Entomology, Ornithology & Herpetology: Current Research
Open Access
ISSN: 2161-0983
ISSN: 2161-0983
Research Article - (2014) Volume 3, Issue 1
Our objective was to study the life fecundity tables of Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) reared on tobacco cv. Anand-119 under controlled condition at 26 ± 1°C. The data revealed that there was no mortality during egg stage and the maximum duration of egg, larval and pupa was 4, 25 and 9 days, respectively. The number that survived from 100 eggs to adult emergence was 58 individuals. The pre-oviposition period was ranged from 39th to 40th days of pivotal age. Females contributed highest number of progeny (mx = 580.13) in the life cycle on the 44th day of pivotal age. The net reproductive potential (Ro) obtained was 786.84 females with the mean length of generation period (T) 43.49 days. The innate capacity for increase (rm) and finite rate of increase (λ) were found to be 0.1542 and 1.1667 females / female / day, respectively with a weekly multiplication rate (λ)7 of 2.94 times. The hypothetical F2 females were found to be 619121.30. The % contribution of eggs, larvae, pupae and adults were 54.81, 44.43, 0.65 and 0.08, respectively at stable age distribution of S. lituraon tobacco.
<Keywords: Life fecundity tables; In vitro; Spodoptera litura; Tobacco
Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum Linnaeus) is an important nonfood narcotic cash crop, belonging to family Solanaceae. Tobacco is grown in almost all parts of world. In India, tobacco is grown on 0.45 M ha of area (accounting for only 0.31% of net cultivated area in the country) with 750 M kg production. The world tobacco production is 7 billion kg, China occupying the first place with 2.35 billion kg. India stands second in tobacco production and exports in the world. Tobacco earns annually 4,402 crores as foreign exchange and 13,853 crores as excise revenue. Its total contribution to the national economy is 18,255 crores. Tobacco crop directly or indirectly supports 36 million people engaged in production, processing, marketing and exports which includes 6 million farmers and 5 million people involved in bidi rolling and tendu leaf-plucking. Thus, the crop is a lifeline for sizeable chunk of population, particularly rural women, tribal and other weaker sections of the society [1]. Spodoptera litura (F.) commonly known as the tobacco caterpillar is generalist herbivore infesting more than 290 species of plants belonging to 80 to 99 families [2], causes significant damage to different types of tobacco [3] both under nursery and field conditions. Damage due to S. litura in tobacco nursery varied from 80 to 100 per cent [4] and 10-25 per cent in the field crop [5] and reduces 23 to 50 per cent tobacco yield [6]. In the nursery the young larvae of S. litura feed gregariously on leaves in the early stage and 1st instar larvae scrap the epidermal layer causing papery leaves and 3rd and 4th instar larvae are particularly voracious feeders which are migrate to other seedlings as they grow in size and become solitary. In case of serious infestation, larvae completely destroy the seedlings necessitating resowing of the nursery [7]. Application of life table, rate of increase and stable age distribution are almost as diverse as the other insects. Such life tables may be analyzed to determine which stage, the life cycle of insect, contribute the most to the population trend [8] and for determining the reproductive ability and biotic potential, statistics was developed to explain population increase [9,10]. The statistics is the innate capacity of increase, which is also called as true intrinsic rate of natural increase (rm). The study determines the finite rate of increase, which signifies the number of individuals added to the population per head per unit. Since, tobacco cv. 119 is grown very extensively in middle Gujarat and no detailed information regarding life fecundity tables of tobacco leaf eating caterpillar Spodoptera litura at constant laboratory temperature is available, keeping the facts in view the preset study was conducted at Bidi Tobacco Research Station, Anand Agricultural University, Anand, Gujarat (India).
Insect culture
The laboratory culture of S. litura was maintained on tobacco cv. Anand-119 leaves for two consecutive generations at constant temperature of 26 ± 1°C in Research Laboratory of Bidi Tobacco Research Station, AAU, Anand. For the study, newly emerged adults from the laboratory culture were kept for egg lying in 30×30 ×45 cm wooden cages (Figures 1A and 1B). The sides of the cage were covered with muslin cloth. Tender leaves of respective host plant were inserted into a conical flash containing fresh water to keep them fresh and turgid and were placed into the cage for resting and oviposition of the adults. Egg masses laid on white muslin cloth or on leaves were used for this study.
