Journal of Hepatology and Gastrointestinal disorders
Open Access
ISSN: 2475-3181
+44-77-2385-9429
ISSN: 2475-3181
+44-77-2385-9429
Case Report - (2022)Volume 8, Issue 4
In my previous case report, I mentioned about the connection between metabolic acidosis and other diseases.
Headache is one of the diseases mentioned in a female patient. For the patient, it was observed that acidosis is the
indicator. Acidosis takes place first.
There can be many reasons for metabolic acidosis.
For this patient it was seen that, food is the trigger, with consistent misbalance in pH level in body it exhibits many
Symptoms like
Palpitations.
Optical swelling.
Shortness of breath.
Altered mental status such as severe anxiety due to hypoxia.
Nausea.
Abdominal pain.
Altered appetite and weight gain.
Muscle weakness, bone pain, and joint pain.
In acidosis the arterial carbon dioxide tension increases, and it can cross the blood-brain barrier and changes
extravascular pH, Headache is trigger.
Patient was treated with Pregabalin, Amitriptyline and Duloxetine combination.
Frequency of headache was less but it was not stopped. Then patient was treated with CGRP receptor blocker
subcutaneous injection but was not able to get rid of the throbbing head pain.
All the above medicines did not fully work because the type of headache may not be migraine.
On using Flunarizine (Sibelium 10 mg) the headache was stopped on second day of medicine taking. It helped in
reducing allergy-like symptoms too.
The calcium channel blocking property of Flunarizine may work in migraine but the other property of Flunarizine,
controlling carbon dioxide tension in CNS, works in acidosis induced headache, greatly. So, the below properties of
Flunarizine work in controlling headache,
Calcium channel blocking, thus controlling neurotransmitter release.
Controlling carbon dioxide tension in CNS.
Controlling histamine to function.
Controlling mast cell degranulation.
The effectivity of Flunarizine in controlling acidosis related headache is well proved.
Metabolic acidosis; Flunarizine; Carbon dioxide tension; CGRP receptor blocker
CGRP: Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide; CNS: Central Nervous System; ASIC3: Acid Sensing Ion Channel 3; CCB: Calcium Channel Blocker
Metabolic acidosis happens when,
1. Body’s acid production increases.
2. Kidney not being able to excrete enough acid.
3. Bicarbonate loss.
4. Body’s bicarbonate buffer is low.
After long observation it was found that the patient is showing below symptoms along with the primary complaint of headache,
• Gas, acid, bloating, nausea.
• Muscle pain, stiffness in back neck.
• Weak muscle.
• Shortness of breath.
• Fast heart rate.
• Constipation.
• Low appetite.
• Mood swing.
• Anxiety and Depression.
• Food craving.
• Shivering, tremor sensation it can be shown in https:// en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metabolic_acidosis
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a gas that is produced as a normal byproduct of our body’s energy production. As per the normal body’s process, CO2 diffuses into bloodstream so that it can be exhaled from lungs. When CO2 level become elevated, the signal reaches brain, then sends signal to the respiratory system to control CO2 level, to decrease the level. Lung starts working heavily; it tries to exhale elevated CO2. So, a deep and faster breathing continues until the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels are balanced again.
In acidosis the arterial carbon dioxide tension increases, and it can cross the blood-brain barrier and changes extra vascular pH. This imbalances pH level of CNS. Blood vessels get dilated. This triggers excitatory neurotransmitter release.
Once released, they travel to the outer layer of brain, the meninges. Which results in inflammation and swelling of blood vessels, causing an increase in blood flow around the brain? This makes the inflammation of the blood vessels resulting in throbbing pain.
Patient was initially treated with Pregabalin, Amitriptyline and Duloxetine combination. The combination worked for some time, but headache was not stopped completely, only the frequency was less [1,2].
Patient took Ibuprofen (600 mg) in Save Our Souls (SOS) basis.
Later patient was given Aimovig (CGRP receptor inhibitor) subcutaneous injection. After taking the injection patient was able to be without headache for 7 consecutive days but after that headache again started.
Unavailability of Flunarizine in the locality was the cause patient was not able to take flunarizine.
Once started with Flunarizine (Sibelium 10 mg) patient was able to get rid of the headache. This implies Flunarizine has the capability to decrease carbon dioxide tension in CNS.
Pregabalin
It works as a selective Calcium Channel Blocker (CCB). This medication is used to treat neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, restless leg syndrome, and generalized anxiety disorder.
Amitriptyline
Inhibits Serotonin Transporter (SERT) and Norepinephrine Transporter (NET). Amitriptyline additionally acts as a potent inhibitor of the serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, the α1Aadrenergic, the histamine H1. It is a non-selective blocker of multiple ion channels voltage-gated sodium channels as shown in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amitriptyline
Duloxetine
It is used to treat fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain. It is a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor as shown in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duloxetine
Erenumab
It targets the Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide Receptor (CGRPR) for the prevention of migraine as shown in https:// en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Erenumab
Flunarizine
It is a selective calcium antagonist. Other actions include,
• Antihistamine.
