Journal of Hotel and Business Management
Open Access
ISSN: 2169-0286
ISSN: 2169-0286
Research Article - (2022)Volume 11, Issue 3
The effective management of employees’ knowledge has been described as a critical ingredient for organisations seeking to ensure sustainable strategic competitive advantage in the market place. The purpose of the study was to investigate the impact of knowledge management on employees’ role clarity and quality of services. The study sampled 300 staff from three private hospitals in Ghana namely: Trust Hospital, Otoo Memorial Hospital and Cocoa Hospital. The purposive sampling technique was employed to select the private hospitals while simple random was used to select staff of the hospitals. The results revealed that service quality has a positive relationship on knowledge management and service quality.
Role clarity; Service quality; Knowledge management; Hospital staff
In this era of globalization and technologically advancement age, hospitals have significant role to play in ensuring the general wellbeing of patient, therefore the need for staff to constantly improve and upgrade their skills and capabilities in order to support the goal and mission of the hospitals. Concerns over knowledge management plays essential role in managing organizations in this modern era because of the perception that the organization or institutions are failing. To avoid organizational failure, especially in hospitals, the onus lies on the staff to ensure that the needs of clients seeking healthcare are accomplished both physically and psychologically as well as their social needs. In the information economy, Knowledge Management (KM) is a practical way for hospital employees to improve their services. This may be done by establishing a hospital-wide organizational culture of information sharing and competence. If hospitals are to consider utilizing those KM techniques that improve efficiency and add value to organizational knowledge, they must first have a clear grasp of what Knowledge Management (KM) means to their operations as well as a strategic resource to the organization [1].
In Ghana, there has been an increasing public demand for improved healthcare delivery in various healthcare facilities within the country. This can be achieved through knowledge management among staff in the hospitals through role clarity. Essentially, role of leadership style determines the organizations performance. This is because the leaders’ style of directing the use of resources, guiding members to implement strategies and convincing members of the organization to work towards expected outcomes will shape the performance of the organization and the staff. Productivity and efficiency scores in several hospitals in Ghana have shown that organizational performances in hospitals are generally very low [2-4]. Studies conducted on district hospitals in Ghana indicates that about 56.2% out of 128 hospitals recorded efficiency scores below average (0.50). Also, the low productivity in the health sector is backed by the World Bank Health Worker Productivity report, which indicates that some regions, districts in Ghana have staff showing low knowledge management skills [5-7].
Literature review and hypotheses development
Concept of knowledge management and role clarity: Knowledge management is an important business tool being used all over the world to enhance capacity building, improve business services, develop basic and incremental innovative products and services services and improve the skills of workers.
Employee’s knowledge when managed efficiently considerably improves the performance and profitability of business organization whether they are functioning in public or private sector. It indicated that individuals’ knowledge consists of intangible awareness, learned facts and information which are manifested as ideas, judgments, talents, root causes, relationships, perspectives and concepts [8].
Knowledge resides in the individual’s mind and only when it is articulated and/or captured it becomes encoded in organization processes, documents, products, services, facilities and systems provided that the employees have the intention to share what they know. Knowledge creation is integral, as knowledge is the only sustainable competitive advantage which is the result of learning. Furthermore, it believes that the creation and transmission of knowledge is seen as strategically significant as one of the fundamental processes that determine organizational learning abilities and innovation although human knowledge is intangible, dynamic, and difficult to measure, without it no organization can survive. Accordingly, organizations should introduce incentives for their employees to share what they know, as well as means of capturing and retaining that knowledge for organizational future use.
The influence of Knowledge Management on role clarity and service quality among private hospitals in Ghana, namely Trust Hospital, Otoo Memorial Hospital, and Cocoa Hospital, was investigated using a cross-sectional survey approach. Purposive sampling was used to choose private hospitals, according to the theory that it relies on the researcher's opinion regarding participants who are typical of the phenomenon or topic being examined [9]. The study's sample consisted of 300 employees who were chosen using a basic random selection technique. The questionnaire was used to gather information. The scale's items were answered on a five-point Likert scale ranging from 1-Never to 5-Always. Inferential statistics were computed from the data acquired through the usage of the questionnaire using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 20. The association between research variables was determined using Pearson's product moment correlation analysis, while the moderating influence of one variable on the relationship between the dependent and independent variables was determined using hierarchical regression analysis. Smart PLS Application was used to conduct Structural Equation Modelling (SEM).
