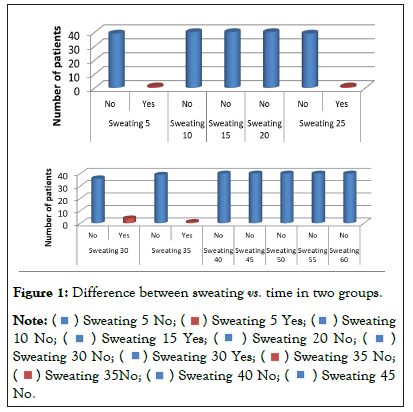
Figure 1: Difference between sweating vs. time in two groups.

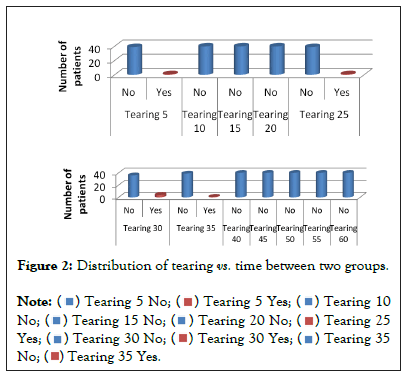
Figure 2: Distribution of tearing vs. time between two groups.
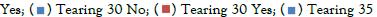
We also found that 2.5% patient had tearing at 5 min,2.5% had tearing at 25 min, 10% patient had tearing at 30 min and 2.5% had tearing at 35 min and those were statistically significant (Figure 3).
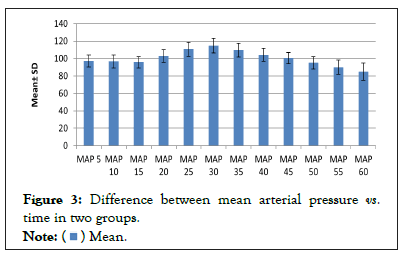
Figure 3: Difference between mean arterial pressure vs. time in two groups.
Present study showed that maximum patients had sweating and tearing at 30 min in trendelenberg position with median BIS 66 which were statistically significant. No sweating or tearing seen at 40 and 60 minutes. MAP was highest in trendelenburg position at 30 minute and it decreased in neutral position but further decrease seen in head up (reverse trendelenburg) position at 50, 55 and 60 min and these are statistically significant (Figure 4).
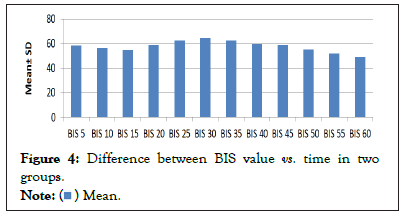
Figure 4: Difference between BIS value vs. time in two
groups.
The ETCO2 and bispectral index were unchanged after induction. MAP decreased with anaesthesia, from 102 (91 to 108) to 72 (65 to 76) mmHg, then remained unchanged. Cardiac index decreased with anaesthesia and with pneumoperitoneum. Multiple regression analysis attributed the fall in internal carotid artery blood flow to reduced cardiac index (both HR and SV index contributing) and MAP (P <0.001). Vessel diameter also declined (P<0.01) [8].
Heart rate also varied with different time interval. Maximum decrease in HR was seen after assuming reverse trendelenburg position at 55 minute with median BIS score 53. Finally in BIS score, we found that in trendelenburg position (At 20, 25 and 30 min) BIS increased at different time interval, highest median value of 66 at 30 minute. BIS score decreased after onwards and maximally decreased after patient put in reverse trendelenburg position at 50, 55 and 60 minutes and 6 found that there was a significant increase in BIS values in head-down position (median 47 vs. 40) compared with neutral position, whereas head-up position significantly decreased BIS (39 vs. 41) compared with neutral position (P<0.05). Changing a patient’s position significantly affects the BIS values, which might affect the interpretation of anaesthetic depth [6] also showed that during comparison between two groups with different angulations, TBG >30° showed a higher BIS value than TBG <30°C. This statistically significant (P<0.05) trend was observed at all the 30, 60, 90, and 120th min interval. Interestingly, BIS values returned to preoperative levels following adopting final supine position. No incidence of awareness was reported in both the series throughout the study. Though awareness remains unaltered BIS value gets increased with higher angle of inclination in TBG position during LAVH operation.
Trendelenburg position resulted in increased BIS value whereas reverse trendelenburg position decreases BIS value. Trendelenburg position causes increase in MAP, sweating and tearing of patients. Changes in patient position during surgery under general anaesthesia significantly changes BIS score and thereby depth of anaesthesia.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Citation: Chakrabarti A, Choudhury J, Reang R, Paul S (2023) Comparison of Anaesthetic Depth by Bispectral Index Score in Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg Position in Elective Open Cholecystectomy Under General Anaesthesia. J Anesth Clin Res. 14:1097.
Received: 01-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. JACR-23-21671; Editor assigned: 03-Feb-2023, Pre QC No. JACR-23-21671 (PQ); Reviewed: 17-Feb-2023, QC No. JACR-23-21671; Revised: 24-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. JACR-23-21671 (R); Published: 03-Mar-2023 , DOI: 10.35248/2155-6148.23.14.1097
Copyright: © 2023 Chakrabarti A, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.