Journal of Hotel and Business Management
Open Access
ISSN: 2169-0286
+44 1478 350008
ISSN: 2169-0286
+44 1478 350008
Short Communication - (2024)Volume 13, Issue 4
This study proposes an innovative methodology for forecasting hotel occupancy rates in the United States of America, drawing connections between solar activity cycles, geomagnetic disturbances and fluctuations in the hospitality industry. While traditional analyses primarily focus on economic indicators, this research explores the hypothesis that solar-induced geomagnetic activity may significantly influence human behavior and decision making processes related to travel and accommodation choices.
Hotel occupancy rate; Solar activity; Geomagnetic activity; Hospitality industry; Economic cycles; Socionomic theory
The hospitality industry, is an important component of the USA economy, experiences periodic fluctuations in occupancy rates. Conventional explanations for these variations typically involve economic cycles, technological advancements, changing travel trends, global events and demographic shifts.
However, this study posits that these observable trends may be underpinned by a more fundamental driver: The cyclical nature of solar activity.
Theoretical framework
Solar activity follows a well-documented 11-year cycle, characterized by variations in solar radiation, sunspot activity and the frequency and intensity of solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
These phenomena induce geomagnetic disturbances on Earth, which have been associated with various physiological and psychological effects in humans, including individual behavioral ones as those that may lead to homicides and collective behavioral ones, as in those that lead to recessions [1-4].
The central hypothesis of this study is that geomagnetic disturbances, stemming from solar activity, may trigger subtle yet measurable changes in human moods and behaviors. These changes could influence individuals’ propensity for leisure activities, including travel, thereby affecting hotel occupancy rates on a broad scale (Figure 1).
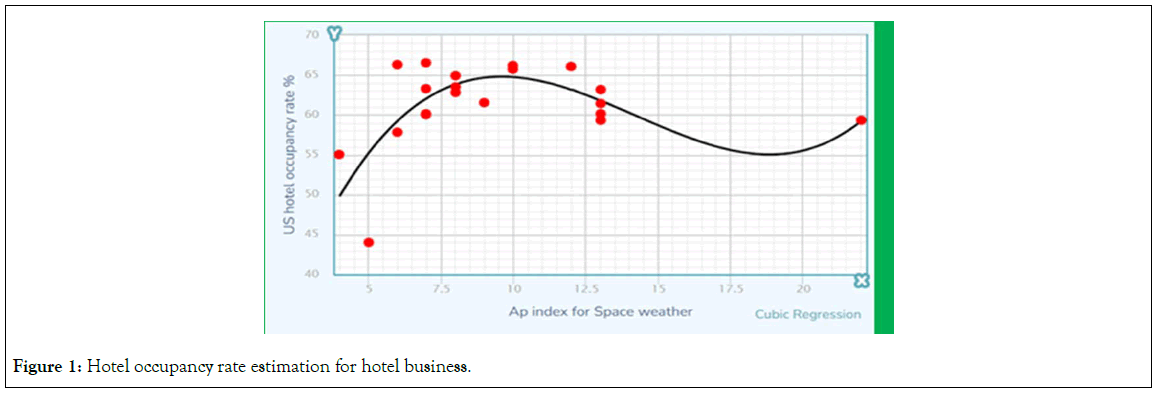
Figure 1: Hotel occupancy rate estimation for hotel business.
This study employs a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative analysis of historical solar activity data, geomagnetic disturbance records and hotel occupancy rates over a two-decade period. Additionally, a qualitative review of existing literature on the physiological and psychological effects of geomagnetic activity provides context for the potential mechanisms of influence.
The research also draws upon socionomic theory as a potential explanatory framework for how individual responses to geomagnetic disturbances might manifest as collective behavioral trends. However, socionomics is not central to the argument but rather serves as one possible mechanism through which solar-induced geomagnetic effects might propagate through populations.
The potential predictive power of this model represents its most compelling aspect. If a robust correlation can be established between solar activity cycles, geomagnetic disturbances and hotel occupancy rates, it could provide a novel tool for long-term forecasting in the hospitality industry and revolutionize long-term strategic planning for hotels, resorts and travel-related businesses. The relatively predictable nature of solar cycles could enable projections of occupancy trends far in advance of traditional economic indicators (Video 1).
This study presents a novel approach to understanding and potentially predicting hotel occupancy rates by considering the influence of cosmic phenomena on human behavior and economic trends. While acknowledging the need for rigorous empirical validation, this research underscores the importance of exploring unconventional perspectives in an increasingly complex and interconnected world. It invites further investigation into the possibility that the keys to understanding and predicting economic trends may lie not just in traditional economic indicators, but also in the broader cosmic environment in which human activity takes place.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Citation: Behrens A, Beltrão KI, D’Almeida AL (2024). Solar Activity as a Potential Predictor of Hotel Occupancy Rates: A Novel Interdisciplinary Approach. J Hotel Bus Manag.13:096.
Received: 08-Jul-2024, Manuscript No. JHBM-24-32765; Editor assigned: 10-Jul-2024, Pre QC No. JHBM-24-32765 (PQ); Reviewed: 23-Jul-2024, QC No. JHBM-24-32765; Revised: 30-Jul-2024, Manuscript No. JHBM-24-32765 (R); Published: 05-Aug-2024 , DOI: 10.35248/2169-0286.24.13.096
Copyright: © 2024 Behrens A, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.