Medicinal & Aromatic Plants
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-0412
ISSN: 2167-0412
Research Article - (2021)Volume 10, Issue 9
An ethno-medicinal plant species survey of Vijayapur District of Karnataka comprising thirteen Talukas was conducted during March 2018 to July 2021. The purpose of this survey was to document the Ethno- medicinal plant species used for animal and insect bite. The present study was initiated with an aim to identify Ethno-medicinal plant species resources from traditional practitioners of Vijayapur District. There are about 21 plant species of angiosperms belonging to 20 genera and 15 families were found to be used as animal and insect bite.
Ethno-medicinal plant species; Animal and insect bite; Vijayapur; Karnataka
Animal and insect bite is common in villages. Dog, rat, frog, cat, spider, centipede and honey bee bites explained in this paper. Bites can be identified by two puncture marks where they inject their venom into the skin. The area around the bite may become red and swollen. Pain, redness, and swelling begin immediately upon being bitten. These symptoms may last anywhere from several hours to several days Other symptoms may also occur and could indicate a severe allergic reaction, including extreme swelling at the site of the bite, chills, itching, extreme swelling at the site of the bite. People of rural area are unable to reach city hospital as early as possible. Traditional herbal medicines are and easily available. Ethnomedicine deal with traditional health care which encompasses the knowledge, skill and methods practices concerning healthcare. The present study was initiated with an aim to identify Ethno- medicinal plants resources from traditional practitioners of Vijayapur District to treat animal and insect bite.
Ethnobotanical data collection
Ethno- medicinal plants survey conducted on March 2018 to July 2021 in Vijayapur District. For this, frequent field trips were made to 45 villages belonging to all 13 tehsils of the district. Thirty-two traditional practitioners (43 men and 2 women) data and information recorded in the standard questionnaire Prior Informed Consent (PIC).
Voucher specimen collection and identification
Collected data and information include, Vernacular name of traditionally used medicinal plants, part used, method of preparation and dosage. Medicinal plant species were photographed in the field. Plant specimens were identified consulting with experts, by referring Flora of Gulbarga District [1], three volumes of the Flora of Presidency of Madras [2]. The voucher specimens were stored at the herbarium centre, Department of post graduate studies and Research in Botany, Karnataka State Akkamahadevi Womens University,Vijayapur (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Map of the study area.
Data analysis
The collected data were organized and Relative Frequencies Citation (RFC=FC/N) N is the total informant; FC is the Number of informants suggested same plant species for same medication.
Study area
Vijyapur District is plain Deccan plateau, which is from 365-610 met height above sea level. This region is slope towards west to east. The river Doni, Krishna, Bheema, and their tributaries are flows according to the slope. The total area of Vijayapur district is 10541 sq km. There are thirteen talukas of Vijayapur District i.e., Vijayapur, Muddebihaal, Sindagi, Basavanbagevaadi, Indi, Talikote, Devara Hipparagi, Chadachan, Tikota, Babaleshwar, Kolhar, Nidagundi, Almel. Bordered by the Bheema River in the north and the River Krishna in the south, the district consists of the dry and arid tract of the Deccan Plateau. The temperature varies between 42°C during summer and 15°C during winter season respectively. In May mean maximum temperature is 40°C. The climate of this region is arid, tropical and steppe type. The soil of Vijayapur District area is rich in content of basalt rock, magnetite, magnesium, aluminium and iron oxide. The Vijayapur District receives normal rainfall 578.0 mm and the vegetation of this region is mainly dry and deciduous and may broadly as vegetation on plains. The natural vegetation near Alamatti Dam area is like dry and hot having rich flora. Many local traditional practitioners collect the plants from this area to cure the diseases.
