
Journal of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Open Access
ISSN: 2736-6588

ISSN: 2736-6588
Research Article - (2021)Volume 4, Issue 8
Soluble polymer supported bisheterocycles has been synthesized using a convergent synthesis under microwave assisted synthesis. All sequential steps carried out 7-(1H-Benzoimmidazol-2-yl)10H benzo-4,5-imidazo-1,2-a 1,3,5- triazine-2,4-dione monitored by the spectroscopic analytical data reported. 4-fluro-3-nitrobenzoicacid with various amines nucleophilic substitutions subsequent reduction followed by the acid functional repeated unit of 4 fluro-3- nitro benzoicacid heterocyclization lead to the bisheterocyclic scaffold further sequential transformation of nucleophilic substitution with fluoro functional group with various amines followed by reduction of nitro to the amine; to the terminal diamine using cyanobromide leaves bisbenzimidazole with an amine; all steps carried out sing the polymerethleneglycol as support under microwave irradiations all steps compared and analytical spectroscopic data produced. Further under basic conditions bisheteroamine under microwave reaction condition with cloroacetylesters and chloroacetylisocyanates reacts to diamines of benzimidazole with 7-(1H-Benzoimmidazol-2- yl)10H benzo-4,5-imidazo-1,2-a 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-dione. Further under KCN methanol polymer support leaves to molecular scaffolds. A microwave-promoted three-component one pot reaction has been developed to provide access the core 7 (1H Benzoimmidazol-2-yl) 10H benzo-4,5-imidazo-1,2a-1,3,5 triazine-2,4-dione scaffold, which is common to several families of alkaloids with significant biological activities.
Microwave; Bisbenzimidazole; Chloroacetylesters; Chloroacetylisocyanate; Cyanobromide; 7-(1HBenzoimmidazol- 2-yl)-10H benzo-4,5-imidazo-1,2-a 1,3,5 triazine-2,4-dione
Microwave-assisted organic synthesis has impacted synthetic chemistry significantly since the introduction of precisioncontrolled microwave reactors (Figure 1) [1].
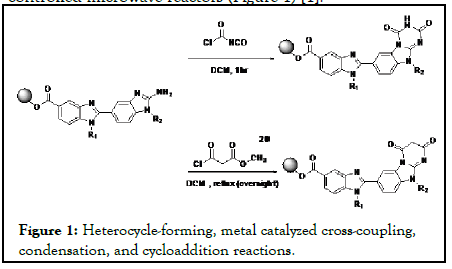
Figure 1:Heterocycle-forming, metal catalyzed cross-coupling, condensation, and cycloaddition reactions.
Numerous reactions including heterocycle-forming, metal catalyzed cross-coupling, condensation, and cycloaddition reactions have been explored under microwave conditions [2]. In addition, microwave-heating technology has been applied in the total syntheses of natural products [3]. Imidazolin-4-ones (1) constitute an important class of pharmacologically active compounds. The present invention relates to therapeutic compounds and methods of use of these therapeutic compounds for treating cellular proliferative disorders. The invention also provides three-dimensional structures of a Polo-like kinase and methods for designing or selecting small molecular inhibitors using these structures, and the therapeutic use of such compounds. The invention also includes a method for identifying phosphopeptide-binding domains by screening peptide libraries. The carboxy-terminal region of the cell cycle regulating kinase Plk-1 encodes a phosphopeptide recognition domain that consists of the non-kinase region of the protein (Figure 2) [4-6].
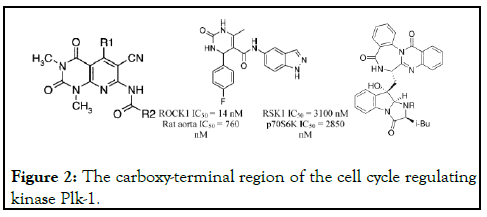
Figure 2:The carboxy-terminal region of the cell cycle regulating kinase Plk-1.
High-content screening has emerged as a new and powerful technique for identifying small molecule modulators of mammalian cell biology. The authors describe the development and execution of a high-content screen to identify small molecules that induce mitotic arrest in mammalian cancer cells. In this context it should be emphasized that not all micro-waveassisted reactions proceed to completion within five or ten minutes. In the case of the Liebeskind–Srogl coupling for example, a reaction time of one hour at 130°C was required to achieve full conversion and high isolated product yields [7].
The synthesis of a library of thirty compounds using automated sequential processing therefore needed 30 h of processing time. While automated sequential microwave synthesis has been a very successful concept for the construction of small compound libraries, this method may become impractical if one considers the generation of larger compound collections since the timesaving aspect of high-speed microwave synthesis is diminished by having to irradiate each reaction mixture individually.
In case of the Liebes-kindSrogl reaction, the same dihydropyrimidine library could also be synthesized in a parallel microwave fashion producing similar individual product yields in one single irradiation experiment employing a larger microwave reactor in combination with a multi vessel rotor system.
Parallel microwave synthesis under controlled conditions can be carried out in a variety of formats, including the use of microtiter plates allowing the simultaneous processing of 200 or more individual microwave reactions [8].