Life table studies
In order to construct life tables, freshly 100 eggs were collected carefully from the egg masses in the cage with the help of wet camel hair brush and placed in ten Petri dishes (1.0×5.0 cm) in batches of ten each (Figures 1C and 1D). On hatching, the larvae were transferred individually into plastic vials containing leaves of tobacco cv. Anand-119. Fresh leaves were provided daily in the morning. Observations on hatching, larval development, formation of pupae and successful emergence of adults and fecundity were recorded daily. Age specific mortality in different developmental stages like eggs, larvae, pupae and adults were also recorded. With a view to determine the age specific fecundity, total number of adult emerged on the same day were caged in acrylic oviposition cage (30×30×30 cm.) for oviposition. As the sex ratio was 1:1, the number of eggs obtained / female were divided by two to get the number of female birth (mx). The column headings for the construction of the life fecundity tables proposed by [10] and [11] were used in this study, viz., x = Pivotal age in days; lx = Survival of female at age ‘X’; mx = Age schedule for female births at age ‘X’.
Net reproductive rate (Ro)
The values of ‘x’, ‘lx’ and ‘mx’ were calculated from the data given in life tables. The sum total of the products ‘lxmx’ is the net reproductive rate (Ro) [12]. The ‘Ro’ is the rate of multiplication of population in generation measured in terms of females produced per generation. The number of times a population would multiply per generation was calculated by the following formula, Ro = Σlxmx.
Mean duration of generation (Tc)
The appropriate value of generation time (Tc) i.e. the mean age of the mothers in a cohort at the birth of female offspring was calculated by using the following formula:
Tc = Σxlxmx/Ro
Innate capacity for increase (rm)
Total number of individuals survived and mean number of female offspring births were recorded at each age interval. From these data, the arbitrarily value of ‘rm (rc)’ was derived by the following formula:
rm = logeRo/Tc
Tc = Mean generation time
The intrinsic rate of increase (rm) was subsequently calculated from the arbitrarily ‘rm’ by taking two trial values selected on either side of it differing in the second decimal place and substituting in the equation Σe7–rmx. lxmx [11]. Thus, the two values of the equation were found which lay immediately above or below 1097.
The values of e7–rmx. Lxmx obtained from the two trials were plotted against their respective arbitrarily ‘rm’ which give a straight line. The straight line was intersected by a vertical line drawn from the described value at 1097.The two point of intersection gave the accurate ‘rm’ value. The precise generation time (T) was calculated by using the following formula: T = logeRo/rm.
The finite rate of natural increase (λ)
The number of females per female per day i.e. finite rate of increase was determined as: λ = antilog erm
From this data, the weekly multiplication of the population was calculated. The hypothetical F2 females were also be worked out with the formula (Ro)2.
Stable age distribution
The stable age distribution (per cent distribution of various age groups) of S. lituraon tobacco cv. Anand-119 was worked out with the knowledge of ‘rm’ and the age specific mortality of the immature and mature stages were also calculated. The stable age distribution table was constructed by following the method of [11] and [13]. The ‘Lx’ (Life table age distribution) was calculated from the ‘lx’ table by using the following formula: Lx = Life table age distribution = (lx + (lx + 1))/2. Per cent distribution of each age group (x) was calculated by multiplying the Lx with e–rm (x + 1). By putting together the percentage under each stage viz., egg, larval, pupal and adult stages, the expected per cent distribution was work out.
Life table for computing life expectancy of S. litura
Life expectancy of the pest was worked out by using columns x, lx, dx, 100qx, Lx, Tx and ex.
Where, x = Pivotal age (days); lx = Number of surviving at the beginning of age interval out of 100; dx = Number dying during ‘x’; 100qx = dx.100 /lx, Mortality rate per hundred alive at the beginning of age interval; Lx = lx + (lx + 1) /2, Alive between x and x + 1; Tx = Number of individual’s life days beyond ‘x’ and 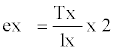 , Expectation of further life Equations were formulated after processing the data in MS-Excel.
, Expectation of further life Equations were formulated after processing the data in MS-Excel.