In the present account, 21 species of angiosperms belonging to 20 genera and 15 families were reported for animal and insect bite. The predominant family is Fabaceae with 5 species, followed by Solanaceae with 3 species, Amaranthaceae, Rutaceae, Lilliaceae, Acatnthaceae, Asclepidaceae, Apiaceae, Cucurbitaceae, Menispermaceae, Aristalochiaceae, Asteraceae, Convolvulaceae, Lamiaceae, Boraginaceae with one species each (Figure 2). Data obtained from the survey is compiled in Table 1. All plant species scientific name, family, local name, Habit, Part used and mode of administration are provided (Figure 3). Different plant parts were used piles treatment. Among these leaves were used (30.43%), followed by root (21.73%), stem (17.39%), seeds (17.39%), fruit (8.69%) and flower bud (4.34%) decreasing order. Among the reported plant species for animal and snakebite treatment (Figure 4) Relative Frequency of Citation (RFC) has calculated, the most frequently cited species is Solanum xanthocarpum (15.55), Teprosia purpurea Alium sativum (6.66). Acacia arebica, Albizia lebbeck, Calotropis procera, Datura stremonium, Ipomea remiformis, Luffa achinata, Ocimum sanctum, Pimpinella heyneana, Pongamia pinnata, Sesamum indicum, Solanum nigrum, Trichodesma zeylanicum (4.44). Achyranthus aspera, Aristolochia indica, Cocculus hirsutus, Dichoma tomentosa, Indigofera tictoria, Limonia acidissima (2.22). In Karnataka, Ethno medicine practice for snake and scorpion bite studies conducted in Chitradurga [3] and Tumkur [4] districts. In India ethno medicinal plants to treat snake bite and scorpion bite practice documented in Rahatgoan Hard [5], Paliyar’s Tribes of Sathpur Hills [6], Eastern Ghats of Kolli Hills, Tamilnadu [7], Hingoli District of Maharastra [8] and [9]. However Ethno-medicine practices for animal and insect bite in Vijayapur (Bijapur) [10] district has been reported still. Most of the people dependent on traditional herbal medicine because availability of effective drug plants. Hence, these plants can be taken up for further pharmacological and clinical studies.
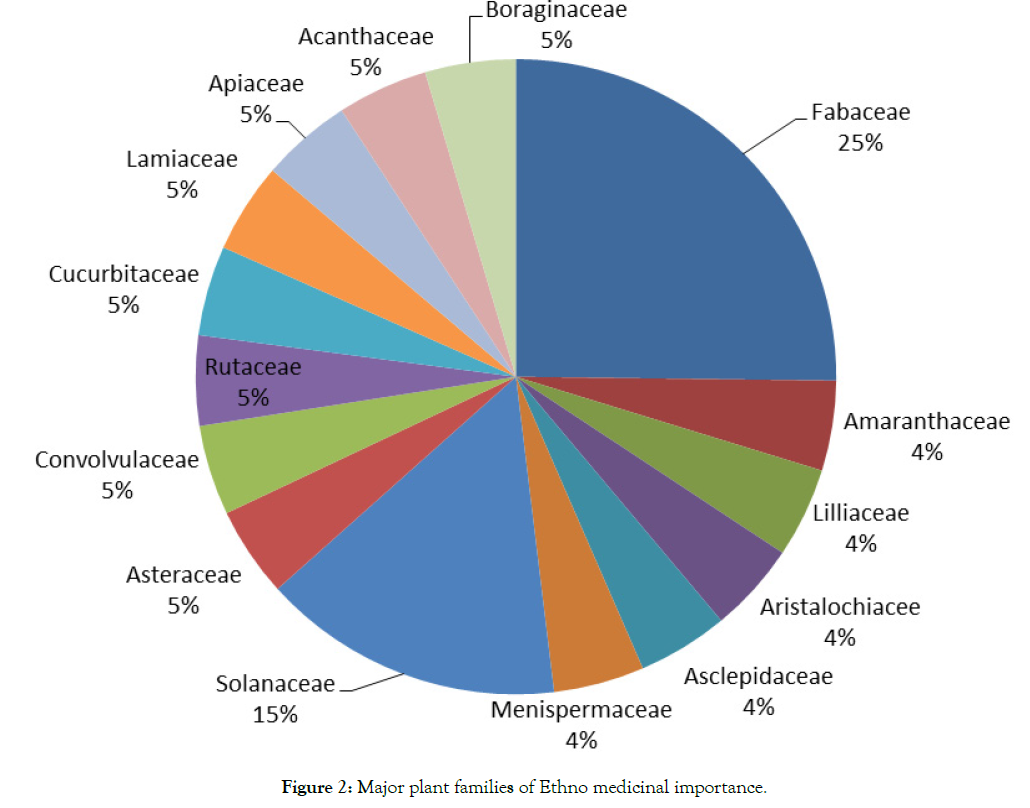
Figure 2: Major plant families of Ethno medicinal importance.
