Internal Medicine
Open Access
ISSN: 2165-8048
ISSN: 2165-8048
Research Article - (2021)Volume 11, Issue 1
COVID-19, an ephialtes of mankind in the year 2020, is causing painful demise of many lives due to insufficient treatment and hence, creating a devastating history in making. This pandemic brought the world together and led many researches from different biomedical fields to find treatments and potent drugs; ought to help in managing the pandemic and future loss. However, till date no standard treatment has been discovered for COVID-19. Probably, preventing the severe respiratory infection cause by SARS-CoV-2 will give time for finding the most potent treatment for this disease. Easy and manageable methods are there for isolation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) which attracted the attention for number of therapeutic applications. Considering the present situation, treatment using Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) has been suggested as a satisfactory therapeutic approach. A noteworthy population of cells accumulates in the lungs after intravenous transplantation of MSCs which results in increasing the immunomodulatory effect that leads the protection of alveolar epithelial cells, refurbishment of the pulmonary microenvironment, and, prevent lung dysfunction and pulmonary fibrosis. There are several ongoing clinical trials based on MSCs for exploring out its efficiency in the treatment of COVID-19 patients. However, till date MSCs based treatment for COVID-19 is still not approved. This review involves the aspects of MSCs in the proposed treatment of COVID-19 and contains brief discussion on related ongoing clinical trials.
Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSCs); COVID-19; Clinical trials; Immunomodulatory
The announced pandemic of [1] COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019), broke out with numerous cases at the end of 2019 in Wuhan, China exhibiting serious respiratory dysfunctions. It was initially identified for infections, and was supposed to be a seasonal flu outbreak by considering those patients who have background of work in wholesale market of shrimp and fish. A few days back, after the rejection of Seasonal grippe infection, avian influenza, adenovirus, SARS, and other pathogens. This novel coronavirus shows 5% genetic correlation with SARS and is a subclass of Sarbecovirus [2]. Since SARS-CoV is zoonotic in origin, this has resulted in the tentative mass culling of the masked palm civets. However, further studies later revealed that no widespread infections were found in wild or farmed civets and clinical symptoms of SARS were only overt in the municipalities sold on the markets, suggesting that civets were unlikely to have been the primary/natural reservoir host [3,4]. Now, the virus has been narrowly called SARS-CoV-2, the name was designated by the World Health Organization (WHO) [5].
With the help of several samples, phylogenetic and sequencing analysis were done which reports that it belongs to coronavirus family (Orthocoronavirinae subfamily) [6] in Betacoronavirus-2B lineage and shows 96% identity with the bat SARS-CoV (Bat Cov RaTG13) [7]. The virus, use its S1 and S2 subunits of hetero-trimeric spike proteins to interact with the human cell receptor, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) [8], to infect a host cell. SARS-CoV-2 infect lungs (Figure 1) by causingangiocentric inflammation, thrombosis and micro-angiopathy, and angiogenesis [9].
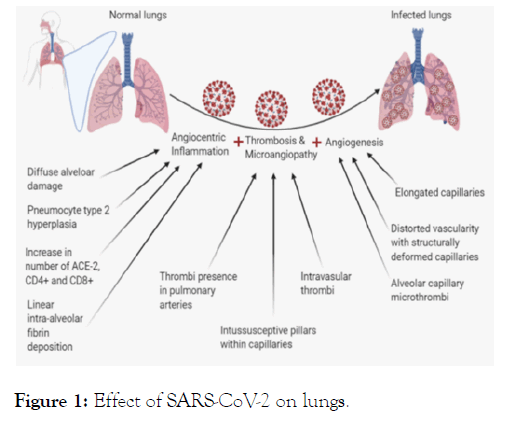
Figure 1: Effect of SARS-CoV-2 on lungs.
