Internal Medicine
Open Access
ISSN: 2165-8048
ISSN: 2165-8048
Research Article - (2021)Volume 11, Issue 6
Background and Aims: The 2019 novel COVID-19 arose in Wuhan, China, and was portrayed as a pandemic by the World Health Organization. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is chronic conditions with devastating multi-systemic complication and may be associated with severe form of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). We conducted a study in order to investigate the association between DM and poor outcome in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and its impact on mortality.
Methods: In this study, 198 patients were enrolled keeping in view a predetermined inclusion criterion. Their clinical and laboratory characteristics such as age and gender demographics, medical history, clinical tests and x-rays were observed and recorded. The diagnosis for diabetes and severity of COVID 19 was established e by examining the medical history and according to NIH guidelines. The results were produced by doing statistical analysis through SPSS Software.
Results: There are several investigations which showed diabetic patients susceptibility towards coronavirus. A China study showed significant number of diabetic patients in hospitals, having prevalence of 7%-20%. A case study of 70,000 individuals infected with virus, a Chinese CDC reported more death about 7.3% in diabetic patients than general population (2.3%). A study showed prevalence of comorbidities in corona infected patients. Epidemiology study of Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention investigated 20,982 patients of COVID-19 showing hypertension, diabetes and CVD were associated 13%, 5% and 4% of patients. In other Italian study found diabetes in about 36%, whereas CVD was associated with 43% of 355 patients infected with COVID-19. During a survey in Lahore which included about 400 participants concluded that the lockdown had negative impact on people. Another study in Lahore stated that along with other tissues effecting in disease it also caused oral cavity infection or effected its cells and tissues causing plague, susceptibility to infection, delayed healness etc. and also showing adverse correlation with periodontal as it negatively relates with diabetes.
Conclusion: There is association between Covid-19 and Diabetes Mellitus as patients who have diabetes are more prone to Covid-19.
Covid-19; Diabetes mellitus; CVD; CDC; WHO
The COVID-19 flare-up was treated as an instance of pneumonia with obscure etiology showed up in the Wuhan city of China, toward the completion of December 2019, which spread the nation over to worldwide with a high rate [1,2]. A flare-up of a baffling pneumonia portrayed by fever, dry hack, and lethargy, and periodic gastrointestinal indications occurred in a fish discount fresh food market, the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, in Wuhan, Hubei, China [3]. The underlying episode was accounted for in the market in December 2019 and included about 66% of the staff there. The market was closed down on January 1, 2020, after the declaration of an epidemiologic caution by the neighborhood wellbeing expert on December 31, 2019 [4,5].
The COVID-19 is one of the significant infections that focus on the respiratory system of the human [6].
The Chinese analysts named the infection as 2019-nCoV [7]. Afterward, the International Committee on Taxonomy of Virus named the novel COVID as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) [8].
Around the same time, February 11, 2020 the World Health Organization (WHO) name the Pneumonia as Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) [2,9].
The COVID-19 idea the third flare-up of the COVID which influenced in excess of 209 nations including Pakistan. As per the World Health Organization (WHO), complete of 226 844 344 affirmed cases with 4 666 334 mortalities.
Until now, the quantity of most elevated positive cases experienced in USA followed by Italy and Spain World health organization (WHO).
The line nations of Pakistan exceptionally influenced including China, where the COVID-19 episode experienced first time. In the west, Italy with largest number of COVID-19 mortalities whiles in the north, Iran countless mortalities after the Italy [10]. In Pakistan, the main instance of COVID-19 has been affirmed by the Ministry of Health, legislature of Pakistan on February 26, 2020 in Karachi, Sindh territory.
Around the same time one more case affirmed by the Pakistan Federal Ministry of Health in Islamabad [11]. Inside fifteen days, the quantity of complete affirmed cases (COVID-19 Positive) came to twenty out of 471 speculated cases with largest numbers in the Sindh area followed by the Gilgit Baltistan.