| Scientific Name | Family | Local/ Vern Name | RFC | Habit | Part Used | Animal/Insect | Mode of Administration | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acacia arebica | Fabaceae | Jaali | 4.44 | Tree | Leaves | Dog | Leaves juice one spoonful cow ghee taken orally | |
| Achyranthus aspera | Amaranthaceae | Utharani | 2.22 | Herb | Root | Rat | Seeds+Honey taken orally for seven days | |
| Seed | Dog | Seeds+Honey taken orally. Aloe Vera and black salt mixed equal quantity apply on bite for three days | ||||||
| Alium sativum | Lilliaceae | Bellulli | 6.66 | Herb | Stem | Scorpion | Garlic juice apply on bite | |
| Stem | Dog | Clean the bite side with water. Apply garlic juice on bite and suggest to drink decoction of garlic | ||||||
| Albizia lebbeck | Fabaceae | Shirasal gida | 4.44 | Tree | Seed | Frog | Seeds ground with Euphorbia tirucalli, apply on bite | |
| Aristolochia indica | Aristalochiacee | Ishwari | 2.22 | Shrub | Root and Leaves | Spider |
|
|
| Calotropis procera | Asclepidaceae | Ekke | 4.44 | Shrub | Stem | Dog | Stem latex+jaggary+seesam oil apply on bite | |
| Cocculus hirsutus | Menispermaceae | Dagadi balli | 2.22 | Herb | Root | Rat | Root+Jaggery ground and taken orally | |
| Datura stremonium | Solanaceae | Madagunaki | 4.44 | Herb | Leaves | Rat | Juice of the leaves applied on bite keep charcoal on it | |
| Dichoma tomentosa | Asteraceae | Navanandi | 2.22 | Herb | Root | Cat and rat | Rubbed the root apply on bite and ground the root taken orally | |
| Indigofera tictoria | Fabaceae | Neeli gida | 2.22 | Under shrub | Leaves | Dog | Ground the leaves taken orally | |
| Ipomea remiformis | Convolvulaceae | Ilikivi | 4.44 | Herb | Leaves | Rat | Leaves ground apply on bite. Aswal as taken two spoonful orally | |
| Limonia acidissima | Rutaceae | Balaval kaayi | 2.22 | Tree | Seed | Rat | Seed oil is applied on bite | |
| Luffa achinata | Cucurbitaceae | Bandal Devadal |
4.44 | Climber | Fruit | Rat | Fruit powder mixed in curd advice to drink. | |
| Ocimum sanctum | Lamiaceae | Thulasi | 4.44 | Herb | Leaves | Rat | Leaves ground and apply on bite | |
| Pimpinella heyneana | Apiaceae | Ajavan | 4.44 | Herb | Seed | Honey bee | Seeds ground with cow ghee apply on bite | |
| Pongamia pinnata | Fabaceae | Honge gida | 4.44 | Tree | Stem | Rat | Rub the stem bark and seeds apply on bite | |
| Sesamum indicum | Acanthaceae | Ellu | 4.44 | Herb | Flower bud | Spider | Flower bud and curcum rubbed and apply | |
| Solanum nigrum | Solanaceae | Kaaki gida | 4.44 | Herb | Root | Dog | Rub the root apply on bite | |
| Solanum xanthocarpum | Solanaceae | Nelagullu | 15.55 | Herb | Fruit | Dog | Ground the fresh fruit apply on bite, tie wet cottan cloth | |
| Trichodesma zeylanicum | Boraginaceae | Ethina nalige | 4.44 | Herb | Leaves | Dog | Leaves burnt, ash stored in glass bottle. Apply with coconut oil on bite | |
| Teprosia purpurea | Fabaceae | Koggi | 6.66 | Herb | Seed | Rat | Ground the seeds mix in glass of butter milk taken orally | |
Table 1: Ethno-medicinal plant species used for animal and insect bite of Vijayapur (Bijapur) district.
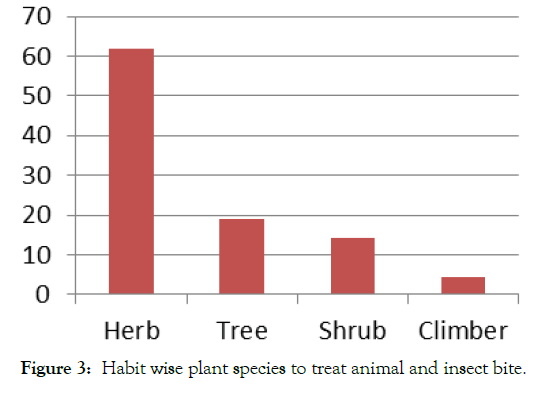
Figure 3: Habit wise plant species to treat animal and insect bite.