While short reaction times are generally considered as a valuablebut not essential-feature in organic chemistry, they are an indispensable requirement for the synthesis of short-lived radio labelled (for example F) substances used in the field of Positron Emission Tomography (PET).Several research groups have exploited high-speed microwave chemistry for the synthesis of a variety of different radiotracer materials (Figure 3) [9].
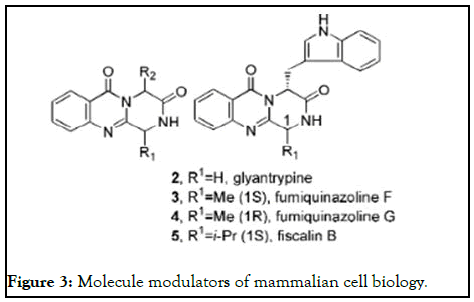
Figure 3: Molecule modulators of mammalian cell biology.
A cycloaddition is a synthetic response, wherein "at least two unsaturated particles (or portions of a similar atom) join with the development of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net decrease of the bond multiplicity." The subsequent response is a cyclization response. Numerous yet not all cycloadditions are coordinated and subsequently pericyclic. Nonconcerted cycloadditions are not pericyclic. As a class of addition response, cycloadditions license carbon–carbon bond arrangement without the use of a nucleophile or electrophile. A heterocyclic compound is a cyclic compound that has carbon and undoubtedly another component as a feature of its ring structure. Their overall construction takes after cyclic natural mixtures that contain rings of just carbon. In any case, the presence of heteroatoms like nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur gives heterocyclic mixtures particular physical and chemical properties. One of the earliest named responses in this classification was found in 1882 by A. Hantzsch who consolidated two counterparts of ethyl acetoacetate with one of acetaldehyde and alkali to acquire a completely substituted symmetrical dihydropyridine. A cross-coupling response in organic chemistry is a response where two sections are consolidated with the guide of a metal catalyst. In one significant response type, a fundamental group organometallic compound of the sort R-M (R=natural part, M=primary gathering place) responds with a natural halide of the kind R'-X with development of another carbon–carbon security in the item R-R'. Cross-coupling reaction is a subset of coupling responses. It is generally expected to be used in arylations. Catalyst is regularly founded on palladium, which is every now and again chosen because of high practical group resilience. Organopalladium compounds are for the most part stable towards water and air. Palladium catalysts can be tricky for the pharmaceutical industry, which faces broad guideline in regards to heavy metals. Numerous chemists endeavor to utilize coupling responses right off the bat underway to limit metal follows in the item. Heterogeneous catalysts dependent on Pd are additionally evolved. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a practical imaging strategy that utilizes radioactive substances known as radiotracers to picture and gauge changes in metabolic cycles, and in other physiological exercises including blood stream, provincial compound creation, and ingestion. Various tracers are utilized for different imaging purposes, contingent upon the objective cycle inside the body. For instance, 18F-FDG is generally used to identify disease, NaF-F18 is broadly utilized for distinguishing bone arrangement, and oxygen-15 is now and then used to gauge blood stream. PET is a typical imaging procedure, a clinical scintillography strategy utilized in atomic medication. A radiopharmaceutical, a radioisotope joined to a drug is infused into the body as a tracer. Gamma beams are produced and identified by gamma cameras to frame a threedimensional picture, likewise that a X-beam picture is caught. PET scanners can join a CT scanner and are known as PET-CT scanners. PET sweep pictures can be recreated utilizing a CT check performed utilizing one scanner during a similar meeting. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a useful imaging procedure that utilizes radioactive substances known as radiotracers to picture and quantify changes in metabolic cycles, and in other physiological exercises including blood stream, territorial compound arrangement, and assimilation. Various tracers are utilized for different imaging purposes, contingent upon the objective interaction inside the body. For instance, 18F-FDG is normally used to identify disease, NaF-F18 is generally utilized for distinguishing bone arrangement, and oxygen-15 is in some cases used to gauge blood stream. PET is a typical imaging procedure, a clinical scintillography strategy utilized in atomic medication. A radiopharmaceutical a radioisotope joined to a drug is infused into the body as a tracer. Gamma beams are produced and identified by gamma cameras to frame a three-dimensional picture, along these lines that a Xbeam picture is caught. PET scanners can join a CT scanner and are known as PET-CT scanners. PET scan images can be reproduced utilizing a CT filter performed utilizing one scanner during a similar session.
