Journal of Defense Management
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-0374
ISSN: 2167-0374
Research Article - (2017) Volume 7, Issue 1
Naval base as part of integrated fleet weapon system has an important role in maintaining the strategic environment in the region of Indonesia. Naval base with a strategic location will support Indonesian navy?s main duty to carry out the administrative and logistical support. Due to the limitation of naval base?s condition, feasibility study will be required to relocate the naval base. In this feasibility study, a combination of methods between SWOT analysis and Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) is used. The results of the Internal Factors Evaluation (IFE) matrix analysis is 4.72 and External Factors Evaluation (EFE) matrix analysis is 2.91. In general, the balance of power between the IFE Matrix and EFE Matrix is located in quadrants I and thus, the aggressive strategy is supported. While the matrix analysis? result of Internal-External (IE) showed that the score of IFE and EFE located in quadrant II and VII.
Keywords: Feasibility study; Naval base; SWOT; AHP
Indonesia is a maritime country comprising over 17.000 islands. It is located between the Pacific and Indian Oceans and links Asia land with the Pacific world (Figure 1) [1]. The geo-strategic of Indonesian is a potential tool to controls several critical paths across the oceans in the world [2]. Under the changing circumstances of operational environment and in the face of new security environment which is more complex and ambiguous than before, modern armies have started to look for alternatives or better options to surpass the challenge of transition in the new era [3]. The prospect of declining budgets and the changing geostrategic environment had also urged the Navy to change its strategy decision [4].
Therefore, to protect Indonesia’s marine territory, Indonesian Navy holds a program to strengthen the defense with the integrated fleet weapon system. That program consists of navy vessel, aircraft, troops (marines) and naval base. As part of integrated fleet weapon system, the naval base should be able to carry out its functions optimally to resolve cases of violations in Indonesia’s marine territory [5]. One of the Indonesian navy strategic plans in the dynamics of change is to relocate the naval base into a better place because the current condition of the naval base is still lacking the ability to carry out its duties.
The feasibility study on the relocation of the naval base is carried out by doing an investigation the areas and supporting facilities in terms of technical and strategic aspects along with interviewing Indonesian navy’s officer. The technical aspects of a port include Hinterland/ area of influence aspect and geography and oceanography aspect [6]. Geographically, military also considers of militarism perspective and spatial perspective [7]. This is because globalization and economic power are worthless without the existence of military [8]. A strategic position is an important element for the operation of a concept [9]. Strategic Decisions (SD) are made based on the special characteristics of the decision (both the perceived characteristics and typology objectives strategic decisions) which is part of the management leadership characteristics and has contextual factors refer to the external and internal environment [10]. The purpose of this feasibility study is to provide a more realistic perspective from key decision makers in decision making process [11]. This study is necessary to determine the effectiveness and to manage the risks of some system that will be used [12].
Therefore, this feasibility study to relocate the naval base is part of a research operation based on Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM). The core of the operations research is to develop approaches for optimal decision making. A prominent class of such problems is multi-criteria decision making (MCDM). The typical MCDM problem deals with the evaluation of alternatives in a set of decision criteria [13]. One way MCDM approach is to use a SWOT and AHP analysis. The combined use of the AHP and SWOT analysis has been widely used to support strategic decision making processes [14].
SWOT analysis is an important part of feasibility study [15]. A SWOT analysis is able to identify conditions, potentials, and problems with related aspects which resulted in the decision of a number of factors or variables [16]. This combination can efficiently evaluate SWOT subcriteria and thus give them priority in order to allow decision-makers to determine which of those should be given attention first [17]. To obtain the scale ratio from the actual measurement or the fundamental scale that reflects the relative strength, AHP method is used [18]. There are some basic principles in resolving the problems with the AHP method, namely decomposition, comparative judgment, synthesis of priority, and logical consistency [19].
By combining SWOT and AHP analysis stages, the right strategies can be determined for planning the relocation of the naval base. Furthermore, this strategic planning can be used as a tool of organization to start and manage their strategic functions of the organization [20]. This study is necessary in order for the naval base to function optimally and effectively. This study determines the strategic priorities of location and relocation of the naval base. It also provides a feasibility study for the development of naval base as a guideline in planning other naval bases and facilities in future.
