Organic Chemistry: Current Research
Open Access
ISSN: 2161-0401
ISSN: 2161-0401
Research Article - (2015) Volume 4, Issue 2
Among the family of heterocyclic compounds, The nitrogen containing six membered heterocyle, the piperidine structural was the most dominant and very prevalent element in nature and often found to be naturally occurring bioactive compounds such as alkaloids. Piperidin-3-one derivatives are used as precursors for the synthesis of antimalarial agents febrifugine and Isofebrifugine. Piperidin-4-ones mostly display varied and potent biological properties such as antiviral, antitumour, analgesic, antimicrobial, fungicidal, herbicidal, insecticidal, antihistaminic, anti-inflammatory and anticancer. CNS stimulant and recent reports suggest that compounds containing piperidin-4-one moiety elicit excellent activity when aromatic substitutions are present at 2- and/or 6-positions. In this work, the compound N-nitroso-2,6- diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone has been prepared and analyzed. The product showed positive nitrogen test (Lassign test), a single spot in TLC and sharp melting point for the purity of the compound. The structure of the compound was further confirmed from the CHN analysis FT-IR, and 1H NMR Spectral data and the compound have being screened for its antimicrobial activity against gram positive bacteria Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus and Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli by using ciprofloxacin as standard and fungi Candida albicans by using cetramazole as standard. The compound exhibited significant activities against all the tested bacterial and fungal strains.
Keywords: N-nitroso-2; 6-Diphenylpiperidin-4-ones; Semicarbazone; NMR; IR; Antimicrobial activity
Among the family of heterocyclic compounds, The nitrogen containing six membered heterocyle, the piperidine structural was the most dominant and very prevalent element in nature and often found to be naturally occurring bioactive compounds such as alkaloids [1]. Piperidin-3-one derivatives are used as precursors for the synthesis of antimalarial agents febrifugine and isofebrifugine [2]. Piperidin- 4-ones mostly display varied and potent biological properties such as antiviral, antitumour [3], analgesic [4], antimicrobial, fungicidal, herbicidal, insecticidal, antihistaminic, anti-inflammatory, anticancer [3]. CNS stimulant and recent reports suggest that compounds containing piperidin-4-one moiety elicit excellent activity when aromatic substitutions are present at 2- and/or 6-positions [3]. Mannich reaction is one of the multicomponent reactions for the carbon-carbon and carbon heteroatom sequential bond formation. Mannich type condensation involving aromatic aldehydes, ammonium acetate and ketones having two active methylene groups, resulting in the formation of 2,6-diarylpiperidin-4-ones, was first reported by Noller and Baliah [5]. The extensive studies undertaken in the past on 4-piperidones have their relation to the synthesis of drugs and consequently from an essential part in the molecular frame work of important drugs. Also, these compounds have been found to be valuable synthetic intermediates for the synthesis of variety of natural products. Specifically, piperidine based chemical entities with aryl substituent at C-2 and C-6 of the piperidine ring has been documented as potent microbial agents [6]. The phenyl or para substituted phenyl substituent at C-2 and C-6 positions have a wide range of antimicrobial activity. Further, blocking of its keto group have also proved to exhibit antibacterial and antifungal activities [7]. The piperidine-4-ones and its derivates are biologically important class of compounds owing to their pharmacological activities and the presence of ring skeleton in a variety of alkaloids. The conformational features of piperidin-4-ones are quite interesting and thought provoking. Literature report reveals that, the derivatives of 2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-ones and their stereochemistry have been reported but however a much work on derivative like N-substituted semicarbazone have not been reported so far. This envisaged that in the present work, the synthesis of the derivative like N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone, and its characterization by CHN, IR and 1H NMR. An antimicrobial and antifungal property of N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone derivative was also evaluated.
All the solvents used were of spectral grade. The melting points of the compounds were measured in open capillaries and are uncorrected. The 1H NMR spectra were obtained on a Bruker Avance spectrometer at 300 and 100 MHz respectively by using tetramethylsilane (TMS) as an internal standard. Chemical Shifts are given in parts per million (ppm). Splitting patterns are designated as follows: s-singlet, t-triplet, and m-multiplet. The FT IR spectra were obtained on a Perkin-Elmer Spectrum paragon 1000 spectrometer. Microanalyses were performed on Vario Micro V2.2.0 CHN analyzer. The reactions were followed on precoated TLC plates (Silica gel 60 F254, Merck) visualizing the spots in iodine chamber.
