Journal of Hematology & Thromboembolic Diseases
Open Access
ISSN: 2329-8790
ISSN: 2329-8790
Original Research Article - (2023)Volume 11, Issue 2
The biochemical model explains the intricate mechanisms of psychobiological life. We still cannot explain what the transition from inanimate to living matter is all about. Where is the threshold and what is its essence, what role do biochemical processes play in the coherence of the soma with consciousness and its impact on the soma and vice versa? A similar problem is with other mental processes, their nature does not fit into the biochemical model of life and is inexplicable on the basis of biochemical interactions, and again it is much easier to describe it in the light of quantum processes-including wave physics. It is similar with the functioning of the heart or other organs, where only the biochemical processes of the cell are considered, ignoring the bioelectronic processes. Man is not only a purely biological construct, but also contains the basis of biochemical, bioelectronic, information and cybernetic processes that are responsible for shaping the psychobiological processes of man. Contemporary biosystems in science are considered at the level of corpuscular structures, ignoring energy and information structures. By shifting the cognitive emphasis towards energy and information structures, the organism can be perceived as a quantum generator of information: Electromagnetic, soliton, acoustic, spin and bioplasma. This bioelectronic construction creates homo electronicus with his electronic personality.
Bioelectronic processes; Transformation; Spin; Soliton wave; Free radical; Heart pulse
The work of the heart in the human body is performed on the basis of a flooding pump, which is designed to maintain proper blood circulation. This organ consists of ventricles and atria, to which blood is supplied through the vena cava and pulmonary veins. The contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles is called the action of the heart, or the action of the heart, which causes blood circulation in this organ and throughout the body. Cardiac activity begins already in the embryonic period, in the 5-6th week of pregnancy [1].
The main control of the heart resides with the medulla oblongata. There is an area called the cardio acceleratory center, or presser center, in the upper part of the medulla oblongata, and an area called the cardio inhibitory center, or depressor center, in the lower part. Together they are called the cardio regulatory center, since they interact to control heart rate, etc. [2].
An electrical conduction system regulates the pumping of the heart and timing of contraction of various chambers. Heart muscle contracts in response to the electrical stimulus and receives system generated electrical impulses and conducts them throughout the muscle of the heart, stimulating the heart to contract and pump blood. Among the major elements in the cardiac conduction system are the sinus node, atrioventricular node, and the autonomic nervous system [3].
Heart conduction system
The Figure 1 explains sinus node is the heart's natural pacemaker [4]. The sinus node is a cluster of cells situated in the upper part of the wall of the right atrium. The electrical impulses are generated there (The sinus node is also called the senatorial node). The electrical signal generated by the sinus node moves from cell to cell down through the heart until it reaches the atrioventricular node (the AV node), a cluster of cells situated in the center of the heart between the atria and ventricles. The AV node serves as a gate that slows the electrical current before the signal is permitted to pass down through to the ventricles. This delay ensures that the atria have a chance to fully contract before the ventricles are stimulated. After passing the AV node, the electrical current travels to the ventricles along special fibers embedded in the walls of the lower part of the heart. The autonomic nervous system (the same part of the nervous system as controls the blood pressure) controls the firing of the sinus node to trigger the start of the cardiac cycle. The autonomic nervous system can transmit a message quickly to the sinus node so it in turn can increase the heart rate to twice normal within only 3 to 5 seconds. This quick response is important during exercise when the heart has to increase its beating speed to keep up with the body's increased demand for oxygen [4].
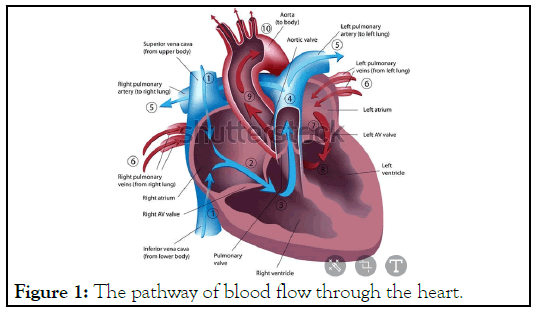
Figure 1: The pathway of blood flow through the heart.
Heart rate and the causes of its malfunction
The pulse is the undulating movement of the arteries that results from the contractions of the heart and the elasticity of the arterial walls [6]. The ejection of blood from the heart into the main artery causes an increase in pressure and this is a shock wave. The heart rate, allows you to assess the state of functioning of the circulatory system, shows us how quickly the heart pumps blood to all organs of the body. It depends mainly on two factors-the heartbeat, which pumps blood to the arteries, and the condition of the blood vessels that we are examining. The pulse should be consistent with the heartbeat, symmetrical and regular. A normal adult heart rate is about 60 to 90 beats per minute at rest. A heart rate above 100 beats per minute is called tachycardia, or tachycardia. A pulse below 60 is bradycardia. Both of these results are worrying and require consultation with a specialist doctor [1].