SWOT and AHP integration is used for the flowchart in this research (Figure 2) [21]. SWOT provides the basic frame to perform an analysis of the decision situation, and the AHP assists in carrying out SWOT more analytical and elaborating the analysis so that alternative strategic decisions can be prioritized [22]. The aim of applying the combined method is to improve the quantitative side of strategic planning [21].
Naval base environment
Naval base is expected to be the spearhead force in carrying out the task of supporting the warships operation [23]. The main duty of the naval base is to carry out administrative and logistical support in order to develop the concept of logistics operations support [24]. The requirements of Indonesian naval base include port facility, maintenance and repair facility, supplies or logistics facility, personnel care facility, and training base facility (Table 1).
| NO. | Standard bases of Indonesian navy | Basic building coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| Port facility | Capable in leaning all kinds of warships, at least one task force | 20% |
| Maintenance and repair facility | Able to carry out maintenance and repairs up to the intermediate level for all types of warships both system, weapons and platform | 10% |
| Supplies or logistics facilitiy | Able to support Class Logistics (food, individual field equipment, tools, oils, drugs) for at least one task |
10% |
| Personnel care facility | Support personnel includes: messing, medical facilities / hospital, sports and recreation facilities, religious facilities, and training facilities to at least one task force. | 30% |
| Training base facility | 1.The Common Facilities, capable of providing officefacilities and infrastructure activities on the base. 2.Freight Services Facilities, able to support the transport and postal personnel by land, sea and air. 3.Defense Base Facilities, capable of providing defense and security against threats from the air, sea and land as well as infiltration / sabotage. |
30% |
Table 1: Indonesian naval base standard facility.
The others general environment which includes the socioeconomic, educational, legal–political, and cultural aspects, usually operates within a specific geographic area. The specific environment is comprised of the suppliers, distributors, government agencies, and competitors which a military organization should interact [25], including the effect of the population, political institutions, geo-culture, and others in determining the exact location [26].
SWOT analysis
SWOT is a method used to analyze operational environment with a systematic approach. This analysis is also utilized for strategic planning [27]. SWOT analysis is based on the logic of maximizing the strength and opportunities as well as minimizing the weaknesses and threats simultaneously [28]. SWOT analysis is obtained from the identification of the conditions, potentials and problems with aspects related to use SO (Strength Opportunity)/maxi-maxi strategy, wo (weakness opportunity)/mini-maxi strategy, st (strength threat)/maximini strategy, WT (weakness threat)/mini-mini strategy (Table 2) [29].
| SWOT Matrix | Strength (S) Positive internal aspects that can be controlled and can be strengthened in the planning. |
Weakness (W) The strategy of internal negative aspects that can be controlled and can be corrected in the planning. |
| Opportunity (O) Positive external conditions that can’t be controlled and can be taken advantage. |
SO Strategy Utilizing Internal strength to take advantage of external opportunities. |
WO Strategy Improving internal weaknesses by taking the clappers of external opportunities |
| Threat (T) Negative external conditions that can’t be controlled and may be minimized impact. |
ST Strategy Using force to avoid or reduce the impact of external threats |
WT Strategy Defensive tactics directed at reducing internal weaknesses and avoid external threats |
Table 2: SWOT Matrix.
Stages of AHP
Additional value from SWOT analysis can be achieved by performing pair-wise comparisons between SWOT factors and analyzing them by means of eigenvalue technique as applied in AHP means of eigenvalue technique as applied in AHP [29]. Relative importance weights of the SWOT factors and sub-factors were obtained by Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) model, as well as the ranking of identified strategies. It was performed by several experts [30]. The stages of decision-making with AHP method are as follows:
1. Define problems and determine solutions.
2. Creating a hierarchical structure.
3. Pairwise comparison matrix formed by choice or judgment of the decision maker to assess the level of importance of an element than any other element.
4. Normalize the data.
5. Calculating eigen values vector and tested for consistency.
6. Repeat steps 3, 4, and 5 for all levels of hierarchy.
7. Calculating eigen vector of each pairwise comparison matrix.
8. Test the consistency of the hierarchy in the form of relationship priorities as eigen vector against consistency.
If that assessment is perfect in any comparison, aij.ajk = aik then for all, and A matrix is called consistent (21).