The results on number of individuals survived during development of S. litura on tobacco cv. Anand-119 revealed that there was no mortality during egg stage and the maximum durations of egg, larva and pupa were 4, 25 and 9 days, respectively (Table 1). The number that survived from 100 eggs to adult emergence was 58 individuals. Similar results were reported by [14] at Anand (Gujarat) he studied the life fecundity tables of S. lituraon different varieties of tobacco and the data revealed that the highest survival of immature stages was recorded on GTH-1 followed by GT-5 and GT-7. According to [15], S. litura takes 51 and 55 days to complete its life cycle on mungbean and urdbean, respectively. In both crops survival sharply decreased initially, and then gradual decreased until the end of the generation and the maximum apparent mortality during the egg stage was 37 and 32 per cent on mungbean and urdbean, respectively. The survival fraction was lower and the mortality survival ratio was higher at the egg stage in both crops. The total generation mortality was similar (0.3979) in both crops. The mean length of one generation was higher on urdbean (36.99 days) as compared to mungbean (33.64 days).
| No. of eggs | survived Number (Days) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Egg stage (0-4) | Larval stage (5-29) | Pupal stage (30-38) | |
| 10 | 10 | 9 | 5 |
| 10 | 10 | 7 | 6 |
| 10 | 10 | 9 | 7 |
| 10 | 10 | 10 | 6 |
| 10 | 10 | 8 | 7 |
| 10 | 10 | 5 | 5 |
| 10 | 10 | 7 | 6 |
| 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 |
| 10 | 10 | 7 | 6 |
| 10 | 10 | 6 | 5 |
| 100 | 100 | 78 | 58 |
Table 1: Survival of different life stages of Spodopteralitura on tobacco cv. Anand-119.
Life fecundity tables were constructed to determine the survival of female (lx) and age specific fecundity (mx). The life fecundity data presented in Tables 2 and 3, Figure 2 indicated that pre-oviposition period ranged from 39th to 40th days of pivotal age. Females deposited first batch of eggs on 41st day and stopped it after 47th day with lx values being 0.58 and 0.10, respectively. The lx decreased gradually after 42nd day of pivotal age due to adult mortality. The females contributed highest number of progeny (mx = 580.13) in the life cycle on the 44th day of pivotal age.
| Pivotal age in days (x) | Survival of female at different age interval (lx) | Age schedule for female birth (mx) | (lxmx) | (xlxmx) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-38 | Immature stages | |||
| 39-40 | Pre-oviposition stage | |||
| 41 | 0.58 | 86.7 | 50.29 | 2061.73 |
| 42 | 0.53 | 215.17 | 114.04 | 4789.68 |
| 43 | 0.47 | 460.77 | 216.56 | 9312.16 |
| 44 | 0.45 | 580.13 | 261.06 | 11486.57 |
| 45 | 0.30 | 348.51 | 104.55 | 4704.89 |
| 46 | 0.13 | 252.37 | 32.81 | 1509.17 |
| 47 | 0.10 | 75.35 | 7.54 | 354.15 |
| Ro=∑lxmx =786.84 |
∑xlxmx =34218.35 |
|||
Table 2: Life table (for female) and age specific fecundity of Spodopteralituraon tobacco cv. Anand-119.
| Population growth statistics | Formula | Calculated values |
|---|---|---|
| Net reproductive rate | Ro=∑lxmx | 786.8426 |
| Mean length of generation | Tc=∑xlxmx/Ro | 43.48817 days |
| Innate capacity for increase in numbers | 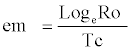 |
0.1534 Females/female/day |
| Arbitrarily 'rm' (rc) | 0.15 and 0.16 | |
| Corrected 'rm' | ∑e7-rmx.lxmx | 0.1542 Females/female/day |
| Corrected generation time | 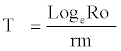 |
43.25 days |
| Finite rate of increase in numbers | λ = antilog erm | 1.1667 Females/female/day |
| Weekly multiplication of population | (λ)7 | 2.9425 |
| Hypothetical F2 females | (Ro)2 | 619121.3 |
Table 3: Mean length of generation, innate capacity for increase in numbers and finite rate of increase in numbers of Spodopteralituraon tobacco cv. Anand-119.
