Journal of Chromatography & Separation Techniques
Open Access
ISSN: 2157-7064
+44 1300 500008
ISSN: 2157-7064
+44 1300 500008
Research Article - (2013) Volume 4, Issue 6
A stability indicating Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) method was developed and validated for the simultaneous determination of Atorvastatin Calcium (ASC) and Amlodipine Besylate (AMB) in tablets. The chromatographic separation was performed on acquity UPLC, Kromasil C18, 50×2.1 mm, 3.5 μm using gradient elution of acetonitrile and 0.1% v/v Triethyl amine buffer (pH 3 ± 0.05) at flow rate of 0.8 ml/min. UV (Ultra Violet) detection was performed at 240 nm. Total run time was 2.2 min within which main compounds and degradants were separated. Stability indicating capability was established by forced degradation experiments. The method was validated for accuracy, repeatability, reproducibility and robustness. Linearity, Limit of Quantification (LOQ) and Limit of Detection (LOD) was also established.
Keywords: Ultra performance liquid chromatography; Validation; Stability indicating
Amlodipine besylate [1] is a long-acting calcium channel blocker. Amlodipine besylate is chemically described as 3-Ethyl-5-methyl(±)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-l,4-dihydro-6-methyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, monobenzenesulphonate. Its empirical formula is C20H25CIN2O5•C6H6O3S, and its structural formula is:
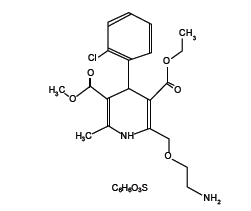
Amlodipine besylate is a white crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 567.1. It is slightly soluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol.
LIPITOR [2] is a synthetic lipid-lowering agent. Atorvastatin is an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, an early and rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis. Atorvastatin calcium is [R-(R*, R*)]-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-β, δ-dihydroxy- 5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-[(phenylamino)carbonyl]-1H¬pyrrole- 1-heptanoic acid, calcium salt (2:1) trihydrate. The empirical formula of atorvastatin calcium is (C33H34FN2O5)2Ca•3H2O and its molecular weight is 1209.42. Its structural formula is:
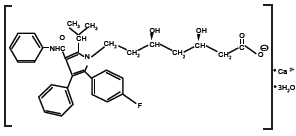
Atorvastatin calcium is a white to off-white crystalline powder that is insoluble in aqueous solutions of pH 4 and below. Atorvastatin calcium is very slightly soluble in distilled water, pH 7.4 phosphate buffer, and acetonitrile; slightly soluble in ethanol; and freely soluble in methanol.
The combination of ASC+AMB is the first medicine to treat two different conditions, high blood pressure and high cholesterol. It is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, chronic stable angina and vasospastic angina (Prinzmetals or variant angina). It is also indicated for primary dysbetalipoproteinemia, elevated serum TG levels, hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia. Several analytical methods such as HPLC [3-8], UPLC [9-11], LC-MS [12-13] and Spectrophotometry [16-18], are reported for determination of ASC and AMB. Literature survey reveals that there is no stability indicating assay method reported for simultaneous estimation of Atorvastatin Calcium and Amlodipine Besylate in pharmaceutical dosage form by RP-UPLC. Ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) is a recent technique in liquid chromatography, which enables significant reductions in separation time and solvent consumption.
The purpose of this study was to develop a stability indicating method for the simultaneous determination of ASC and AMB in tablets. The proposed method was able to separate these compounds as well as other unknown degradation products within a run time of 2.2 min. Thereafter, this method was validated as per ICH guidelines and successfully applied for simultaneous determination of Amlodipine Besylate and Atorvastatin Calcium in tablet dosage forms.
Chemicals and reagents
Reference standards of ASC and AMB were kindly gifted by Ranbaxy Research Laboratories, Gurgaon. All the standards were used as received. Acetonitrile for validation was obtained from Spectochem pvt Ltd., Mumbai, India. Analytical grade Ortho Phosphoric acid and Triethyl amine were obtained from Qualigens pvt Ltd, Mumbai, India.