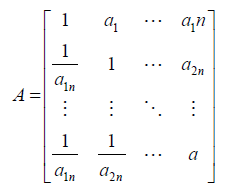
The values of the comparison matrix A can be expressed into the following forms:
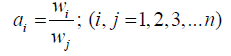 (1)
(1)
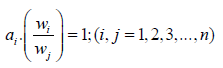 (2)
(2)
Consequences:
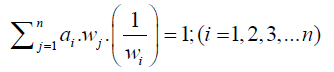 (3)
(3)
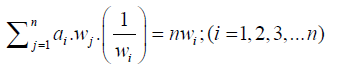 (4)
(4)
Equation (4) in the form of a matrix becomes:
A.w = n.w (5)
If Z1, Z2, Z3, ..., Zn are numbers that is in accordance with equation A.w = Z.w (Z is eigen value of the matrix, and if= 1 to i) then an equation becomes
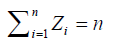
if is a pairwise comparison matrix, to obtain the priority should be sought W vector satisfying the equation
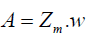 (7)
(7)
Indicators of consistency measured using Consistency Index (CI) were formulated
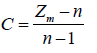 (8)
(8)
And for measuring the consistency of assessment is used Consistency Ratio (CR)
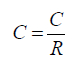 (9)
(9)
A certain level of consistency is required in determining the priority to obtain valid results. CR value should not be more than 10% or 0.10. If not then need to be revised (21). Random Index (RI) value can be seen in the following Table 3:
| n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RI | 0 | 0 | 0.58 | 0.9 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 1.41 | 1.45 | 1.49 | 1.51 | 1.54 | 1.56 |
Table 3: Random Index (RI).
SWOT data processing in primary data collection is done by interviewing officer of Indonesian naval base facilities services, hydrooceanographic office and naval expertise competence. The results of the interview data were processed by expert choice software into criteria and weighting data in accordance with the numerical calculation (Tables 4 and 5).
| No | Internal criteria | Total count |
|---|---|---|
| Strengths | ||
| S.1 | Policy | 52 |
| S.2 | Main duties naval base | 48 |
| S.3 | General requirements of naval base | 47 |
| S.4 | Availability of logistics region | 47 |
| S.5 | Topography | 47 |
| S.6 | Classificationof naval base | 47 |
| S.7 | Function of naval base | 47 |
| S.8 | Personnel readiness | 47 |
| Weaknesses | ||
| W.1 | Areas of operation | 44 |
| W.2 | Supporting facilities | 43 |
| W.3 | Layout design | 43 |
| W.4 | Geology | 42 |
| W.5 | Availability of shipyard | 40 |
| W.6 | Availability of public facilities | 40 |
Table 4: Internal criteria of primary data of strengths and weaknesses.
| No | External criteria | Totalcount |
|---|---|---|
| Opportunities | ||
| O.1 | Regional spatial | 48 |
| O.2 | Availability of land | 47 |
| O.3 | Oceanography | 47 |
| O.4 | Sedimentation | 47 |
| O.5 | Geostrategic and geo-economy | 47 |
| O.6 | Unit support | 45 |
| O.7 | Availability of public pier | 44 |
| Threats | ||
| T.1 | Community support | 38 |
| T.2 | Sailing volume | 38 |
| T.3 | Road access | 38 |
| T.4 | Supporting facilities | 36 |
| T.5 | Level of insecurity | 28 |
Table 5: External criteria primary data of opportunities and threats.
Weight determination and critical value
Data processing in critical weight determination and value at AHP SWOT performed using expert choice software. Furthermore, the data was presented in excel format to determine the criteria for scale rating score (Table 6).