This pandemic influenced all the clinicians and researchers worldwide to gather from various branches of biomedicines for seeking a plan or therapy/vaccine to handle the pandemic [10]. Most of the current preclinical and clinical data on antiviral therapy are available from other viruses, including SARS-CoV-1 (first reported in 2003), Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), (recorded for the first time in 2012) and non-coronavirus (example- outbreak of the Ebola virus). It is not obvious about how efficiently these details can be extrapolated to SARS-CoV-2. In fact, scientific importance of in vitro antiviral behavior defined as semi-maximal Efficacy Concentration [EC50] values appears undefined, given in the absence of pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics or surgical evidence. This equalizes the workable concentrations compared to these levels to an effect of treatment [11]. Diagnosis is also challenging as a number of studies from Singapore [12] and Germany [13], inferred about the asymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by viral shedding.
From various published literatures one can infer that the Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are active against viral infection and these are attributable in the involvement of specific cytokines improved the efficiency [14]. Therefore, MSCs should be presumed to thrive even though they are transplanted to a patient reported for COVID-19. As, there is a discrepancy in the MSCs therapy for the diagnosis of COVID-19, we have integrated the clinical literature and trials to convey valuable knowledge in the review. The review provides a deep insight of the role of MSCs in the disease and representation of action of MSCs in SARS-CoV-2 life cycle illustrated in (Figure 2). It is necessary to alert readers that new data appears approximately every hour considering the Medical conditions, care, options to prevent and outcomes of COVID-19.
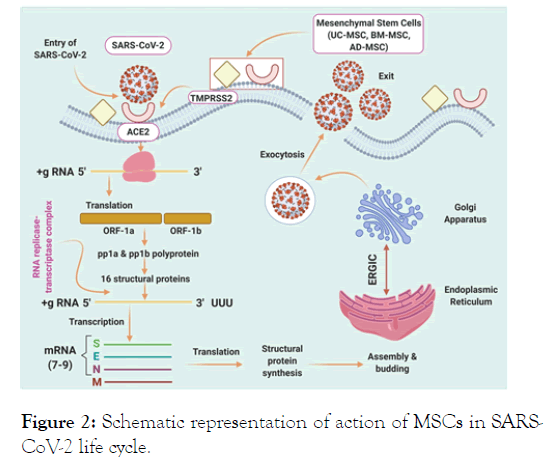
Figure 2: Schematic representation of action of MSCs in SARSCoV- 2 life cycle.
Morphology of SARS-COV-2
SARS-CoV-2 is a spherical or pleomorphic enveloped particles with club-shaped glycoprotein projections [15]. SARS-CoV-2 was assessed for its size ranging between 70-90 nm, observed under electron microscope which also suggested its wide variety of intracellular organelles [16]. As it shows high sequence similarity with SARS-CoV, the structure of SARS-CoV-2 is speculated to be the same as SARS-CoV [17]. It is found that the envelope, membrane, and spike protein of coronavirus are embedded in host membrane derived lipid bilayer which encapsulates the helical nucleocapsid comprising viral RNA [18] illustrated in (Figure 3). The single stranded RNA is approximately 30 kb long having positive polarity with 5’ cap and 3’ Poly-A tail [19]. Almost all structures of protease [20] and spike [21] of SARSCoV- 2 have been resolved which leads an opportunity to develop or repurpose the drugs for treating COVID-19.
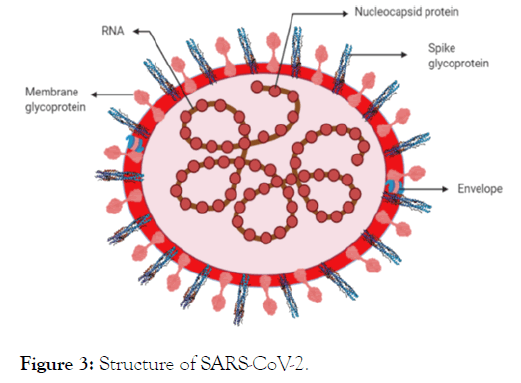
Figure 3: Structure of SARS-CoV-2.
Therapeutic intervention of COVID-19
As per 31 August, 2020; neither any drugs nor any biologics is/are established to be efficient for the prevention/treatment of COVID-19 infection. Many antivirals, parasitic drug combinations, immunotherapies, and vaccines are under trials and their efficacy against COVID-19 is still dilemmatic. The only mode of treatment, widely in use for COVID-19 is repurposing of drugs [22]. Drugs like Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine [23], Mefloquine [24], certain flavonoid compounds [25], Lopinavir [26], Remdesivir [27], Quercetin [28] and other reported drugs are currently in use to treat COVID-19 patients.