The investigation began by determining the model's dependability. There were two types of reliability used. Reliability of indicators (items) and composite reliability The square of each of the outside loadings was used to calculate indicator reliability (items). However, a significantly higher number for indicator reliability than the minimum permissible level of 0.4 should be considered. Larger indicator reliability ratings suggest that the items used to measure the variables adequately explain the variables. Figure 1 present the results of the indicator reliability. The cumulative or composite reliability of the variables was also examined.
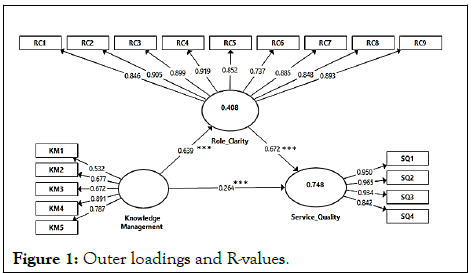
Figure 1: Outer loadings and R-values.
According to Hair, the composite dependability cut-off score is 0.7. The figure reveals that all of the items and variables meet the condition of dependability, indicating that our variables are trustworthy. The variables' convergent validity was also calculated. This indicates that a construct's items should have a large proportion variance. The Average Variance Extracted (AVE) for each variable should be greater than the specified cutoff of 0.50 to ensure this validity. It revealed that all of the AVE values were larger than the acceptable threshold of 0.5, indicating that convergent validity had been established. Using a Smart PLS process called bootstrapping, the researchers calculated the T-statistics to see if the model was significant. The structural model contained a path coefficient assessment to show the strength of the relationships between the R-square value and the latent variables (both independent and dependent variable). As a statistical conclusion measure, a 5% significance level (p=0.05) was chosen. The t-values were used to establish the level of significance. Hair claims that t-values greater than the cut-off condition (1.96) suggest model relevance. The results are summarized. Knowledge management (KM) may explain 41.1 percent of the variability in Role Clarity and 75 percent of the variability in Service Quality, according to the analysis [10].
The accuracy and usefulness of the model was also estimated using Stone-Geisser Indicator (Q2) and Cohen’s Indicator (f2). The Stone-Geisser Indicator (Q2) measures the model quality or significance model. As per Hair, to obtain a good prediction quality, indicator value greater than zero should be obtained. However, a perfect model would have Q2=1, which indicates the model reflects reality and is without any errors. Also, Cohen’s Indicator (f2) measures the usefulness of each construct. For Cohen’s Indicator (f2), Values of 0.02, 0.15 and 0.35 are considered small, medium, and large respectively. The values of Q2, as well as those of f2, indicate that the model is accurate and that the constructs are important for the general adjustment of the model [7].
This research work also shows that the adoption of E-learning like online classes through likes of WhatsApp, Facebook, and YouTube was a major breakthrough for schools during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown. About 53.3% and 26.7% amounting to 80% of the respondents as agrees that adopting Elearning help solve some educational crises during the pandemic lockdown period [8]. 40% strongly agree and 23.3% agree and in total of 6.3% agree that E-learning was effective as a means of transmitting knowledge to student during the COVID-19 pandemic. After the lockdown policies by different countries to curb crowded environments and to restrict movement, electronic learning was helpful in transmitting information and knowledge to various student while at home to balance up school academic calendar and make teaching easier for teachers when schools resume. On the issues of adopting electronic learning fully in Nigeria educational system, 50% of the respondents agree that electronic learning is a way forward in Nigeria educational system while 43.3% of the respondents disagree due to some disadvantages that electronic learning posed.
After analyzing all the data collected in the course of this study, it is important to note that E-learning was instrumental during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown which about 80% of the respondents as agrees that the adoption of E-learning help solve some educational crises during the pandemic lockdown period and it was a useful tool in balancing up school academic curriculums and has the possibilities of making teaching easier for teachers when schools resume.
Citation: Kankam G (2022) Knowledge Management and Role Clarity as Antecedents of Service Quality in Private Hospitals in Ghana. J Hotel Bus Manage. 11:015.
Received: 23-May-2022, Manuscript No. JHBM-22-17157; Editor assigned: 25-May-2022, Pre QC No. JHBM-22-17157 (PQ); Reviewed: 09-Jun-2022, QC No. JHBM-22-17157; Revised: 16-Jun-2022, Manuscript No. JHBM-22-17157 (R); Published: 24-Jun-2022 , DOI: 10.37532/2169-0286.22.015
Copyright: © 2022 Kankam G. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.