| SWOT groups | Importance of the SWOT criteria |
SWOT sub-criteria | Local importance of SWOT sub-criteria |
Weight total (N) |
Score (J) |
Rating score (N) × (J) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths (S) | 0.337 | 1 | Policy | 0.239 | 0.081 | 52 | 4.19 |
| 2 | Main duties naval base | 0.157 | 0.053 | 48 | 2.54 | ||
| 3 | General requirements naval base | 0.147 | 0.050 | 47 | 2.33 | ||
| 4 | Availability of logistics region | 0.123 | 0.041 | 47 | 1.95 | ||
| 5 | Topography | 0.109 | 0.037 | 47 | 1.73 | ||
| 6 | Classification of naval base | 0.087 | 0.029 | 47 | 1.38 | ||
| 7 | Function of naval base | 0.081 | 0.027 | 47 | 1.28 | ||
| 8 | Personnel readiness | 0.058 | 0.020 | 47 | 0.92 | ||
| Total | 1.00 | 0.337 | |||||
| Weaknesses (W) | 0.295 | 9 | Areas of operation | 0.244 | 0.072 | 44 | 3.17 |
| 10 | Supporting facilities | 0.202 | 0.060 | 43 | 2.56 | ||
| 11 | Layout design | 0.182 | 0.054 | 43 | 2.31 | ||
| 12 | Geology | 0.140 | 0.041 | 42 | 1.73 | ||
| 13 | Availability of shipyard | 0.122 | 0.036 | 40 | 1.44 | ||
| 14 | Availability of public facilities | 0.111 | 0.033 | 40 | 1.31 | ||
| Total | 1.00 | 0.295 | |||||
| Opportunities (O) | 0.223 | 15 | Regional spatial | 0.228 | 0.051 | 48 | 2.44 |
| 16 | Availability of land | 0.214 | 0.048 | 47 | 2.24 | ||
| 17 | Oceanography | 0.142 | 0.032 | 47 | 1.49 | ||
| 18 | Sedimentation | 0.126 | 0.028 | 47 | 1.32 | ||
| 19 | Geostrategic and geo-economy | 0.123 | 0.027 | 47 | 1.29 | ||
| 20 | Unit support | 0.085 | 0.019 | 45 | 0.85 | ||
| 21 | Availability of public pier | 0.083 | 0.019 | 44 | 0.81 | ||
| Total | 1.00 | 0.223 | |||||
| Threats (T) | 0.146 | 22 | Community support | 0.291 | 0.042 | 38 | 1.61 |
| 23 | Volume sailing | 0.246 | 0.036 | 38 | 1.36 | ||
| 24 | Road access | 0.206 | 0.030 | 38 | 1.14 | ||
| 25 | Supporting facilities | 0.152 | 0.022 | 36 | 0.80 | ||
| 26 | Level of insecurity | 0.104 | 0.015 | 28 | 0.43 | ||
| Total | 1.00 | 0.146 | |||||
Table 6: Critical value weighting of SWOT criteria.
Internal factors evaluation (IFE) matrix analysis: From the analysis above, the score of 4.72 was relatively obtained. This result was ranging in the scale of 4 and indicates that these factors are very strong in influencing internal factors of naval base relocation (Table 7).
| SWOT groups Level 1 |
Internal SWOT sub-criteria | Local importance | Rating | Score (2) × (3) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | ||
| Strengths (S) | 1 | Policy | 0.239 | 4.19 | 1.00 |
| 2 | Main duties naval base | 0.157 | 2.54 | 0.40 | |
| 3 | General requirements of naval base | 0.147 | 2.33 | 0.34 | |
| 4 | Availability of logistics region | 0.123 | 1.95 | 0.24 | |
| 5 | Topography | 0.109 | 1.73 | 0.19 | |
| 6 | Classification of naval base | 0.087 | 1.38 | 0.12 | |
| 7 | Function of naval base | 0.081 | 1.28 | 0.10 | |
| 8 | Personnel readiness | 0.058 | 0.92 | 0.05 | |
| Total | 1.00 | 2.45 | |||
| Weaknesses (W) | 9 | Areas of operation | 0.244 | 3.17 | 0.77 |
| 10 | Supporting facilities | 0.202 | 2.56 | 0.52 | |
| 11 | Layout design | 0.182 | 2.31 | 0.42 | |
| 12 | Geology | 0.140 | 1.73 | 0.24 | |
| 13 | Availability of shipyard | 0.122 | 1.44 | 0.18 | |
| 14 | Availability of public facilities | 0.111 | 1.31 | 0.15 | |
| Total | 1.00 | 2.27 | |||
Table 7: Internal Factors Evaluation (IFE) matrix analysis.