Mesenchymal stem cells therapy
Amidst the COVID-19 rush for various drugs like Hydroxychloroquine and Remdesivir etc. and various vaccines, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have recently approved the use of MSCs for coronavirus treatment under the discretion of expanded accesses. At present, cell-based therapy and stem cell therapy in particular has been a remarkable medical domain in which potential to cure incurable diseases is foreseen [29]. MSCs have drawn interests owing to the possible source, high rate of proliferation, minimal intrusive treatment and clear of ethical problems. MSC rehabilitation is significantly better as applied to other therapies [30]. They are widely available and can be isolated from different tissues, such as bone marrow and adipose tissues, including the umbilical cord, dental pulp, menstrual blood, buccal fat pad, fetal liver and others. MSCs can expand efficiently to clinical volume in adequate time period and for repeated diagnostic utilization it can be processed. Moreover, MSC therapy have the potential to prevent the storm of cytokines and can advance the endogenous repair by its regenerative and reparative property [31,32] illustrated in (Figure 4). MSCs therapy has been commonly employed in the diagnosis and treatment of type 2 diabetes, autoimmune disorder, spinal cord damage, GVHD and many other disorders, with strong antibody levels [33-36]. Although MSCs do not have clear anti-viral effects, studies have shown that they are immune to viral interaction by the presence of Interferon Gamma Stimulated Genes (ISGs) found in them prior to differentiation. MSCs frequently control our body's adaptive and innate immune systems by destroying T-cells, maturing dendritic cells, decreasing activation and proliferation of B-cells, and hindering NK cell proliferation and cytotoxicity by soluble factors or cellto- cell pathways (Figure 3) [31,32]. Recently, [37] the use of these cells in the therapeutic diagnosis of H5N1 viral infections with related consequences on the lung has also been proposed [38]. Thus their role in regulating immune malfunctioning is widely reported and can be extrapolated as an eminent tool for COVID-19 research and treatment.
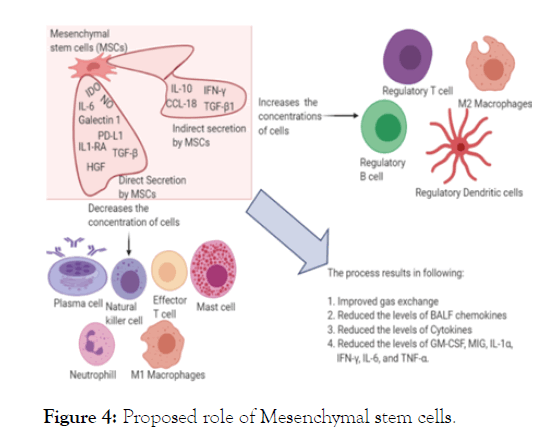
Figure 4: Proposed role of Mesenchymal stem cells.
MSCs related clinical trials for COVID-19
There are total 3201 clinical studies registered on ClinicalTrials.gov [39] for treating COIVD-19 out of which only 54 studies are related with MSCs. All 54 clinical studies’ title and their status are tabulated in Table 1. In the related trials, one study is withdrawn and fourteen studies are not recruited yet. However, one study has been completed in china by using umbilical cord derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) but there results are not posted yet.