Important characteristics of the heart rate
Pulse frequency: Means the number of beats of the pulse wave per minute. The pulse rate depends on many factors related to both physiology and abnormal processes in the body.
Regularity of the pulse: Means the regularity of the beats of the pulse wave. The intervals between successive strokes should be the same, and their strength should be similar. Irregular heart rate occurs, for example, during tachycardia.
Pulse filling: Means filling the artery with blood and is related to the pulse amplitude (difference between systolic and diastolic pressure). We distinguish here high pulse, low pulse, thread pulse and bizarre pulse.
Pulse voltage: Indicates the amount of arterial pressure. We distinguish hard pulse (clear), soft pulse (weak) and double beat pulse (two waves during one contraction).
Pulse rate: Means the rate at which the vessel fills with blood and collapses during one heart cycle. We distinguish between fast and lazy pulses, pulse height.
Pulse symmetry: Means that the pulse wave is symmetrical in all limbs. It is a simple way for the initial diagnosis of many diseases, such as atherosclerosis or arterial congestion [5].
The effects of an abnormal pulse depending on its type
A small and lazy pulse occurs with aortic stenosis of the heart. A rapid or low pulse indicates shock, dehydration, and fever.
Hypokinetic heart rate: This heart rate tells you that the heart is incapable of pumping blood because it is inefficient, or the blood vessels are damaged by disease, they put up a lot of resistance and it is difficult to pump blood into them.
Fast and high pulse: Indicates "intensive" blood flow, it happens during fever or during intense physical exertion, but also in heart defects, i.e. aortic regurgitation and patent duct of Botalli (congenital heart disease).
Hyperkinetic pulse: This is a strongly palpable pulse that occurs in aortic regurgitation, patent duct of Botalli (congenital heart disease).
Double pulse: When we feel two pulse waves during one heartbeat. This is the case in some complex heart defects, mainly involving the heart valves.
A dicrotic pulse is when the doctor feels a pulse wave under his fingers while hearing the heart contract, and then feels a second wave as the heart begins to relax. These are usually alarming symptoms in severe heart failure and shock. A bizarre pulse is diagnosed if there are palpable changes in the pulse rate during breathing during inspiration the pulse filling decreases significantly or even disappears.
Alternating pulse: It consists in the fact that pulse waves with large and small amplitude are felt alternately, i.e. more and less perceptible. This is how the heart rate is described in left ventricular failure.
Twin pulse: Each normal heart beat is accompanied by an additional, extra, and thus second pulse wave. Such a pulse occurs in some cardiac arrhythmias.
A pulse deficit is a situation when more heartbeats are registered per minute than are sensed by counting the pulses in the peripheral arteries. This means that not every heartbeat generates a pulse wave. This happens, for example, during rapid atrial fibrillation [6]. If differences in pulse amplitude on symmetrical arteries. When the doctor senses the pulse differently on the corresponding arteries on the right side than on the left side such a symptom indicates changes in a given artery or vessels on the side on which a given artery branches off. The most common cause is atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels [7].
In his medical achievements, Józef Struś distinguishes simple and complex pulses. In the range of simple pulses, the following are the basis for the division: The amount of diastole, the quality of movement, the length of time at rest, the quality of strength and the quality of the artery. Due to the size of the diastole, there are high, medium and low pulses, depending on the quality of movement: Fast, medium, slow; due to the length of the pause: Frequent, medium, rare; due to the quality of strength: Violent, medium, frail; due to arterial quality: Soft, medium, hard. Compound pulses are composed of simple pulses. The ratio between the pulses depends on the order and ataxia, i.e. disturbance of order-rhythm, equality and inequality. Rhythm is the relationship between diastolic and systolic movement qualities. Quality, on the other hand, is speed, slowness and what is intermediate between the two [8].
An abnormal heart rate is associated with heart problems or abnormalities in the arteries. In healthy people, the heart rate follows the heartbeat, is symmetrical and regular [9]. The center that generates the heart rhythm is not working properly electrical signals are not produced often enough
The electrical signal is slowed down or blocked as it travels through the heart these are called conduction disorders [10]. The causes of too slow heart rate and too slow pulse can also be:
• Medicines, especially those used to treat high blood pressure.
• Some infections
• Sleep apnea
• Anorexia
Pulse disorders can have a very diverse background, which is why further more detailed diagnostics are necessary [10].
Bioelectronics interpretation of the work of the heart
In the process of functioning, the heart contracts and then relaxes. When the heart contracts, it pumps (or ejects) blood from the lower chambers and when the heart relaxes, the ventricles fill with blood [11].