The net reproductive potential (Ro) was worked as 786.84 females/ female with the mean generation time (T) was 43.49 days. Almost similar results were reported by [16] at 26°C they reported a net reproductive rate of (Ro) 799.82 days with the mean generation time of 41.08 days, respectively. The more or less similar results were also reported by [17] a net reproductive rate of 873.13 days females/female on castor. Bharathi [18] at Rajahmundry (Andhra Pradesh) found that the highest net reproductive rate (Ro) was 338.74 in lanka tobacco followed by hookah (310.38) and cigar wrapper (235.54). The results differed from those reported by [19] at Kandukur (Andrha Pradesh), who found that the net reproductive rate (Ro) was 324.59 females per female per day, potential fecundity (Pf) (1783.64) and mean generation time (27.84 days) of S. litura when reared on FCV tobacco. Sundaram [20] at TNAU (Coimbatore) studied the life tables of S. litura on cauliflower leaves treated with gibberellic acid and Pseudomonas fluorescence and they revealed that the value of net reproductive rate (Ro) was 420.05 and 360.90, indicating that the population of S. litura was able to multiply 420.05 and 360.90 times on the untreated and treated leaves in the generation time (T) of 33.18 and 34.03 days, respectively. The species had an intrinsic rate of natural increase of 0.179 and 0.170 females per day on untreated and treated leaves with a daily finite rate of increase (λ) of 1.199 and 1.188 females per day.
The fact that cultivar Anand-119 gave high fecundity rate or net reproductive rate could be due to the presence of high protein (13.78%) content, high total soluble sugar (TSS) 3.1g/00g content as well as the nitrogen content 2.20 per cent in the green leaves of the cultivar.
The intrinsic rate of increase (rm) and finite rate of natural increase in numbers (λ) was 0.1542 and 1.1667 females/female/day, respectively. Weekly multiplication of population was calculated 2.94 times per week. The hypothetical female’s population in F2 generation was 619121.30. The similar results were reported by [14] the intrinsic rate of natural increase in numbers (rm) ranged from 0.1503 to 0.1594 females per female per day on different varieties. Similarly, the finite rate of increases in numbers (λ) ranged from 1.162 to 1.173 females per female per day on GTH-1, GT-5 and GT-7 varieties of tobacco. However, [18] reported that the intrinsic rate of increase (rm) was maximum (0.2014) on hookah tobacco followed by lanka (0.1907) and cigar wrapper tobacco (0.1811).
The shortest mean generation time was 20.09 days recorded on hookah tobacco followed by cigar wrapper (30.23 days) and natu (30.49 days), whereas, the longest mean generation time 32.20 days on cigar filler. In the present investigation the contribution of each developmental stage towards the stable age distribution was also calculated (Table 4). The data showed that adults contributed only 0.09 per cent to the population of stable age and that of eggs, larvae and pupae was 54.82, 44.44 and 0.08 per cent, respectively.
| Pivotal age (days) 'x' | Lx | e-rm(x+1) | Lx.e-rm(x+1) | Per cent contribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.00 | 0.8571 | 0.8571 | 14.5748 |
| 1 | 1.00 | 0.7346 | 0.7346 | 12.4921 |
| 2 | 1.00 | 0.6296 | 0.6296 | 10.7070 |
| 3 | 1.00 | 0.5397 | 0.5397 | 9.1769 |
| 4 | 1.00 | 0.4626 | 0.4626 | 7.8656 |
| =54.8164 | ||||
| 5 | 1.00 | 0.3965 | 0.3965 | 6.7416 |
| 6 | 0.99 | 0.3398 | 0.3364 | 5.7204 |