Buffer preparation
0.1% v/v Triethyl amine buffer was prepared by adding about 1ml of Triethyl amine in one litre of Milli Q water. The pH of this solution was adjusted to 3 ± 0.05 with Ortho Phosporic acid. The buffer preparation was found stable with respect to pH and visual clarity for 48 h.
Chromatographic system
Analysis was performed on Acquity UPLC system (Waters, Milford, USA), consisting of a binary solvent manager, sample manager and PDA detector. The detector was set at sampling rate of 20 points/s and filter time constant of 0.2 s. System control, data collection and data processing were accomplished using Waters Empower version 2.0 chromatography data software. The analytical column used was Kromasil C18, 50×2.1 mm, 3.5 μm. The separation of ASC and AMB was achieved by gradient elution using Acetonitrile and Triethyl amine (pH 3.00, 0.1% v/v). The mobile phase was pumped through the column at a flow rate of 0.8 ml/min. The column oven temperature was maintained at 45°C. The detection was carried out at 240 nm.
Assay solution preparation
Standard solution preparation: Standard solution was prepared by dissolving standard substances in methanol and diluted up to the mark to obtain solution containing 800 μg/ml of ASC and 100 μg/ml of AMB.
Sample solution preparation
Twenty tablets were crushed to fine powder. An accurately weighed portion of the powder equivalent to 80 mg of ASC and 10 mg of AMB was taken in 100 ml volumetric flask. About 20 ml of methanol was added to this flask and sonicated in an ultrasonic bath. The volume was made up to the mark with the diluent (1:1 v/v Acetonitrile and water). It was then filtered through 0.22 μ filter.
The main criteria for development of successful UPLC method for simultaneous determination of ATO and AMD in tablets was that the method should be accurate, reproducible, robust, stability indicating, free of interference from degradation products and straightforward enough for routine use in quality control laboratory. The UPLC method was initiated with isocratic program and optimum resolution was not achieved. Then a gradient program was tried with different mobile phases and columns. Finally the method was optimized using a column Kromasil C18, (50 mm×2.1 mm i.d., 3.5 μm) as a stationary phase with a mobile phase consisting of buffer (0.1% v/v Triethyl amine) and acetonitrile with a gradient program at a flow rate of 0.8 ml/min. The detection was done at a wavelength of 240 nm. The optimized method parameters and gradient program is as shown in Tables 1 and 2.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Column name | Kromasil 100 C–18 (50 × 2.1 mm), 3.5 μ |
| Mobile phase* | Acetonitrile: TEA buffer (0.1%TEA, pH 3±0.05 with OPA) |
| Flow rate | 0.8 mL/min |
| Weak Wash | 9:1 (MQ water: Acetonitrile) |
| Strong Wash | 1:9 (MQ water: Acetonitrile) |
| Detection | UV at 240 nm |
| Column Temperature | 40°C |
| Sample Temperature | 25°C |
| Injection volume | 2 μL |
| Run time | 2.2 min |
Table 1: UPLC Method Parameters.
| Time (min) | % A, 0.1% v/v TEA Buffer | %B, Acetonitrile |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 70 | 30 |
| 0.30 | 70 | 30 |
| 0.50 | 64 | 36 |
| 0.90 | 64 | 36 |
| 1.30 | 40 | 60 |
| 2.00 | 40 | 60 |
| 2.05 | 70 | 30 |
| 2.20 | 70 | 30 |
Table 2: Gradient program.
After satisfactory development of method it was subjected to method validation as per ICH guideline. The method was validated to demonstrate that it is suitable for its intended purpose by the standard procedure to evaluate adequate validation characteristics (accuracy, precision, linearity, robustness and stability indicating capability).
System suitability
System suitability parameters were evaluated to verify system performance. It was determined by six replicate injections of standards of both ASC and AMB (Figure 1). Other suitability parameters like capacity factor, theoretical plates and resolution were also evaluated (Table 3).
| System suitability Parameter | Amlodipine Besylate Observation(n=6) | Atorvastatin Calcium Observation ( n=6) | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | - | 17 | NLT 2.5 |
| Tailing Factor | 1.26 | 1.08 | NMT 3.0 |
| Theoretical plates | 48332 | 28944 | NLT 2000 |
Table 3: System Suitability Parameters.