The entirety of the affirmed cases had ongoing travel history from Iran, Syria and London. Furthermore, presently these cases increment by high rate and the circumstance is most noticeably terrible COVID-19 live dashboard (Pakistan): National institute of health Islamabad.
As per the Ministry of Health, legislature of Pakistan, there are absolute of 1,221,261 affirmed positive cases in the country with 27,135 mortalities on Saturday, Sep 18, 2020.
The most noteworthy cases showed up in the Sindh region (449,349) trailed by Punjab region (420,615), Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (170,738), Balochistan (32,722), Gilgit baltistan (10,232) and Azad Jammu and Kashmir have 33,682 affirmed cases. Until this point in time, the largest number of mortalities happened in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa with 5,374, trailed by Punjab (12,365), Sindh (7,243), Gilgit Baltistan (182), Balochistan (344).
An aggregate of 412,544 contaminated individuals have been recuperated in Sindh region, trailed by KP (158,240), Balochistan (32,071), and Punjab (385,108) GB (9,827) and AJK have 31,783 recuperation till date as summed up in Table 1.
| S.No | Province | Confirmed cases | Mortalities | Recovered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sindh | 4,49,349 | 7,243 | 4,12,544 |
| 2 | Punjab | 4,20,615 | 12,365 | 3,85,108 |
| 3 | Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | 1,70,738 | 5,374 | 1,58,240 |
| 4 | Federal (ICT) | 1,03,923 | 899 | 99,989 |
| 5 | Gilgit Baltistan | 10,232 | 182 | 9,827 |
| 6 | Balochistan | 32,722 | 344 | 32,071 |
| 7 | Azad Jammu and Kashmir | 33,682 | 728 | 31,783 |
Table 1: The current figures of COVID-19 flare-up in Pakistan.
The death rate in Pakistan is 2.2% and recuperation rate is 92.5%. The Ministry of National Health Services. Regulation and coordination.
In unindustrialized nation like Pakistan, infection flare-ups significantly challenge the medical services framework. Absence of fundamental wellbeing offices, lacking wellbeing arrangements, frail administration, and an uninterested mentality of the general population towards general defensive measures further demolish the situation [12].
The quantity of emergency clinics and isolate offices being not satisfied as required. In the event that these clinical offices improved, then, at that point it won't be hard to control the transmission of infections and treatment of patients. As of now the testing offices are a lot of lower than the necessary objective. The testing offices could increment by five to ten (5 to 10) folds. The right advances ought to be taken to control the circumstance all the more most noticeably awful for example, remaining at homes, lockdown, social removing, utilizing sanitizers, and face veil when vital. Pakistan needs more evaluating offices for the appearances just as for the takeoffs. It is trusted that Pakistan will surpass the COVID-19 [2]. The urgent illustration to gain from battles is that our haggard and decrepit medical care framework is a limited source. The study of disease transmission and microbial science come up short on the precision of physical science. Thus, our specialists can give just approximates and guidance on administration decisions. Despite the fact that Pakistan has restricted sources, it can utilize them. It needs to show a restrained, clear, substantial, quick, complete, objective, and aggregate reaction. This can be accomplished by testing a huge extent of people and afterward separating those cases after sure test aftereffects of COVID-19, presenting PPE, building medical care limit, and taking regulatory measures to guarantee better security is given to medical services experts. Likewise, to give assets to medical services staff in the most ideal manner assists them with battling this pandemic. Fixing essential and optional medical services frameworks is likewise required, as they will ease the heat off the tertiary medical services frameworks. In the event that significant issues in the administration framework are fixed, a significant effect can be made [12,13].