| 7 | 0.97 | 0.2912 | 0.2825 | 4.8039 |
| 8 | 0.96 | 0.2496 | 0.2396 | 4.0750 |
| 9 | 0.96 | 0.2140 | 0.2054 | 3.4927 |
| 10 | 0.96 | 0.1834 | 0.1760 | 2.9936 |
| 11 | 0.95 | 0.1572 | 0.1493 | 2.5391 |
| 12 | 0.95 | 0.1347 | 0.1280 | 2.1762 |
| 13 | 0.95 | 0.1155 | 0.1097 | 1.8653 |
| 14 | 0.95 | 0.0990 | 0.0940 | 1.5987 |
| 15 | 0.94 | 0.0848 | 0.0797 | 1.3558 |
| 16 | 0.94 | 0.0727 | 0.0683 | 1.1621 |
| 17 | 0.93 | 0.0623 | 0.0580 | 0.9854 |
| 18 | 0.93 | 0.0534 | 0.0497 | 0.8446 |
| 19 | 0.92 | 0.0458 | 0.0421 | 0.7161 |
| 20 | 0.92 | 0.0392 | 0.0361 | 0.6138 |
| 21 | 0.92 | 0.0336 | 0.0309 | 0.5261 |
| 22 | 0.92 | 0.0288 | 0.0265 | 0.4509 |
| 23 | 0.92 | 0.0247 | 0.0227 | 0.3865 |
| 24 | 0.92 | 0.0212 | 0.0195 | 0.3312 |
| 25 | 0.92 | 0.0181 | 0.0167 | 0.2839 |
| 26 | 0.92 | 0.0156 | 0.0143 | 0.2433 |
| 27 | 0.90 | 0.0133 | 0.0120 | 0.2040 |
| 28 | 0.90 | 0.0114 | 0.0103 | 0.1749 |
| 29 | 0.90 | 0.0098 | 0.0088 | 0.1499 |
| =44.4353 | ||||
| 30 | 0.88 | 0.0084 | 0.0074 | 0.1256 |
| 31 | 0.88 | 0.0072 | 0.0063 | 0.1077 |
| 32 | 0.88 | 0.0062 | 0.0054 | 0.0923 |
| 33 | 0.88 | 0.0053 | 0.0047 | 0.0791 |
| 34 | 0.88 | 0.0045 | 0.0040 | 0.0678 |
| 35 | 0.88 | 0.0039 | 0.0034 | 0.0581 |
| 36 | 0.88 | 0.0033 | 0.0029 | 0.0498 |
| 37 | 0.88 | 0.0029 | 0.0025 | 0.0427 |
| 38 | 0.88 | 0.0024 | 0.0022 | 0.0366 |
| =0.6596 | ||||
| 39 | 0.58 | 0.0021 | 0.0012 | 0.0207 |
| 40 | 0.58 | 0.0018 | 0.0010 | 0.0177 |
| 41 | 0.58 | 0.0015 | 0.0009 | 0.0152 |
| 42 | 0.53 | 0.0013 | 0.0007 | 0.0119 |
| 43 | 0.47 | 0.0011 | 0.0005 | 0.0090 |
| 44 | 0.45 | 0.0010 | 0.0004 | 0.0074 |
| 45 | 0.30 | 0.0008 | 0.0002 | 0.0042 |
| 46 | 0.13 | 0.0007 | 0.0001 | 0.0016 |
| 47 | 0.10 | 0.0006 | 0.0001 | 0.0010 |
| =5.8807 | =0.0888 |
Table 4: Age specific distribution of Spodopteralituraon tobacco cv. Anand-119 (rm = 0.1542).
The computation of life expectancy table of S litura on tobacco cv. Anand-119 (Table 5) clearly showed that the life expectancy of newly deposited eggs was 15.06 days. Further, it has been clearly observed that the mortality rate was comparatively high at the age of 40 to 45 days, when the expectation of further life was reduced to 2.73 days from 15.06 days in the beginning. Almost similar observations of S. litura was recorded on tobacco and [14] at Anand and [18,21] at Rajahmundry also found more or less similar observations on life fecundity tables when S. litura reared on different tobacco hosts.
| Pivotal age (Days) (x) | Number of surviving to the beginning of age interval | Number of dying during ‘x’ | Mortality rate per hundred alive at beginning of age interval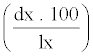 |
Alive between age ‘x’ and 'x+1'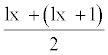 |
No. of the individual’s life days beyond ‘x’ | Expectation of further life 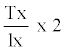 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (lx) | (dx) | (100 qx) | (Lx) | (Tx) | (ex) | |
| 0-5 | 100 | 4 | 4.00 | 100.5 | 753.00 | 15.06 |
| 5-10 | 96 | 2 | 2.08 | 96.5 | 652.50 | 13.59 |
| 10-15 | 94 | 0 | 0.00 | 94.5 | 556.00 | 11.83 |
| 15-20 | 92 | 2 | 2.17 | 92.5 | 461.50 | 10.03 |
| 20-25 | 92 | 4 | 4.35 | 92.5 | 369.00 | 8.02 |
| 25-30 | 88 | 6 | 6.82 | 88.5 | 276.50 | 6.28 |
| 30-35 | 88 | 24 | 27.27 | 88.5 | 188.00 | 4.27 |
| 35-40 | 58 | 28 | 48.28 | 58.5 | 99.50 | 3.43 |
| 40-45 | 30 | 20 | 66.67 | 30.5 | 41.00 | 2.73 |
| 45-50 | 10 | 0 | 0.00 | 10.5 | 10.50 | 2.10 |
Table 5: Life table for computing life expectancy of Spodopteralitura on tobacco cv. Anand-119.