The left ventricle is the main chamber that pumps blood from the heart and the doctors usually measures the left ventricular ejection fraction. This is called the left ventricular ejection fraction, or LVEF. The LVEF for a healthy heart is between 55% and 70%. LVEF may be lower if the heart muscle has been damaged as a result of a heart attack, heart failure, or other heart disease.
The author of this paper is of the opinion that water and acoustic solitons are generated during the ejection fraction of blood in the heart. A soliton is a solitary wave of unchanging shape, located in time and space. There are solitons of light, water and sound that can strongly interact with other solitons, but after a collision they remain unchanged, only a phase shift occurs. Form and structure remain unchanged. This means that they penetrate each other without losing their identity [12-13] (Figure 2 and 3).
Figure 2: Image of a soliton for an acoustic wave.
Figure 3: Image of a soliton for a water wave.
Solitons can spread across the universe and do not disappear. They exist from the beginning of life until the present. The cosmos is densely filled with a solitonic network, carrying content and meaning [14].
Solitons are responsible for the proper functioning of a biological cell. The human biological system has the ability to generate and receive soliton fields, which take an active part in the processes of human life and determine their health, illness and personality development. The movement of solitons is affected by the density and thickness of the biological membrane in the cell, as it determines the size of the piezoelectric, pyroelectric and feroelectric effect from which the electric field flows, interacting with the solitons [15,16].
Solitons bring signals, meanings, conceptual content from the cosmos to the human psychosphere. It happens in such a way that the DNA molecules of the genetic material emit laser light, which creates the Bose-Einstein condensate needed to generate solitons. Laser radiation also activates ion pumps on cell membranes and helix bioplasmic antennas that pull solitons from outer space to the inside of the cell, and simultaneously to the bioplasma of the biological system [17,18].
One of the nucleobases, thymine, is ferroelectric and therefore piezoelectric and pyroelectric [19].
The authors of these studies present the thesis that ferroelectricity of thymine can find wide possibilities in creating new bases that are currently unknown and at the same time reconstructing the bases present in the DNA of the genetic chain. This opens a new way to use thymine in the treatment of infectious diseases. All this will be done on a piezoelectric and ferroelectric basis, in which the electric field will play an important role [20].
In the DNA molecule, thymine is connected to adenine through two hydrogen bonds, thus stabilizing the composition of the nucleic acid and taking part in pairing and replication. The most important feature of ferroelectrics is polarization, i.e. connecting thymine to adenine through the electric field of direct current and the work of solitons [8].
Ferroelectrics are bodies in which a spontaneous polarization appears in a certain temperature range in the absence of an external electric field. The direction of spontaneous polarization can be changed by the action of an external electric field and by external pressure. Ferroelectrics undergo deformation under the influence of an external electric field, which is proportional to the square of the field strength. This phenomenon is called electrostriction, which generates an acoustic wave. All ferroelectrics except electrostriction exhibit the piezoelectric effect [21].
In pyroelectrics, spontaneous polarization exists over the entire temperature range, up to the melting point. Ferroelectrics are a special case of pyroelectrics, in which spontaneous polarization also occurs, but only in a certain temperature range [22].
Researchers from the University of Washington investigated the ferroelectric properties of the protein tropoelastin [4].
Elastin, as a key protein found in connective tissues, is an important structural component of the lungs, heart and arteries, is ferroelectric has important physiological functions in vascular morphogenesis [8,17], homeostasis and in the regulation of cell functions [23].
It provides the necessary elasticity and elasticity to the aorta, lungs, ligaments and skin subjected to repeated mechanical and physiological loads [3,24].
The ferroelectric polarization of elastin affects the proliferation and organization of smooth muscles, vessels and contributes to arterial morphogenesis [6,25].
Piezoelectricity and pyroelectricity are a constant feature of a biological system, through them we can influence biological structures - DNA and RNA, which will allow us to control the functioning of a biological cell [26].
Solitons require the presence of the physical environment as an information carrier, therefore they cannot propagate in a vacuum, which is not required by other elementary particles [15,27].
The electric field in the human biological system is the carrier of solitons, which contain the primary information called "ingeneza". Ingeneza programs are quantized and create all stages of development, cell, organism, biosphere and cosmos. Water molecules are also carriers of this information (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Ingeneza controls snowflake development and honeycomb construction.
Ingeneza designs the shape of a snowflake, but also the structure of honeycombs. The bee will always produce the same comb pattern. Solitons are also responsible for supplying the human body with nutrients needed for life, such as vitamins, minerals, elements, fatty acids and amino acids. They regulate blood pH, osmotic pressure, and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood [28,30,31].
The heart is a key organ of our body, also in the context of the use of quantum techniques. According to Ampere's law, when an electric current flows through a conductor, it creates a magnetic field. The magnetic field lines form concentric circles around the conductor. The human body is also an amazing conductor. For its functioning, it uses the phenomenon of bioelectric streams through which cells communicate. This is how a biomagnetic field is created [32] (Figure 5).