Diabetes mellitus is taken from the Greek word diabetes, which means siphon-to go through and the Latin word mellitus meaning sweet. An audit of the set of experiences shows that the expression "diabetes" was first utilized by Apollonius of Memphis around 250 BC to 300 BC. Old Greek, Indian, and Egyptian civilizations found the sweet idea of pee in this condition, and henceforth the spread of the word Diabetes Mellitus appeared. Mering and Minkowski, in 1889, found the job of the pancreas in the pathogenesis of diabetes. In 1922 Banting, Best, and Collip filtered the chemical insulin from the pancreas of cows at the University of Toronto, prompting the accessibility of a successful treatment for diabetes in 1922. Throughout the long term, outstanding work has occurred, and various disclosures, just as the board procedures, have been made to handle this developing issue. Shockingly, even today, diabetes is one of the most widely recognized constant sicknesses in the nation and around the world. In the US, it stays as the seventh driving reason for death [14].
Diabetes mellitus has become one the most squeezing and common issue over the most recent couple of many years, with the rising obesity emergency, and is currently the seventh driving reason for death in the USA just as around the world, with 5.2 million demises internationally ascribed to diabetes, a death pace of 82.4 per 100,000, with 252,806 demises in the USA alone in 2015 [15]. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a metabolic illness, including improperly raised blood glucose levels. DM has a few classifications, including type 1, type 2, development beginning diabetes of the youthful (MODY), gestational diabetes, neonatal diabetes, and auxiliary causes due to endocrinopathies, steroid use, and so forth The fundamental subtypes of DM are Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), which traditionally result from inadequate insulin discharge (T1DM) as well as activity (T2DM). T1DM presents in youngsters or teenagers, while T2DM is thought to influence moderately aged and more established grown-ups who have drawn out hyperglycemia because of helpless way of life and dietary decisions. The pathogenesis for T1DM and T2DM is radically unique, and in this way each type has different etiologies, introductions, and medicines [16].
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is one of the most pervasive ongoing conditions with crushing multi-fundamental difficulty and was assessed to have caused 463 million individuals in 2019 [16]. It isn't yet realized whether individuals with DM are more helpless to COVID-19, yet a few investigations have announced the relationship between extreme COVID-19 disease with DM [17,18]. Diabetes may work with disease by COVID-19 because of expanded viral section into cell and hindered safe reaction [19]. It was proposed that the angiotensin changing over protein 2 (ACE2) might be the conceivable clarification of this affiliation in Figure 1 [20,21].
DM was related with mortality, serious COVID-19, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), and infection advancement in patients with COVID-19 [22]. Diabetes in patients with COVID-19 is associated with a two-fold increase in mortality as well as severity of COVID-19, as compared to nondiabetics [23]. In this study, we meant to play out an efficient survey and meta-examination to explore the relationship among DM and helpless result in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Our theory is that DM is related with helpless result in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. To the best of the creators’ information, this is the primary precise survey, metaexamination, and meta-relapse that completely depict the relationship among DM and result in COVID-19.
Study Design, Criteria and Participants.
Methods
The study was a retrospective, single center study. The study participants were 198 laboratory confirmed cases of COVID-19 according to guidelines issued by the National Health Committee of the People’s Republic of China [23].
The study’s inclusion criteria contained the following points:
• All of the participants should be over 18 years of age
• The diagnosis should be made by PCR test
Exclusion criteria contained the following points:
• Type 1 diabetes
• Lost clinical history of participants
• Missing laboratory data of the participants
• Secondary Diabetes Mellitus
Five patients out of the 198 patients were excluded keeping in view the exclusion criteria. Eventually 193 patients were included who provided complete medical records and they were monitored for a specific follow up period. All of the patients were community dwelling and gave explicit consent for participation.
Data collection
The clinical and laboratory data and was observed and collected. Clinical data included age demographics, gender, medical history (cardiovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, liver disease, diabetes and associated comorbidities, symptoms (diarrhea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, cough, fever and headache). Laboratory tests (CBC, Liver function, random and fasting blood glucose, renal function, thyroid, inflammatory markers, troponin, lipid, CRP, IL-2, IL-10, TNF TNFα and Ferritin). Chest X-rays were also obtained and observed. The treatment provided the number of days that the participants stayed in hospital from diagnosis to hospital admission, duration of stay in ICU and ultimate outcome were monitored and noted down.