| Sl.No. | Trial no | Title of the study | Place | Intervention | Status | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NCT04339660 | Clinical research of human mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia. | China | Biological: UC-MSCs Other: Placebo |
Recruiting | I and II |
| 2 | NCT04428801 | Autologous Adipose-derived Stem Cells (Ad-MSCs) for COVID-19. | - | Biological: Autologous adipose derived stem cells | Not yet recruiting | II |
| 3 | NCT04252118 | Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) treatment for pneumonia patients infected with COVID-19. | China | Biological: MSCs | Recruiting | I |
| 4 | NCT04361942 | Treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (COVID-MSC). | Spain | Biological: Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Other: Placebo |
Recruiting | II |
| 5 | NCT04398303 | ACT-20 in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. | - | Biological: ACT-20-MSC Biological: ACT-20-CM Biological: Placebo |
Not yet recruiting | I and II |
| 6 | NCT04444271 | Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) infusion for COVID-19 infection. | Pakistan | Drug: Mesenchymal stem cells Other: Placebo |
Recruiting | II |
| 7 | NCT04362189 | Efficacy and safety study of allogeneic HB-adMSCs for the treatment of COVID-19. | United States | Drug: HB-adMSC Drug: Placebo |
Active, not recruiting | - |
| 8 | NCT04429763 | Safety and efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in the management of severe COVID-19 pneumonia. | - | Biological: Umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells Biological: Placebo |
Not yet recruiting | II |
| 9 | NCT04467047 | Safety and feasibility of allogeneic MSC in the treatment of COVID-19. | - | Biological: Mesenchymal Stromal Cells infusion Intravenous 1*10E6 MSCs/kg body weight Mesenchymal Stromal Cells infusion | Not yet recruiting | - |
| 10 | NCT04336254 | Safety and efficacy study of allogeneic human dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells to treat severe COVID-19 patients. | China | Biological: Allogeneic human dental pulp stem cells (BSH, BTC & tooth BTC) Other: Intravenous saline injection (Placebo) |
Recruiting | I and II |
| 11 | NCT04313322 | Treatment of COVID-19 patients using Wharton’s jelly-mesenchymal stem cells. | Jordan | Biological: WJ-MSCs | Recruiting | I |
| 12 | NCT04348435 | A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial to determine the safety and efficacy of Hope Biosciences Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy (HB-adMSCs) to provide protection against COVID-19. | United States | Drug: HB-adMSCs Drug: Placebos |
Enrolling by invitation | - |
| 13 | NCT04461925 | Treatment of coronavirus COVID-19 pneumonia (pathogen SARS-CoV-2) with cryopreserved allogeneic P-MMSCs and UC-MMSCs. | Ukraine | Procedure: Placenta derived MMSCs; cryopreserved placenta derived multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells Drug: Antibiotics Drug: Hormones (and 2 more) |
Recruiting | - |
| 14 | NCT04315987 | NestaCell® Mesenchymal Stem Cell to treat patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. | Brazil | Biological: NestaCell® Biological: Placebo |
Not yet recruiting | II |
| 15 | NCT04273646 | Study of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of severe COVID-19. | China | Biological: UC-MSCs Drug: Placebo |
Not yet recruiting | - |
| 16 | NCT04346368 | Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment for severe patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). | China | Biological: BM-MSCs Biological: Placebo |
Not yet recruiting | - |
| 17 | NCT04366830 | Intermediate size Expanded Access Program (EAP), Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSC) for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) due to COVID-19 infection. | United states | Drug: Remestemcel-L | No longer available | - |
| 18 | NCT04288102 | Treatment with human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). | China | Biological: UC-MSCs Biological: Saline containing 1% human serum albumin (solution without UC-MSCs) |
Completed | II |
| 19 | NCT04456439 | Intermediate size Expanded Access Program (EAP), Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSC) for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) associated with coronavirus disease (COVID-19). | - | Biological: Remestemcel-L Drug: Hydrocortisone |
Available | - |
| 20 | NCT04293692 | Therapy for pneumonia patients infected by 2019 novel coronavirus. | - | Biological: UC-MSCs Other: Placebo |
Withdrawn | - |
| 21 | NCT04349631 | A clinical trial to determine the safety and efficacy of Hope Biosciences Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy (HB-adMSCs) to provide protection against COVID-19. | United States | Drug: HB-adMSCs | Enrolling by invitation | II |