Synthesis of 2, 6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one
A mixture of acetone (0.1 mol) and benzaldehyde (0.2 mol) and anhydrous ammonium acetate (0.05 mol) was heated in a boiling water bath maintaining the temperature 50-55°C with stirring until the colour of the solution changed to deep red orange. The solution immediately cooled in ice water, after cooling ether (100 ml) was added to it, the ether insoluble bispidine (2,4,6,8-tetra phenyl-3,7-diazabicyclo (3.3.1) nonan-9-one, m.p (235-236°C) was filtered off and 5 ml conc. HCl was added to the filtrate. The precipitated 2,6-diphenylpiperidine-4-one hydrochloride was collected by filtration and washed with 3:1 mixture of ether and ethanol. The hydrochloride (m.p 215-216°C) obtained was dispersed in minimum amount of acetone and ammonia solution was added drop wise to it until a clear solution was obtained. The clear solution was poured into cold water (500 ml) and solid obtained was filtered and dried. The solid obtained was recrystallized using ethanol (yield 25%) melting point 103-104°C [8] (Scheme 1).
Synthesis of N-nitroso-2, 6-diphenvlpiperidin-4-one
0.0l g of 2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one dissolved in the ethanolwater mixture (60 ml+40 ml) and add 1.0 ml of concentrated HCl to this solution, the solution heated and stirred at 49-55°C. Sodium nitrite dissolved in 25 ml of ethanol: water mixture (10 ml+15 ml) and take this solution in an addition funnel. This solution was added in drops over a period of 1.5 hours while the mixture was stirred at 50-60°C. After the addition was completed stirring continued for another 4 hours. To this reaction mixture about 75 ml of ether was added. The product soluble in ether was separated by using a separation funnel. The separated ether was allowed for evaporation. The solid obtained is recrystallized from ethanol [9] (Scheme 2).
Scheme 2
Synthesis of N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone
The compound N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone is prepared by dissolving N-Nitroso-2,6-dipheny lpiperidin-4-one in 10 ml of methanol and heated over a water bath at (50-60)°C. 1.0 g of semicarbazide hydrocholoride was dissolved in 3 ml of ammonia solution drop by drop, an equal amount of methanol was also added to it in 1:1 ratio. This solution was added to the above reaction mixture in three portions at an interval of 30 minutes. After the addition was completed the heating and stirring are continued at another five hours. Then the reaction mixture was poured into ice cold water with shaking. The pure solid separated are filtered washed with water and dried and purified through short column, m. p 150°C [10] (Scheme 3).
Antibacterial activity by disc diffusion method
Nutrient agar plates were prepared under steriled conditions and incubated overnight to detect contamination. About 0.2 ml of working stock culture was transferred into separate nutrient agar plates and spread thoroughly using a glass spreader. Whitman No.1 discs (6 mm in diameter) were impregnated in the test compounds dissolved in DMSO (200 mg/ml) for about half an hour. Commercially available drug disc (ciprofloxacin 10 μg/disc) was used as positive reference standard. Negative controls were also prepared by impregnating the disc of same size in DMSO solvent. The discs were placed on the inoculated agar plates and incubated at 37 ± 1°C for about 18-24 h. Antibacterial activity was evaluated by measuring the zone of inhibition against the test organism [11].
Antifungal activity by disc diffusion method
Sabouraud’s dextrose agar (SDA) medium was used for the growth of fungi and testing was done in Sabouraud’s dextrose broth (SDB) medium [12]. The subculture and the viable count were carried out by the same procedure used for in antibacterial studies except the temperature, which should be maintained at 28 ± 1°C for about 72 h. Similarly for disc diffusion method, the petridishes were incubated at 28 ± 1°C for about 72 h [13]. The same concentration of the test compound, solvent (DMSO) and cetramazole (standard) prepared previously were used for the antifungal studies.