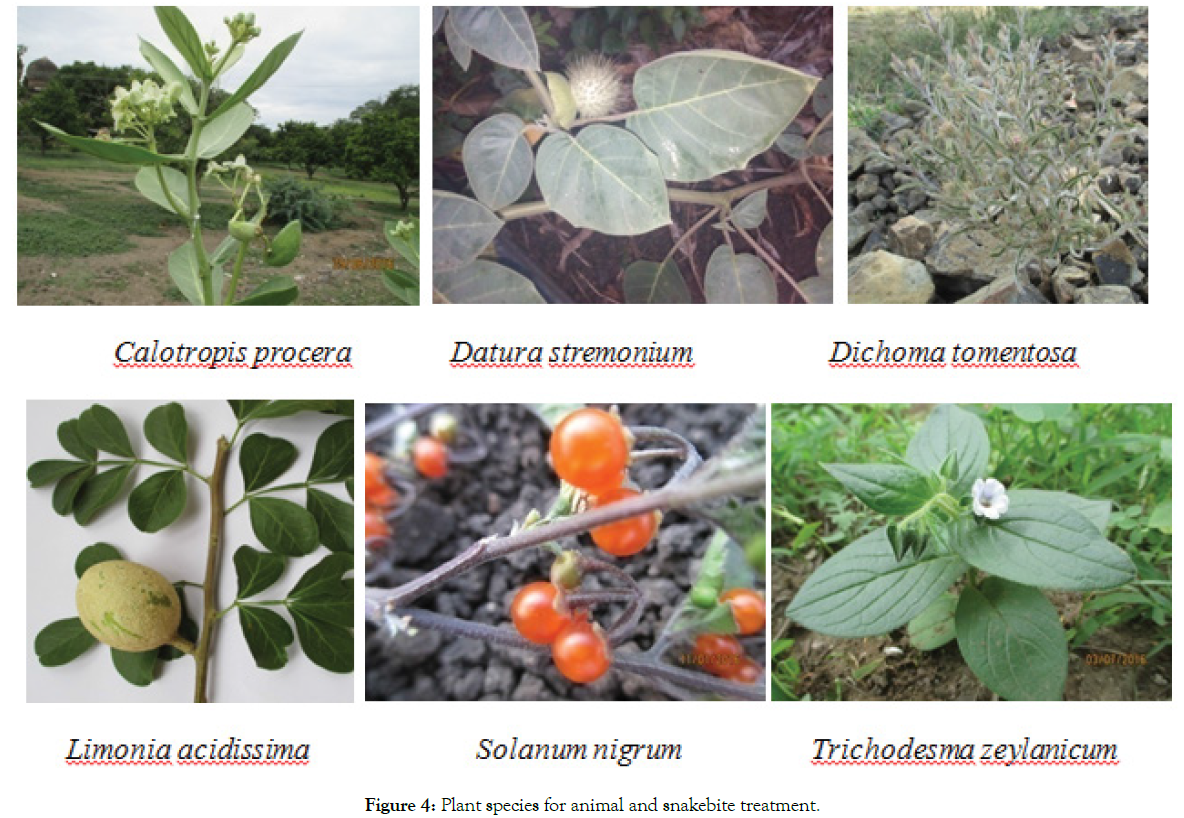

Figure 4: Plant species for animal and snakebite treatment.
Ethno- medicinal plants survey conducted on March 2018 to July 2021 in Vijayapur District. The main purpose of this survey was to document the traditional use of medicinal plants for animal and insect bite treatment in vijayapur District. 21 species of angiosperms belonging to 20 genera and 15 families were found to be used. The scientific name, family, local name, habit along with part used and mode of their administration are provided. This traditional knowledge can transfer from one generation to generation. The study also suggested that the present information on medicinal plant species used for animal and insect bite treatment by the traditional practitioners of Vijayapur District may be used for phytochemical and pharmacological research in future for the development of new sources of drugs.
Authors are thankful to traditional practitioners of Vijayapur District, who cordially co-operated in sharing their knowledge and in helping collection of plant material pertaining to the research.
Citation: Laddimath A (2021) Ethno-Medicinal Plant Species Used for Animal and Insect Bite (Sting) of Vijayapur (Bijapur) District of Karnataka, India. Med Aromat Plants (Los Angeles) 10: 408.
Received: 07-Sep-2021 Accepted: 23-Sep-2021 Published: 30-Sep-2021 , DOI: 10.35248/2167-0412.21.10.408
Copyright: © 2021 Laddimath A. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.