| 22 | NCT04416139 | Mesenchymal Stem Cell for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) due for COVID-19. | Mexico | Biological: Infusion IV of Mesenchymal Stem cells | Recruiting | II |
| 23 | NCT04400032 | Cellular immuno-therapy for COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)-Vanguard. | Canada | Biological: Mesenchymal Stromal Cells | Not yet recruiting | I |
| 24 | NCT04366271 | Clinical trial of allogeneic mesenchymal cells from umbilical cord tissue in patients with COVID-19. | Spain | Biological: Mesenchymal cells Drug: Standard of care |
Recruiting | II |
| 25 | NCT04397796 | Study of the safety of therapeutic Tx with immunomodulatory MSC in adults with COVID-19 infection requiring mechanical ventilation. | United States | Biological: BM-Allo MSC Biological: Placebo |
Recruiting | I |
| 26 | NCT04377334 | Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in inflammation-resolution programs of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (IARDS). | Germany | Procedure: Biological samples specific to research Procedure: Clinical examination Procedure: Telephone follow-up |
Recruiting | II |
| 27 | NCT04352803 | Adipose mesenchymal cells for abatement of SARS-CoV-2 respiratory compromise in COVID-19 disease. | - | Biological: Autologous Adipose MSCs | Not yet recruiting | I |
| 28 | NCT04525378 | MSC based therapy in COVID-19 associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). | Brazil | Other: Mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapy | Recruiting | I |
| 29 | NCT04390139 | Efficacy and safety evaluation of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of patients with respiratory distress due to COVID-19. | Spain | Drug: XCEL-UMC-BETA Other: Placebo |
Recruiting | I and II |
| 30 | NCT04456361 | Use of mesenchymal stem cells in acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by COVID-19. | Mexico | Biological: Mesenchymal Stem Cells derived from Wharton jelly of umbilical cords | Active, not recruiting | Early I |
| 31 | NCT04452097 | Use of hUC-MSC product (BX-U001) for the treatment of COVID-19 with ARDS. | - | Biological: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells + best supportive care | Not yet recruiting | I |
| 32 | NCT04355728 | Use of UC-MSCs for COVID-19 patients. | United States | Biological: umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells + heparin along with best supportive care Other: Vehicle + heparin along with best supportive care |
Active, not recruiting | I and II |
| 33 | NCT04490486 | Umbilical Cord Tissue (UCT) Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) versus placebo to treat acute pulmonary inflammation due to COVID-19. | United States | Biological: UCMSCs Other: Placebo |
Not yet recruiting | I |
| 34 | NCT04345601 | Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 induced acute respiratory failure (COVID-19 disease). | United States | Biological: Mesenchymal stromal cells Other: Supportive care |
Not yet recruiting | Early I |
| 35 | NCT04366323 | Clinical trial, multicenter, randomized and controlled, to assess the safety and efficacy of intravenous administration of allogeneic adult mesenchymal stem cells of expanded adipose tissue in patients with severe pneumonia due to COVID-19. | Spain | Drug: Allogeneic and expanded adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells | Recruiting | I and II |
| 36 | NCT04457609 | Administration of allogenic UC-MSCs as adjuvant therapy for critically-ill COVID-19 patients. | Indonesia | Drug: Oseltamivir Drug: Azithromycin Biological: Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells |
Recruiting | I |
| 37 | NCT04399889 | hCT-MSCs for COVID19 ARDS. | United States | Biological: Human cord tissue mesenchymal stromal cells | Recruiting | I and II |
| 38 | NCT04348461 | Battle against COVID-19 using Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs). | - | Drug: Allogeneic and expanded adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stromal cells | Not yet recruiting | II |
| 39 | NCT04366063 | Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome in coronavirus infection: a phase 2-3 clinical trial. | Iran | Biological: Cell therapy protocol 1 Biological: Cell therapy protocol 2 |
Recruiting | II and III |
| 40 | NCT04466098 | Multiple dosing of mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with ARDS (COVID-19). | United States | Biological: Mesenchymal stromal cells Other: Placebo |
Recruiting | II |
| 41 | NCT04371393 | MSCs in COVID-19 ARDS. | United States | Biological: Remestemcel-L Drug: Placebo |