• Serotonin receptor blocking.
• Dopamine D2 blocking activity.
• It has been theorized that it may act not by inhibiting calcium entry into cells, but rather by an intracellular mechanism such as antagonising calmodulin.
• It readily passes the blood–brain barrier.
In research, it has been found that flunarizine can decrease the carbon dioxide tension in CNS. So, for acidosis induced headaches, flunarizine is the best as shown in https:// en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flunarizine
As flunarizine has antihistamine property, it should be able to stop allergy induced headaches.
It has been observed in the patient that, calcium channel blocker drugs help in reducing symptoms of allergy.
• It may happen that CCB drugs restrict the degranulation of the mast cells.
• Now, to get rid of allergy there are two ways,
• Drug that inhibits histamine H1 receptor. In that case the other mediators, receptors are not inhibited and it is not possible to restrict downstream action of all mediators.
• Stopping the unnecessary degranulation of mast cells.
Pregabalin can help in reducing the mast cell granulations. So, it contributes to allergy induced acute headaches. That is why use of pregabalin can lower the acute headache frequency.
Amitriptyline has the property of several receptor blockers. This helps to inhibit the receptors when the degranulation has already taken place, and mediators are playing and contributing to acute headache trigger.
That is why the combination of medicines Pregabalin, and Amitriptyline can lower the frequency of acute headache but cannot stop them.
Another aspect is the medicines work well when the headache type is migraine. But there are side effects too. Patient is suffering from acidosis, so she already had problem of Chronic Idiopathic Constipation (CIC) due to lazy gut. Pregabalin works as muscle relaxant, so it increases the problem of CIC [3].
It has been seen that during migraine headache CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide is released around the brain. When CGRP is released, it causes intense inflammation in the coverings of the brain (the meninges) and starts the headache. CGRP also contribute to linger the headache up to several hours as shown in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ Calcitonin_gene-related_peptide
The next question comes, why does CGRP release take place in brain? (Figure 1 and Table 1).
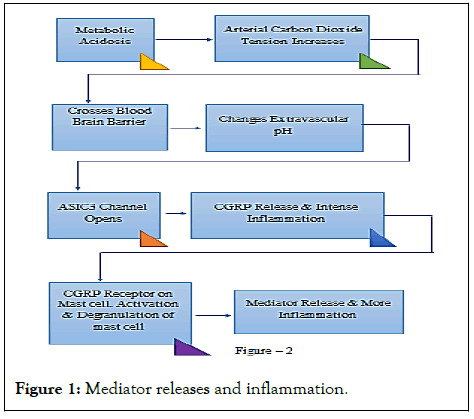
Figure 1: Mediator releases and inflammation.
| To get ride of acute headache | |
|
Electrolytes, decreasing CO2 tension |
|
Increase bicarbonate level (carbonated water) |
|
ASIC3 channel inhibitor |
|
CGRP receptor inhibitor, CCB |
|
H1 receptor inhibitor, CCB |
|
Pain already triggered, painkiller |
Table 1: To get rid of acute headache.
Let us draw a sequence diagram.
CGRP receptor blocking is the 4th Layer. Flunarizine (Sibelium) may have the property of decreasing CO2 tension in CNS. That is how it controls opening the ASIC3 channels. So, CGRP is not released, and no mast cell degranulation happens. As a result, no histamine releases (Figure 2) [4-6].
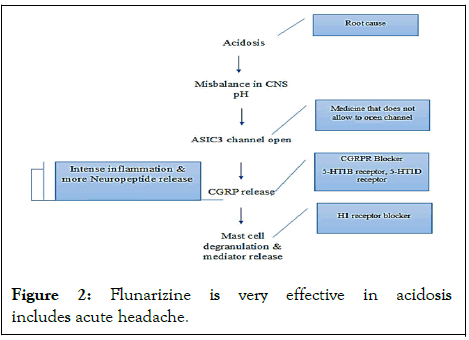
Figure 2: Flunarizine is very effective in acidosis includes acute headache.
Additional depict of the flow.
Many medicines have been tried for the patient for headache. The solution was temporary only. From the discussion, it can be concluded that flunarizine is very effective in acidosis induced acute headaches while the other medicines are not working at the root cause level.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent to publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Competing interest
None
Funding
No funding sources
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Citation: Datta S (2022) Effectivity of Flunarizine in Controlling Acidosis Induced Headache. J Hepatol Gastroint Dis. 8:213.
Received: 21-Jun-2022, Manuscript No. JHGD-22-18027; Editor assigned: 27-Jun-2022, Pre QC No. JHGD-22-18027 (PQ); Reviewed: 08-Jul-2022, QC No. JHGD-22-18027; Revised: 15-Jul-2022, Manuscript No. JHGD-22-18027 (R); Published: 22-Jul-2022 , DOI: 10.35248/2475-3181.22.8.213
Copyright: © 2022 Datta S. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Sources of funding : no source