Criteria for diagnosis
Diabetes was defined as documented history of diabetes and use of antidiabetic drugs. Recently diagnosed diabetes in the participants was based on monitored levels of random blood glucose, fasting blood glucose and any signs of hyperglycemia [24].
Diagnosis of the disease was made when patients were admitted to hospital. The gravity of the disease was determined according to established guidelines by NIH (“Clinical Spectrum”, 2021).
Severe cases of COVID-19 were considered as having one of the following characteristics
• Respiratory rate which is higher than 30/min.
• Oxygen saturation observed to be less than 93%
• The development of shock, respiratory failure resulting in mechanical ventilation and admission to ICU due to organ failure.
The characteristics of moderate cases were defined as follows
• Patients suffering from fever and respiratory symptoms
• Patients having telltale chest findings of COVID-19 from CT Scan (i.e. Ground
The characteristics of mild cases were defined as follows
• Patients having mild symptoms of the disease
• Patients having no chest findings of COVID-19 from CT scan.
Data analysis
The data analysis for the present study was performed by using SPSS software. The demographic factors such as age, gender etc. were presented as percentages while the normal variables were presented as mean ± Standard Deviation (SD) and non-normal variables were presented as mean ± Standard Error Mean (SEM).
Chi square test was performed to observe difference in the categorical variables. Mann Whitney test was done to observe the difference between Diabetes Mellitus status and gender for normally and non normally distributed data respectively. The chi square test and Mann Whitney test were also done in order to determine the differences according to the gravity of the disease and the outcome (release from hospital or death) with adjusted p-values. The treatment and outcomes for all of the participants and significant predicting factors for each outcome were charted out with the help of MS Excel. Cox Regression analysis was used to determine Hazard Ratios (HR). The value taken for Confidence Intervals (CI) was 95%. All comorbidities were included including gender and age demographics as well as Body Mass Index. It was done in order to establish important preexisting conditions that could lead to outcomes of interest. All of the other parameters (medicines and laboratory tests) were age, sex and BMI adjusted. The survival curve for Diabetes Mellitus was plotted using Kaplan Meier statistical analysis. The significance value was set at p<0.05 [25].
There are several investigations which showed diabetic patients susceptibility towards coronavirus. A China study showed significant number of diabetic patients in hospitals, having prevalence of 7%-20%. Same was reported in Italy which had 8% prevalence of patients having diabetics. These patients showed risk towards cardiovascular disease and less fever as compare to others. They need high care unit Corona virus has 80% similarity with SARS-2 and 50% with MERS [26]. Its entry in cell is complex process which involves receptors and proteolytic process for fusion in Figure 1. There is potential mechanism which increases the risk of COVID-19 in diabetic patients including high affinity for binding and entry of virus, low viral clearance, no T cell functionality, having cardio vascular disease, susceptibility to cytokine and hyperinflammmation [27]. A case study of 70,000 individuals infected with virus, a Chinese CDC reported more death about 7.3% in diabetic patients than general population (2.3%). A study showed prevalence of comorbidities in corona infected patients. Other study showing prevalence of diabetics among severe and non-severe patients and among survivors and non survivors. Apart from ACE 2 other cellular proteins involved in entry of virus in cell [28].
