Journal of Medical & Surgical Pathology
Open Access
ISSN: 2472-4971
ISSN: 2472-4971
Image Article - (2020)Volume 5, Issue 2
Cytopathology is a clinical division that examines and identifies cellular-level diseases. George Nicolas Papanicolaou created the discipline in 1928 [1]. In comparison to histopathology which studies entire tissues, cytopathology is typically based on samples of free cells or tissue fragments. Cytopathology is also called, less correctly, "cytology" which means "cell analysis". Cytopathology is widely used to diagnose illnesses affecting a broad range of body locations, mostly to aid with cancer treatment but often in the detection of other respiratory disorders and certain inflammatory conditions [2-4]. Of starters, the Pap smear, a screening technique used to identify precancerous cervical lesions which may contribute to cervical cancer, is a popular method in cytopathology (Figure 1).
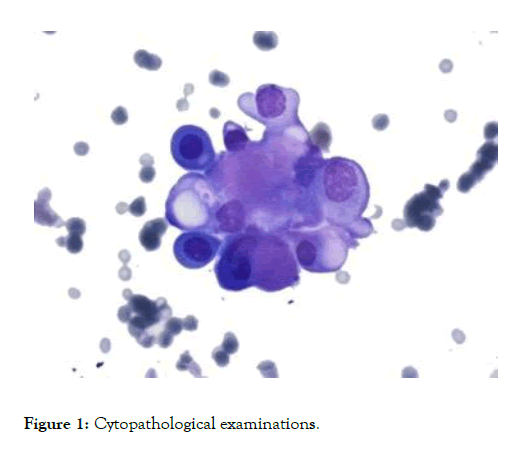
Figure 1: Cytopathological examinations.
Cytopathological examinations are often named smear studies as the samples can be smeared for eventual staining and microscopic inspection via a glass microscope slide. Cytology samples may also be processed in many forms, including cytocentrifugation. Different forms of smear checks can also be used to detect cancer. This is called a cytological smear in this context.
Citation: Gavanji S (2020) Cytopathology is Widely used to Diagnose Illnesses. J Med Surg Patho l. 5:180.
Received: 10-Jul-2020 Accepted: 26-Jul-2020 Published: 01-Aug-2020 , DOI: 10.35248/2472-4971.20.5.180
Copyright: © 2020 Gavanji S. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.