External factors evaluation (EFE) matrix analysis: From the analysis above, the score of 2.91 was obtained. This result is ranging in the scale of 3, indicating that these factors had a higher response above than the average in influencing external factors of naval base relocation (Table 8).
| SWOT GROUPS Level 1 |
External SWOT sub-criteria | Local importance | Rating | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (2) × (3) | ||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| Opportunities (O) | 1 Regional Spatial | 0.228 | 2.44 | 0.56 |
| 2 Availability of Land | 0.214 | 2.24 | 0.48 | |
| 3 Oceanography | 0.142 | 1.49 | 0.21 | |
| 4 Sedimentation | 0.126 | 1.32 | 0.17 | |
| 5 Geostrategic and Geo-economy | 0.123 | 1.29 | 0.16 | |
| 6 Unit Support | 0.085 | 0.85 | 0.07 | |
| 7 Availability of Public Pier | 0.083 | 0.81 | 0.07 | |
| Total | 1.00 | 1.71 | ||
| Threats (T) | 8 Community Support | 0.291 | 1.61 | 0.47 |
| 9 Sailing Volume | 0.246 | 1.36 | 0.33 | |
| 10 Road Access | 0.206 | 1.14 | 0.23 | |
| 11 Supporting Facilities | 0.152 | 0.80 | 0.12 | |
| 12 Level of Insecurity | 0.104 | 0.43 | 0.04 | |
| Total | 1.00 | 1.20 |
Table 8: External Factors Evaluation (EFE) matrix analysis.
Sensitivity analysis
A sensitivity AHP analysis on the weight of the priority criteria can determine the order of priority strategy. Dynamic graph sensitivity can also be characterized as in the Figures 3 and 4 below.
From the condition above, the priority strength was 33.7% and in those conditions, the global priorities of strength were 33.7%, then weaknesses 29.5%, opportunities 22.3% and threats 14.6%.
The formulation of the strategic priorities from IFE and EFE matrix results, it is showed that the intersection of the four lines namely strength, weaknesses, opportunities and threats factor are as follows (Figures 5 and 6):
scores strengths-weaknesses score=2.45 to 2.27=0.17
scores opportunity-threat score=1.71 to 1.20=0.51
In the chart above, the data were obtained through EFI and EFE matrix. The strength comparison stands in quadrant I and it supports the aggressive strategy (Table 9). It is depicted in the graph below:
| Internal factor/External factor | Strengths (S) | Weaknesses (W) |
| Policy | Areas of operation | |
| Main duties naval base | Supporting facilities | |
| General requirements base | Layout design | |
| Availability of logistics region | Geology | |
| Topography | Availability of shipyard | |
| Classifications of naval bases | Availability of public | |
| Function of naval base | facilities | |
| Personnel readiness | ||
| Opportunities (O) | SO Strategy | WO Strategy |
| Regional spatial | Preparation of the administration of relocation | Cooperation of area development |
| Availability of land | ||
| Design plan of naval base (S1)(S2)(S5)(O2)(O3)(O4) | The establishment of economic centres (W2)(W3)(O1)(O2)(O5) | |
| Oceanography | ||
| Sedimentation | ||
| Geostrategic and geo economy | ||
| Unit support | ||
| Availability of public pier | ||
| Threats (T) | ST Strategy | WT Strategy |
| Community support | Empowerment of maritime potency | Cooperation with local companies |
| Sailing volume | Development of the surrounding area (S2)(S7)(O1)(O2) |
Utilization of the existing contour |
| Road access | Implementation of routine operations (W2)(W3)(W6)(T1)(T2) |
|
| Supporting facilities | ||
| Level of insecurity |
Table 9: SWOT matrix research.
Priority strategies
S-O strategy was selected as a priority strategy to relocate the naval base (Figure 7). This strategy can succeed by preparing the location details in advance. Furthermore, the implementation of the relocation of the naval base implemented according to plan with the support of local topography and oceanography state.
In this paper, we have determined the strategic factors significant to relocate naval base by combining the SWOT method with AHP technique. strength and opportunities (S-O) strategy is a strategic priority to support the relocation of the naval base. So that the main duties of the naval base can be successful, especially for warships operation in the Indonesian territory. Chart analysis of IFE and EFE matrix shows that the strategy is in quadrant I, which supports an aggressive strategy by leveraging existing strengths and opportunities. Expectations of future research on any MCDM techniques also can use CBA (Cost Benefit Analyze) method to determine the cost of relocating naval base.
This research has been supported by Indonesia Naval Technology College (STTAL) and Indonesian Naval Base Facilities Services.