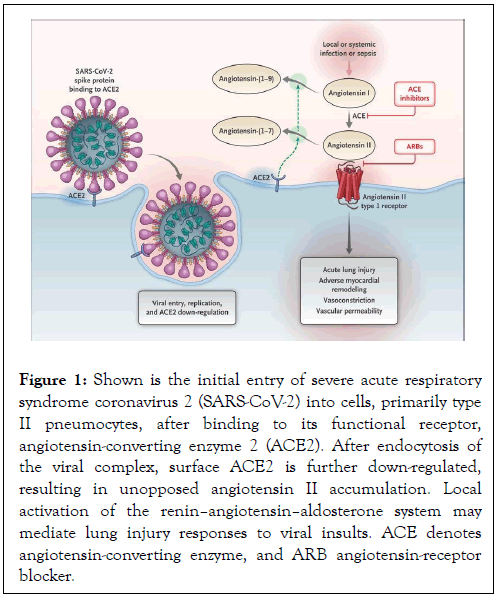
Figure 1: Shown is the initial entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) into cells, primarily type II pneumocytes, after binding to its functional receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). After endocytosis of the viral complex, surface ACE2 is further down-regulated, resulting in unopposed angiotensin II accumulation. Local activation of the reninâ??angiotensinâ??aldosterone system may mediate lung injury responses to viral insults. ACE denotes angiotensin-converting enzyme, and ARB angiotensin-receptor blocker.
Epidemiology study of Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention investigated 20,982 patients of COVID-19 showing hypertension, diabetes and CVD were associated 13%, 5% and 4% of patients. In other Italian study found diabetes in about 36%, whereas CVD was associated with 43% of 355 patients infected with COVID-19. Diabetes is the independent factor.
Contributing to infection and other past viral infections studies also showed this like it tripled risk of hospitalization in 2009 influenza outbreak. During 2012 MERS outbreak diabetics showed 50% prevalence to infection [19].
A study conducted at Karachi where men and women from different categories were taken and analysis by Psychometric scale was done on them which states that mostly suffered depression at mild and moderate level. For this many demographic characteristics were studied and survey was also done and which stated that diabetic patients and females had significant association with fear of corona [29]. There are several studies which showed critical association between COVID-19 and diabetic patients, states that diabetic patients are more prone to virus as it activates stress levels in patients and causes mortality. ‘An unholy situation’ as called by Pal and Bhadada, it nearly causes about millions of persons at risk to cause disease. Not only in Pakistan but also in England, USA, Gubbi and Muniyappa reported these associations and their increasing ratios [30]. Effect of remdesivir was also studied on both diabetic and non-diabetic patients in Pakistan and result analysis showed that non-diabetic patients showed recovery faster as compare to diabetic patients and it does not had any complications with disease. Clinical range of corona virus is wide so care must be taken while treating patients to avoid any risk [31].
In blink of eye as Corona virus spreaded no one had expected, many studies had been conducted till now and had shown mortality rate higher in diabetic patients as it seems to be associated with hyperglycemia as it leads to increased viral infection. Diabetes mostly come in co-existence with hypertension and it shown that higher expression of ACE2 encourages the infection and put patient at risk. But difference reported between females and males and type 1 and type 2 DM is still unclear but there comes some biological factors which must be considered like age, sex and immunity. So patients like them needed to be monitored and extra care management. Other factors which accelerated this disease are lockdown, bound to stay at home, social distancing and canceling of routine checkups of diabetic patients which worsen the situation. So these patients needed to be hydrated, monitor their glucose level regularly and temperature [32].
During a survey in Lahore which included about 400 participants concluded that the lockdown had negative impact on people especially with chronic illness on their mental and physical health their ratio increased because no attention was given to them and lacking medical help when needed. There were trust issues regarding medical measures and health centers [33]. Another study in Lahore stated that along with other tissues effecting in disease it also caused oral cavity infection or effected its cells and tissues causing plague, susceptibility to infection, delayed healness etc. and also showing adverse correlation with periodontal as it negatively relates with diabetes. But by oral hygiene, brushing and visiting dentist can result in positive. This can only be done if someone believed in dental care and considered it as issue. Results showed that only 35% were awared about oral and diabetes complications. Many believed in self-made remedies and about 7% denied the association and 57% were unknown [33]. There were many problems regarding type 1 DM and COVID like insecurities about food, difficulty in accessing supplies, reduction in income, anxiety, useful information, reduction in funds and government support and no or interrupted shipments of insulin [34].