Specificity
Forced degradation studies were performed to demonstrate selectivity and stability indicating capability of the proposed method. The standard was exposed to various degradation conditions - acidic (1N HCl, 60°C, 6 hours), alkaline (1N NaOH, 60°C, 60 min), strong oxidizing (3% H2O2, 60°C, 60 min), thermal (60°C, 48 hours) and photolytic (254 nm, 1 day).
Both ASC and AMB were found to be highly sensitive to acidic, alkali and oxidative degradation. The assay value was dropped to approx 70% in all the above mentioned conditions (Figures 2 and 3). However no degradation was found in thermal and photolytic stress condition (Table 4).
| Type of stress condition | Purity angle | Purity threshold | % Degradation | No. of Degradants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMB | ASC | AMB | ASC | AMB | ASC | ASC | AMB | |
| Acid degradation | 1.592 | 0.114 | 2.681 | 1.070 | 22% | 21% | 2 | 6 |
| Alkaline degradation | 34.63 | 0.103 | 90.54 | 1.078 | 25% | 22% | 1 | 2 |
| Oxidative degradation | 0.302 | 0.025 | 1.465 | 1.268 | 23% | 22% | 3 | 1 |
| Thermal degradation | 0.907 | 0.058 | 1.578 | 1.024 | Both are Not degraded | - | - | |
| Photo degradation | 1.069 | 0.057 | 1.341 | 1.025 | Both are Not degraded | - | - | |
Table 4: Summary of Peak purity data for forced degradation study.
Limit of detection (LOD) and Limit of quantitation (LOQ)
The LOD and LOQ of ASC and AMB were determined by using signal to noise approach (Figures 4 and 5). The concentration (in μg/ml) with signal to noise ratio of at least 3 was taken as LOD and concentration with signal to noise ratio of at least 10 was taken as LOQ. Limits obtained are as shown in Table 5.
| Parameter | Amlodipine Besylate | Atorvastatin Calcium |
|---|---|---|
| *LOD | 0.3 μg/ml | 0.2 μg/ml |
| *LOQ | 0.7 μg/ml | 0.6 μg/ml |
*LOD and LOQ was calculated by S/N ratio method
Table 5: Results for LOD, LOQ.
Linearity
Linearity was demonstrated from 70 to 130% of standard concentration using six calibration levels (70%, 80%, 90%, 100%, 110%, 120% and 130%) for both ASC and AMB. Calibration curve was plotted for peak area against respective concentration. The plot was assessed using linear regression. Linearity was obtained within the range of 56-104 μg/ml for ASC and 7-13 μg/ml for AMB (Figures 6 and 7). For both the compounds the correlation coefficient was found to be greater than 0.9990 (Table 6).
| Level | Concentration μg/ml | Area response for AMB | Concentration μg/ml | Area response for ASC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70% | 7 | 34301 | 56 | 334353 |
| 80% | 8 | 39542 | 64 | 373530 |
| 90% | 9 | 44448 | 72 | 4261526152 |
| 100% | 10 | 49274 | 80 | 473588 |
| 110% | 11 | 54672 | 88 | 524718 |
Table 6: Results for Linearity.
Precision
The precision of the method was verified by repeatability and intermediate precision. Repeatability was checked by injecting six individual preparations of Amlodipine Besylate and Atorvastatin Calcium. System precision and method precision was found to be within permissible limits i.e. 1% and 2% respectively (Table 7). The intermediate precision of the method was also evaluated while performing analysis on different days.
| S.No | Precision | %RSD | Acceptance Limit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMB | ASC | |||
| 1 | Method Precision | 0.530 | 0.303 | NMT 2% |
| 2 | System Precision | 0.550 | 0.312 | NMT 1% |
| 3 | Intermediate Precision | 0.717 | 0.705 | NMT 2% |
Table 7: Results for Precision.
