Anatomy & Physiology: Current Research
Open Access
ISSN: 2161-0940
ISSN: 2161-0940
Research Article - (2014) Volume 4, Issue 3
Complications of respiratory system in patients suffering from chronic renal failure who are treated with regular haemodialysis are well known. However, the effects of interdialytic weight gain on respiratory function in these patients are less known. Hence, this study was designed with the aim to determine the potential differences in spirometry related to the different interdialytic weight gain.
The study included 32 patients, 16 males (50%) aged 51 (± 11), with ESRD who had been treated with repeated haemodialysis. The patients were divided into two groups: Group 1 – patients with interdialytic weight gain < 5% and Group 2 – patients with interdialytic weight gain > 5%. All patients had spiromety done before (A) and after (B) haemodialysis.
The results obtained show vital capacity means (X) measured before (A) and after haemodialysis (B) in group 1: A=2.95 ± 0.9 and B=3.9 ± 1.2 and group 2: A=3.4 ± 1.1 and B=3.8 ± 1.12. Forced vital capacity means (X) measured before (A) and after haemodialysis (B) in group 1: A=2.9 ± 0.85 and B=3.2 ± 1.0 and group 2: A=3.7 ± 1.4 and B=3.8 ± 1.35. Forced expiratory volume in first second means (X) measured before (A) and after haemodialysis (B) in group 1: A=2.4 ± 0.78 and B=2.7 ± 1.1 and group 2: A=3.3 ± 1.25 and B=3.4 ± 1.33.
The results lead us to a conclusion that haemodialysis has a positive effect on pulmonary ventilating function, but this effect is smaller in patients with greater interdialytic weight gain.
Keywords: Spirometry; Uraemia; Haemodialysis
Chronic renal failure (CRF) is a progressive and irreversible impairment of renal function. Besides kidneys, almost all other organs and organic systems are affected at this stage of the disease [1]. Hence, the respiratory system is not spared from the complications of endstage chronic renal disease, although chronic haemodyalisis itself may have the negative effect on lung function as well [1,2]. Most commonly described complications of uraemic syndrome involving respiratory system are: uraemic lung (pulmonary oedema), pulmonary hypertension, pleural effusions, disfunction of respiratory muscles, respiratory infections, uraemic pleuritis and uraemic calcification [3]. Post mortem findings in large number of patients indicate that changes also appear at alveolar-capillary membrane. Pathophysiologic changes that accompany end-stage chronic renal disease, as well as haemodialysis itself, lead to thickening of this membrane, followed by all the consequences that could affect the respiratory system [1-4]. Besides negative effect of uraemia to lungs haemodialysis effects negatively on respiratory system as well. The volume status of a patient on intermittent hemodialysis (HD) therapy varies across the week. During interdialysis period water accumulates in patient's body which leads to weight gain [5-7].
This difference is called interdialytic weight gain [8-12].
Effects of chronic haemodialysis and especially interdialytic weight gain of water on respiratory function along with its complications are less known [4-9]. Literature data on this topic are insufficient and contradictory. Regarding all stated above, this study was designed with an aim to follow the effects of interdialytic weight gain on respiratory function (spirometry tests).
Patients included in this study were treated at the International dialysis centre Banja Luka and they all signed the informed consent for the participation in this study. In this study we observed patients without the presence of any acute or chronic lung disease, cardiac or any chest disease, connective tissue disease and without any immunosupresive treatment (eg cyclophosphamide) and all patients were non-smokers. Patients were treated with haemodialysis three times per week, but were never treated with peritoneal dialisys or had renal transplantation. Duration of haemodialysis per one visit was individually tailored according to patients’ needs and it was between 180 and 240 minutes. Haemodialysis was performed using Gambro and Fresenius machines with controlled ultrafiltration. Bicarbonate module was used as well. Dialisators used were as follows: E4H, F6, F60, F60s. 4000-5000 IU of heparin were given to each patient continuously during haemodialysis.
Medical history of all patients was noted at screening. Basic spirometry testing was performed to all patients along with physical examination. We measured following spirometry parameters: vital capacity (VC), forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1). Three consecutive spirometry testings were performed one hour before (A) and three consecutive spirometry testings were performed one hour after hemodialysis (B).
Out of each three consecutive testings, the best result was included in analysis. We used Jaeger plethysmograph (volume constant model) for lung function testing in our study. Quality control of used plethysmograph was assured by regular testing which was performed according to ATS/ESR criteria in order to gain valuable results. Student t-test was used for statistical analysis. Results are presented using descriptive statistical measures such as mean and standard deviation; p<0.05 was taken as statistically significant. All studied patients were divided in two groups according to interdialytic weight gain of water. The group 1 included of patients patients with interdialytic weight gain < 5% and group 2 included patients with interdialytic weight gain > 5%.