As there is need to confirm preventive measures so study was designed to check the effect of Knowledge, Attitude, Preventive Practices (KAP) on diabetic patients in which mostly were men of about above 40 age. Analysis showed that about 33% had good knowledge and 79% concerning attitude believed that diabetes had association with hypertension and only 44% had practiced good preventive measures and people who didn’t had knowledge were poor in showing preventive measures compared to had knowledge [35]. Diabetes is considered as disturbance in homeostasis of glucose likely in case of COVID-19 but it needed systemic analysis, a study in UK analyzed that there was poor glucose control in patients as indicated by HbA1 and caused more deaths in hospitals than those who had low level of HbA1 and risk is 10% higher. But in Coronado study no such association was observed in 7 days but average value of HbA1 was higher however association was found between plasma glucose concentrations and primary outcomes and indicated that hyperglycemia is good predictor of worst radio imaging of chest. About 11% of patients in Coronado show prevalence and death occurred in about 40% in uncontrolled patients with diabetes.
Type 1 diabetic patients who had fasted in Ramadan were questioned they were from different countries and mostly on therapy and study showed very little difference in their characteristics among those who fast and not patients were aged below and above 18 [36].
People with diabetes are more vulnerable to COVID-19 and are at greater risk due to mortality and this vulnerability may be due to old age, hyperglycemia, hypertension or obesity. So physician need to take more care regarding their health. It is the greatest challenge to them to control glucose level and to handle medical complications occurs during disease.
As study was done on people who fasted during Ramadan with diabetes Type 1 as during this month people changes their lifestyle which may have effected them. But with diabetes patients it is not easy as glycemic control disrupts and may cause hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia however some studies reported negligible incidence of hypoglycemia during this month. It showed better management of diabetes as compare to later years. Some having poor knowledge about COVID-19 and its association with this disease and by following poor preventive practices this may prevails much faster so need here is that there should be seminars or other ways to provide information about COVID-19 and its associate factors, how to prevent ourselves from this and how to make people aware. Many agencies are working on its awareness and its care regarding shortage of insulin shots, other supplies etc. Government should also give funds to them. This can also be done if someone runs social media page and give more awareness, arranges emergency funds and providing health care viable information following international guidelines.
Pakistani psychometric tests showed good properties as compare to others, valid for assessing outcomes most probably fear in COVID-19 and it showed that females are more fear than males and smokers. It shows correlation between age and anxiety towards COVID-19 and effects people Physiological conditions and aggregates depression and more causes fear which can automatically effects health. People needed to do routine checkups to avoid serious complication as seen in China. Many countries are facing this deadly virus and are highly effected economically like under developed countries where rate of disease is already high. Some called it an unholy shit because not only diabetes but also cardiovascular disease patients are also more vulnerable to this virus.
To conclude that if came to therapeutic then one study showed remdesivir have effects on diabetic and non-diabetic patients but delayed result in diabetic patients regarding recovery. But it should be noticed that concentration of people should be drawn towards this so that care can be taken at that point and to increase knowledge regarding metabolic factors which can be serious and cause complications. To end this topmost goal should be vaccination especially diabetic patients and regular monitoring is mandatory.
Many studies are done so far prospective and research based some lack evidences regarding recovery but almost all stated complications regarding already patient of diabetes or cardiovascular and its increasing risk towards COVID-19. So more research is needed to understand the mechanism of virus contributing to glycemic control and in some cases development of new disease and hyperglycemic and hyperosmolar syndrome.
Citation: Riaz S (2021) Molecular Association between COVID-19 and Diabetes Mellitus and its Impact on Mortality in Pakistan. Intern Med. 11:352.
Received: 02-Nov-2021 Accepted: 16-Nov-2021 Published: 23-Nov-2021
Copyright: © 2021 Riaz S. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.