Accuracy
To confirm the accuracy of the proposed method, recovery experiments were carried out by standard addition technique at 80%, 100% and 120% level. The percentage recovery of ASC and AMB at each level and each replicate was determined. The mean of percentage recoveries (n=9) and the relative standard deviation was calculated. The amount recovered was within ± 2% of amount added, which indicates that the method is accurate (Table 8).
| Recovery level | For Amlodipine Besylate | For Atorvastatin Calcium | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount Taken(mg) | Amount Found (mg) | % Recovery | Amount Taken (mg) | Amount Found (mg) | % Recovery | |
| 80% (n=3) | 8 | 7.83 | 99.41 | 64 | 64.15 | 100.13 |
| 8 | 7.95 | 99.41 | 64 | 63.90 | 99.14 | |
| 8 | 8.10 | 100.33 | 64 | 64.20 | 101.05 | |
| 100% (n=3) | 10 | 10.09 | 100.39 | 80 | 80.09 | 100.43 |
| 10 | 10.10 | 101.02 | 80 | 79.60 | 99.47 | |
| 10 | 10.12 | 101.21 | 80 | 80.15 | 100.11 | |
| 120% (n=3) | 12 | 12.17 | 101.31 | 96 | 95.20 | 98.13 |
| 12 | 12.15 | 101.26 | 96 | 95.15 | 99.14 | |
| 12 | 11.97 | 99.79 | 96 | 95.15 | 99.14 | |
| Mean | 100.46 | 99.64 | ||||
| SD | 0.784 | 0.876 | ||||
| %RSD | 0.780 | 0.879 | ||||
Table 8: Results for Accuracy.
Robustness
The robustness is a measure of method capacity to remain unaffected by small, but deliberate changes in chromatographic conditions. It was studied by testing influence of small changes in pH of buffer (± 0.05 units), change in column temperature (± 5°C), change in flow rate (± 10%) and change in mobile phase composition ± 2 from absolute value. No significant change was observed in assay value for all robustness. % RSD was calculated, which was found to be in permissible limit (Table 9).
| S.No. | Robustness parameter | % RSD for AMB | %RSD for ASC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Flow rate–10% (0.72 ml/min) | 0.560 | 0.752 |
| 2 | Flow rate +10% (0.88 ml/min) | 0.720 | 0.430 |
| 3 | pH+0.05 (3.05) | 0.672 | 1.50 |
| 4 | pH–0.05 (2.95) | 1.502 | 1.212 |
| 5 | Column oven temperature-5°C (40°C) | 0.620 | 0.510 |
| 6 | Column oven temperature+5°C (50°C) | 0.320 | 0.481 |
| 7 | Organic phase–2 from absolute value | 0.369 | 1.034 |
| 8 | Organic phase +2 from absolute value | 0.651 | 0.832 |
Table 9: Results for Robustness.
Stability of standard and sample solution
Stability of standard and sample solution was established by storage of standard and sample solution at ambient temperature for 24 h. Both standard and sample solution were analyzed at a time interval of 2, 4, 8 16 and 24 hr. Sample solution did not show any appreciable change in assay up to 24 h and no change in area was observed for both solutions (Table 10).
| S.No. | Time hrs | Standard area | Sample area | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMB | ASC | AMB | ASC | ||
| 1 | 0 | 52447 | 492270 | 76620 | 523640 |
| 2 | 2 | 52964 | 491790 | 76761 | 521339 |
| 3 | 4 | 52147 | 497008 | 76472 | 528518 |
| 4 | 8 | 51394 | 496734 | 77834 | 537485 |
| 5 | 12 | 53508 | 501408 | 78012 | 534153 |
| 6 | 16 | 52492 | 508051 | 76677 | 541954 |
| 7 | 24 | 52203 | 508257 | 76401 | 547165 |
| Mean | 52451 | 499360 | 76968 | 533465 | |
| %SD | 665 | 6818 | 616 | 9526 | |
| %RSD | 1.27 | 1.365 | 0.80 | 1.786 | |
Table 10: Results for Stability of standard and sample solution.
A novel UPLC method was successfully developed and validated for simultaneous determination of ASC and AMB. Both the drugs were found to be well resolved (resolution=17) in a short run time of 2.20 mins. No interference was found with the degradants and excipients. Method validation results have proved the method to be selective, precise, accurate, robust and stability indicating. This method can be successfully applied for the routine analysis as well as for stability studies. Overall, the method provides high throughput solution for determination of ASC and AMB.