Demographic characteristics of all 32 patients are shown in Table 1.
| n | males | females | age ( 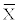 ± SD) ± SD) |
Length of dialysis years ( 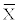 ± SD) ± SD) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD | 32 | 16 | 16 | 51 ± 11,2 | 4.14 ± 12.9 |
| Group 1 | 22 | 9 | 13 | 51.4 ± 12.8 | 3.4 ± 14.7 |
| Group 2 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 48.9 ± 14.6 | 4.05 ± 13.9 |
Table 1: Basic demographic characteristics of patients
Figure 1 shows results of vital capacity (VC) measuring. Vital capacity means(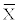 ) are measured before (A) and after haemodialysis (B) in patients with interdialytic weight gain less than 5% (1: A=2.95 ± 0.9 and B=3.9 ± 1.2) and greater than 5% (2: A=3.4 ± 1.1 and B=3.8 ± 1.12). Statistical analysis showed very high statistically significant difference (p<0.01) between the vital capacity values before and after haemodialysis in both tested groups. Apart from the stated comparisons, vital capacity values measured before haemodialysis were compared between groups of patients (groups 1 & 2) and it was found that they were significantly different as well (p<0.05).
) are measured before (A) and after haemodialysis (B) in patients with interdialytic weight gain less than 5% (1: A=2.95 ± 0.9 and B=3.9 ± 1.2) and greater than 5% (2: A=3.4 ± 1.1 and B=3.8 ± 1.12). Statistical analysis showed very high statistically significant difference (p<0.01) between the vital capacity values before and after haemodialysis in both tested groups. Apart from the stated comparisons, vital capacity values measured before haemodialysis were compared between groups of patients (groups 1 & 2) and it was found that they were significantly different as well (p<0.05).
Figure 1: Influence of haemodialysis on vital capacity values. P. relation between vital capacity values measured before haemodialysis in groups 1 & 2 patients. (1) patients with interdialysis weight gain (liquid) < 5%. (2) patients with interdialysis weight gain (liquid) > 5%. (A) vital capacity means before haemodialysis. (B) vital capacity means after haemodialysis. (←) Predicted vital capacity values (mean value)
Figure 2 shows results of forced vital capacity (FVC) measuring. Forced vital capacities means (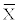 ) were measured before (A) and after haemodialysis (B) in patients with interdialytic weight gain less than 5% (1 A=2.9 ± 0.85 and B=3.2 ± 1.0) and greater than 5% (2: A=3.7 ± 1.4 and B=3.8 ± 1.35). Statistical analysis showed that there were no statistically significant difference (p>0.05) between forced vital capacity values before and after haemodialysis in both tested groups. Comparison of forced vital capacity values measured before haemodialysis between groups of patients (groups 1 & 2) showed statistically significant difference (p<0.05) as well.
) were measured before (A) and after haemodialysis (B) in patients with interdialytic weight gain less than 5% (1 A=2.9 ± 0.85 and B=3.2 ± 1.0) and greater than 5% (2: A=3.7 ± 1.4 and B=3.8 ± 1.35). Statistical analysis showed that there were no statistically significant difference (p>0.05) between forced vital capacity values before and after haemodialysis in both tested groups. Comparison of forced vital capacity values measured before haemodialysis between groups of patients (groups 1 & 2) showed statistically significant difference (p<0.05) as well.
Figure 2: Influence of haemodialysis on forced vital capacity values (P) relation between forced vital capacity values measured before haemodialysis in groups 1 & 2 patients. (1) patients with interdialysis weight gain (liquid) < 5%. (2) patients with interdialysis weight gain (liquid) > 5%. (A) forced vital capacity means before haemodialysis. (B) forced vital capacity means after haemodialysis. (←) Predicted forced vital capacity values (mean value)
Figure 3 shows forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1). Forced expiratory volumes in the first second means (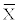 ) were measured before (A) and after haemodialysis (B) in patients with interdialytic weight gain less than 5% (1: A=2.4 ± 0.78 and B=2.7 ± 1.1) and greater than 5% (2: A=3.3 ± 1.25 and B=3.4 ± 1.33). Statistical analysis showed highly significant difference (p<0.01) between forced vital capacity values before and after haemodialysis in group 1, while in the group 2 difference was not significant (p>0.05). Comparison of forced expiratory volume in the first second values between groups of patients (groups 1 & 2) showed statistically significant difference (p<0.05) as well.
) were measured before (A) and after haemodialysis (B) in patients with interdialytic weight gain less than 5% (1: A=2.4 ± 0.78 and B=2.7 ± 1.1) and greater than 5% (2: A=3.3 ± 1.25 and B=3.4 ± 1.33). Statistical analysis showed highly significant difference (p<0.01) between forced vital capacity values before and after haemodialysis in group 1, while in the group 2 difference was not significant (p>0.05). Comparison of forced expiratory volume in the first second values between groups of patients (groups 1 & 2) showed statistically significant difference (p<0.05) as well.