Polyethylene glycol using as support to the 4-floro-3- nitrobenzoicacid starting material to the synthesis of bisbenzimidazole analogues; the coupling with the support done using DCC/DMAP under dichloromethane for about 20 minute reaction under microwave reaction condition under appropriate 120°C temperature. Later on removed DCU precipitate out in diethyl ether [10-13]. To the extent starting material various amines are used nucleophilic substitutions on aromatic benzene ring under microwave reaction condition for about 20 minute 150°C; later on washed and precipitated in diethyl ether. Further nitro functional group reduced to the amine under Zn/NH4 COOH, methanol at room temperature reaction condition. Further the reaction mixture precipitated from diethyl ether. To the reaction mixture the repeating unit for the bis benzimidazol 4-floro-3- nitrobenzoicacid under DCC/DMAP under microwave irradiation for about 20 minutes of reaction temperature 120° C to be form amide bond precipitated from the diethyl ether. Further the reaction mixture using the dichloromethane for about 150°C using dehydrating agents MgSO4 reaction mixture concentrate to washed from the diethyl ether, all the steps monitored by the spectroscopy to confirm the reaction steps to proceed. Further the reactions as we did above the nucleophilic substitution followed by the reduction of the fluoro and nitro functional groups under the microwave irradiation and said reaction temperatures as mentioned above, the amines includes aromatic, aliphatic, cyclic, acyclic, leaving the peg supported diamine bisbenzmidazol scaffold. Further the reaction mixture of diamine with the cyanobromide for about an one day room temperature reaction temperature to be convert the amine function to the peg supported bisbenzimidazole; the heterocyclisation includes the leaving the HBr byproduct and to the protonation to the main subsequent cyclization lead to the free amine of bisheterocycle as an starting material to the further fictionalization (Figure 4) [14-15].
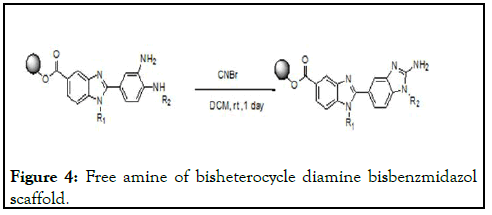
Figure 4:Free amine of bisheterocycle diamine bisbenzmidazol scaffold.
To the polymer supported bisbenzimidazoleamine using a DBU/Et3Nbasic reaction conditions chloroacetylisocyanate for about a 20 minute reaction condition triazinedione heterocyclisation through the amine condensation observed [16]. The reaction mechanism involves ring amine attacked to the electrophilic carbonyl acid chloride forms the amide further ring emine olefinic bond attacks to the isocyanate carbonyl electrophilic center to form the amide bond leaving the heterocyclisation triazinedione. The same reaction done in microwave for about 20 minutes; the same reaction has done using the acetylchloroester under same reaction conditions for the increase in the diversity in the bis ring scaffold (Figure 5) [17].
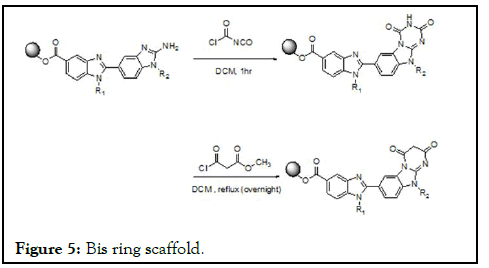
Figure 5: Bis ring scaffold.
Reaction mixture further precipitated from the diethyl ether, all the reaction steps monitored under the spectroscopic studies reported. The entire supported scaffold detached from the support under KCN, methanol to obtain the final compounds to the analytical data (Figure 6).
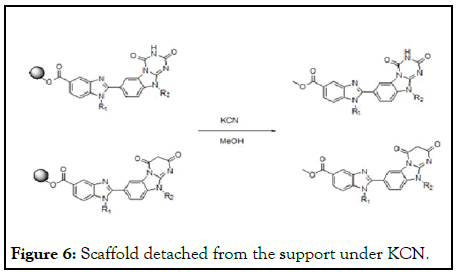
Figure 6: Scaffold detached from the support under KCN.
In this article, we have described the creation of a wellcharacterized and lead-like small molecule library as well as a cell-based high-content assay to identify compounds that induce mitotic arrest. The high-content assay uses a straightforward and inexpensive DNA stain and a new data processing method, which simplifies data analysis, produces a single scaled measurement per well, and is generally applicable to other highcontent assays. The efficient and regioselective construction of 7- (1H-Benzoimmidazol-2-yl)-10H benzo-4,5-imidazo-1,2-a 1,3,5- triazine-2,4 dione and related ring-structures has been shown to be successful even for synthesis of highly poly-functional. Plants and other natural resources used as traditional medicines have been widely explored in drug discovery. Bioassay directed isolation followed by identification and characterization of bioactive compounds leads a development for new medicinal drugs. Triazine-2,4 dione are one of attractive natural products leading to many drug developments. During the improvement stage of such lead compounds, rational drug design-based modification affords synthetic analogues with increased activity, decreased toxicity, or improved pharmacological availability as exemplified by suggestion of a good candidate as a new antimalarial drug from antimalarial triazine-2,4-dione. From this point of view, simple and convenient method for selective synthesis of compounds such as annelation combined with microwave-assisted synthesis and use of polymer-reagents would be in demand continuously as one of the indispensable strategies for development of new drugs.
Citation: Sun CM, Thummanagoti S (2021) Microwave Assisted Soluble Polymer Supported Synthesis of 7-(1H-Benzoimmidazol-2-yl)-10Hbenzo- 4,5 imidazo-1,2-a 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-dione. J Clin Chem Lab Med 4:191.
Received: 04-Oct-2021 Accepted: 18-Oct-2021 Published: 25-Oct-2021 , DOI: 10.35248/jcclm.21.4.191
Copyright: © 2021 Sun CM, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.