Figure 5: The Electromagnetic field of the heart.
The movements of electrical charges in the heart create an electromagnetic field that can also be measured at a considerable distance from the body. Scientists from the Heart Math Institute (USA) consider the heart to be an extremely powerful source of electromagnetic energy in the body, creating a regular electromagnetic field [15]. The heart is the human body's most powerful electromagnetic energy generator, producing the largest rhythmic electromagnetic field of anybody organ. The electromagnetic field of the heart has amplitude 60 times greater than the electrical activity of the brain. In addition, the magnetic field generated by the heart is more than 5,000 times stronger than the magnetic field of the brain and can be detected many meters above the body and is empirically measurable [33].
It turns out that about 60% of heart cells are neurons that process information. Researchers at the Heart Math Institute believe that communication between the heart and the brain takes place through four channels:
• Neurological communication, the vagus nerve.
• Biophysical communication, through pressure and pulse.
• Biochemical communication, through hormones, energy (information) communication, through the electromagnetic field of the heart [34].
Solitons transmit information through vibrations in biological systems, as is the case with nerve impulses. The variety of soliton densities is endless. Solitons show incredible resistance to distortion and interference noise [35,36].
Soliton can generate an electromagnetic wave or absorb it, which results in the creation of a continuous conducting center and transferring information over a distance [37].
The author is of the opinion that for the proper functioning of psychobiological processes taking place in the human biological system, not only electric and electromagnetic fields, acoustic waves and bio plasmas are needed, but also soliton and spin waves. In biological systems, the spin wave is most often the result of the functioning of free radicals. Free radicals are atoms that have no pair. Oxygen atoms in our body should have an even number of electrons. Sometimes it happens that during the transformation of oxygen in mitochondrial processes an electron is lost. The oxygen atom loses its original equilibrium and begins to search for the missing electron in the immediate vicinity, taking electrons from other oxygen atoms. In this way, further incomplete oxygen atoms are formed-free radicals. The long-term process of electron transposition leads to the destruction of the protein structure, i.e. damage to cell membranes or DNA structures, which has a negative effect on our health [38].
The very harmful free radicals include; hydroxyl radical, nitric oxide superoxide and hydroxide. They can activate various types of molecules that appear during metabolic processes or physicochemical processes. In the classical approach, spins take a swirling motion, both to the right and to the left, which triggers a spin field that plays a key role in the functioning of the cells of the human biological system [39].
If the magnetic field strengthens or extends its influence, magnetic soliton vortices are formed, which negatively affect the functioning of the biological cell and the course of the pulse in the biological system. The heart rate is controlled by solitons, the functioning of solitons is conditioned by electric and magnetic fields. Most free radicals negatively affect the process of functioning of biological cells. There are free radicals that have a positive effect on the body, such as the melanin radical. Melanin has the ability to turn a photon into a phonon and vice versa. This is an important phenomenon in the process of functioning of solitons. When a strong magnetic field starts to spin the soliton, which is on the back of the electromagnetic wave, the melanin converts the electromagnetic wave into an acoustic one. After the decay of the electromagnetic wave, the soliton passes into the acoustic wave, retaining its content and potency. Soliton on the acoustic wave does not perceive the magnetic field, it directs attention to metabolic activities [40-45]. To sum up, it should be stated that biological piezo and pyroelectrics are capable of transforming mechanical and thermal energy into electricity (electric field). This field changes the energy state of neighboring cells, integrates the whole organism, regulates metabolic processes, and directs the growth of the organism. It records the perceptual impression not only in the brain, but also in the entire body [46,47]. The electronic interpretation of a living organism turns out to be extremely inspiring, because it takes into account the fact that the organs receiving information from the environment are not only sensory receptors, perceptual and motor systems, but also the entire biological mass of the organism understood as biological piezoelectrics and semiconductors [48-52].
The action of solitons and spins in the human biological system provides the basis for seeing the human psyche in a different light than current psychology. Spin and soliton waves create a different image from the electromagnetic wave received by the sight receptor. It can be concluded that we are dealing with the second center that creates the structure of the image of the world and is responsible for the psychophysical development of man, health and disease. In current biology and psychology, there is no room for solitons and spin functions that quantum physics deals with.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pubmed]
Citation: An R (2023) Soliton Phenomena in the Process of the Functioning of the Heart. J Hematol Thrombo Dis.11.533.
Received: 14-Jan-2023, Manuscript No. JHTD-23-21730; Editor assigned: 16-Jan-2023, Pre QC No. JHTD-23-21730 (PQ); Reviewed: 30-Jan-2023, QC No. JHTD-23-21730; Revised: 06-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. JHTD-23-21730 (R); Published: 13-Feb-2023 , DOI: 10.35248/2329-8790.23.11.533
Copyright: © 2023 An R. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.