Figure 3: Influence of haemodialysis on forced expiratory volume in the 1st second relation between forced expiratory volume in the 1st second values measured before haemodialysis in groups 1 & 2 patients. (1) patients with interdialysis weight gain (liquid) < 5%. (2) patients with interdialysis weight gain (liquid) > 5%. (A) forced expiratory volume means in the 1st second before haemodialysis. (B) forced expiratory volume means in the 1st second after haemodialysis. (←) Referral forced expiratory volume in the 1st second (mean value)
During the research, we observed parameters of respiratory function: VC, FVC, FEV1. Vital capacity, shows change toward recovery after haemodialysis (p<0.01). This result was found in both groups of tested patients (group 1 and 2). Recovery was more noted in patients with lower interdialytic weight gain (group 1) and in those patients haemodialysis improved the vital capacity value up to normal values. The obtained results are in compliance with the results obtained by other authors who observed the stated parameters [3-7,13]. One of the reasons for VC reduction could be accumulation of oedematous liquid in lungs of patients in end-stage renal failure who were treated with repeated haemodialyses (uraemic lung). The exact reason for accumulation of liquid in lungs in these patients has not been completely known yet. Liquid accumulation close to airways leads to its obstruction and dysfunction. Haemodialysis removes the excess liquid and increases ventilation of basal lungs areas, and positive effect is seen in reducing of airways obstruction. This can be one of the reasons for recovery of VC. Vital capacity values obtained before haemodialysis in patients with lower interdialytic weight gain (group 1) are significantly lower (p<0,05) compared to the stated values in patients with greater interdialytic weight gain (group 2). The reason for these findings might be found in difference in heamodialysis duration, sex, age, and some other antropometric parameters (height and weight) that influence vital capacity values [14-20].
Forced vital capacity, dynamic component of spirometry, shows tendency for recovery in both observed groups (group 1 and 2), but without statistical significance (p>0.05). Decrease of FVC values primarily occurs in restrictive diseases, but could be found in expressed congestive diseases (pulmonary oedema) as well. In obstructive diseases (e.g. uraemic lung), FVC values are below vital capacity ones, because, during the forced expiration, intrapleural pressure increases which leads to collapse of small airways. In addition to the stated, respiratory muscles force has a great impact on FVC values, and it is reduced in patients after haemodialysis. Liquid reduction in the body, as the result of haemodialysis, decreases the pressure on airways, and reduces obstruction [17-22]. The stated pathophysiological phenomena may be the reason for FCV values recovery. Therefore, the difference between FVC and VC is in favour of obstruction presence and slower recovery of airways in patients with greater interdialysis liquid gain. In the comparison of post-heamodialysis values of the stated parameters with normal values, it could be observed that recovery was better in patients with lower interdialysis liquid intake (group 1). Forced vital capacity values obtained before haemodialysis in patients with lower interdialysis intake (group 1) are significantly lower (p<0.05) compared to the stated values in patients with greater interdialysis intake (group 2). The reason for these findings might be found in difference in heamodialysis duration, sex, age, and some other antropometric parameters (height and weight) that influence vital capacity values [14-20].
Forced expiratory volume in first second. In group 1, after haemodialysis, FEV1 value is highly improved (p<0.01), while in group 2 (with greater interdialysis gain) FEV1 is recovered, but without statistical significance (p>0.05). Results of other studies conducted on patients suffering from uraemia, show significant FEV1 recovery after haemodialysis, which is similar to our findings [7-13]. Positive effect of haemodialysis on FEV1 is more expressed in group 1 (patients with interdialysis liquid gain < 5%) than in group 2 (patients with interdialysis liquid gain > 5%). These results can be explained by the fact that the patients with less interdialysis liquid gain have lower obstruction degree and impairment of small airways. Greater interdialysis gain in group 2 could have caused less improvements in FEV1. The stated facts show that the patients with interdialysis liquid gain > 5% have greater airways obstruction and consequently slower recovery. Normal values of the observed parameter were not noticed in any of the examined groups, however, recovery was more expressed in patients with lower interdialysis liquid intake (group 1). FEV1 before haemodialysis in patients with lower interdialysis intake (group 1) are significantly lower (p<0.05) compared to the stated values in patients with greater interdialysis intake (group 2). The reason for these findings might be found in difference in heamodialysis duration, sex, age, and some other antropometric parameters (height and weight) that influence vital capacity values [7-22].
From our results we concluded that haemodialysis has a positive effect on ventilating function in patients with ESRD. We also noted that patients who are on haemodialysis with interdialysis body liquids gain above 5% have slower recovery of ventilating functions.