Recruiting | III |
| 42 | NCT04302519 | Novel coronavirus induced severe pneumonia treated by dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells. | - | Biological: Dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells | Not yet Recruiting | Early I |
| 43 | NCT04371601 | Safety and effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of pneumonia of coronavirus disease 2019. | China | Drug: Oseltamivir Drug: Hormones Device: Oxygen therapy Procedure: Mesenchymal stem cells |
Active, Not Recruiting | Early I |
| 44 | NCT04522986 | An exploratory study of adr-001 in patients with severe pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. | Japan | Biological: Mesenchymal stem cell | Not yet recruiting | I |
| 45 | NCT04382547 | Treatment of Covid-19 associated pneumonia with allogenic pooled olfactory mucosa-derived mesenchymal stem cells. | Belarus | Biological: Allogenic pooled olfactory mucosa derived mesenchymal stem cells Other: Standard treatment according to the Clinical protocols |
Enrolling by invitation | I and II |
| 46 | NCT04333368 | Cell therapy using umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in SARS-CoV-2-related ARDS. | France | Biological: Umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived human Other: NaCl 0.9% |
Recruiting | I and II |
| 47 | NCT03042143 | Repair of acute respiratory distress syndrome by stromal cell administration (REALIST) (COVID-19). | United Kingdom | Biological: Human umbilical cord derived CD362 enriched MSCs Biological: Placebo (Plasma-Lyte 148) |
Recruiting | I and II |
| 48 | NCT04392778 | Clinical use of stem cells for the treatment of Covid-19. | Turkey | Biological: MSC treatment Biological: Saline control |
Recruiting | I and II |
| 49 | NCT04397471 | A study to collect bone marrow for process development and production of BM-MSC to treat severe COVID-19 pneumonitis. | United Kingdom | Procedure: Bone marrow harvest healthy volunteer bone marrow harvest | Not yet recruiting | - |
| 50 | NCT04269525 | Umbilical Cord (UC) derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) treatment for the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (nCOV) pneumonia. | China | Biological: UC-MSCs | Recruiting | II |
| 51 | NCT04390152 | Safety and efficacy of intravenous Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells in acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19. | Colombia | Drug: Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells. Drug: Hydroxychloroquine, Lopinavir/Ritonavir or Azithromycin and Placebo (standard therapy) |
Not yet recruiting | I and II |
| 52 | NCT04445454 | Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for severe Covid-19 infection. | Belgium | Biological: Mesenchymal stromal cells | Recruiting | I and II |
| 53 | NCT04447833 | Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome. | Sweden | Drug: Mesenchymal stromal stem cells - KI-MSC-PL-205 | Recruiting | I |
| 54 | NCT04276987 | A pilot clinical study on inhalation of mesenchymal stem cells exosomes treating severe novel coronavirus pneumonia. | - | Biological: MSCs-derived exosomes | Not yet recruiting | I |
Table 1: MSCs based clinical trials for treating COVID-19.
Being free from vital ethical concerns with low risk of teratoma formation, MSCs gains the status of most commonly used stem cells in cell therapy. Moreover, their regenerative capacity immunomodulatory effect, anti-inflammatory effect as well as handling the cytokines storm have made MSCs a potent candidate for preclinical and human clinical trials for viral treatment. However, certain limitations resides in MSC-based therapies should never be neglected. The heterogeneity nature of MSCs might bring the inconsistency in research results. With recent literature it is found that MSCs may not be immunologically silent as assumed previously [40].
To overcome the residing limitations, use of cell-free therapeutic strategies such as MSC-exosomes should be focused more. There are limited clinical trials and study of MSCs on virus-associated diseases and in the case of SARS CoV-2 these investigations are still not completed. Hence, the efficacy and potency of MSCs the treatment of COVID-19 cannot be concluded at this time. This review highlighted the MSCs therapy application and clinical trials for COVID-19.
Citation: Varshney H, Srivastava R, Swati K, Sharma A, Jha SK, Kumar D, et al. (2021) Mesenchymal Stem Cell: Therapeutic Intervention in Covid-19. Intern Med. 11:329.
Received: 17-Dec-2020 Accepted: 31-Dec-2020 Published: 07-Jan-2021 , DOI: 10.35248/2165-8048.21.11.329
Copyright: © 2021 Varshney H, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.