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
The lowest concentration of the test compounds which caused apparently the inhibition of growth of organism, was taken as the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The minimum inhibitory concentration was recorded by visual observation after 24 h (bacteria) and 72-96 h (fungi) of incubation. The sterile distilled water and DMSO did not show any inhibition [14].
The compound N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone has been reported in this work. When analyzed the products showed positive nitrogen test (Lassign test), a single spot in TLC and sharp melting point for the purity of the compound. The product expected should have the following structure based upon stoichiometry of the reaction (Scheme 1). The structure was further confirmed from the CHN analysis FT-IR, and 1H NMR Spectral data
CHN analysis
The CHN analysis is used to determine the empirical formula and there by the molecular formula and double bond equivalence of the compound N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone. The CHN analysis data of the prepared compound was given in Table 1.
| C % | H% | N% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental value | 64.07 | 5.60 | 20.74 |
| Theoretical value | 64.09 | 5.63 | 20.77 |
Table 1: CHN analysis of compound N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone.
Calculation of empirical formula
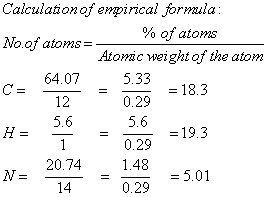
The molecular formula obtained as C18H19N5O2.
From this molecular formula the double bond equivalence has been calculated.
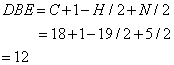
The double bond equivalent value 12 accounts the structure given in Figure 1 for two benzene ring, one cyclic ring, one C=N, one N=O, and one C=O group. The above structure is further confirmed from the IR and 1H NMR spectra.
IR spectral analysis
The important IR data are collected from the spectrum (Figure 2) obtained are given in the Table 2. Assignments of the frequencies were made on the basis of the literature values [15]. The formation of the compound N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone was realized by the analysis of IR data.The IR spectrum of the compound N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone shows a sharp band at 1637 cm-1 which corresponds to C=0 stretching frequency of amide. The literature value of carbonyl group was found to be 1640 cm-1. The band at 1607cm-1 shows the presence of C=N group. This confirms the formation of the product. The presence of a band at 3475 cm-1 is a proof for the presence of N-H of primary amide group. The stretching frequency at 2927 cm-1 corresponds to aromatic C-H stretching frequency. The literature value [16] for aromatic C-H is found to be 3100-3000 cm-1. The stretching frequency at 2857 cm-1 corresponds to cyclic C-H stretching of pyridine ring system, the literature value for such system is 3100-3000 cm-1 The band at stretching frequency 1495 cm-1 corresponds to N-N=0 group.
| Group | Stretching frequency (cm-1) |
|---|---|
| primary amide | 3450 |
| Aromatic C-H | 2927 |
| Cyclic C-H | 2857 |
| ON | 1563 |
| C=O | 1637 |
| N-N=O (Nitroso) | 1452 |
| Secondary amide | 1418 |
Table 2 : IR Data of compound N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone.
1H-NMR spectral analysis
To give further support for the structure of the compound, the important 1H NMR data are collected from the spectrum (Figure 3) obtained and are given in Table 3. Assignment of the chemical shift (δ) values are made on the basis of literature values [17].The 1H-NMR data show that the aromatic proton absorbs in the range δ7.2-7.4 since the compound in (Figure 1) contains two phenyl group. The benzylic protons at C2 and C6 absorb down field at 2.7 and 2.8 respectively. The methyl proton at C3 and C5 protons absorb at δ3.4 and 3.5 respectively. The secondary amine (-NH group) of semicarbazide moiety absorb at δ8.1 presents as a sharp singlet. The primary amine (-NH2 group) of semicarbazide moiety absorbs at δ10.1 as a sharp singlet. Based on the CHN analysis, IR and 1H NMR spectral data the structure of the compound was assigned is given in Figure 1
| Chemical shift (δ) | Nature of peak | No. of Protons | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7.2-7.4 | m | 10 | Aromatic proton |
| 5.5 | t | 1 | Benzylic proton at C-2 |
| 5.6 | t | 1 | Benzylic proton at C-6 |
| 3.4 | m | 2 | Methylene proton at C-3 |
| 3.5 | m | 2 | Methylene proton at C-5 |
| 10.1 | s | 2 | 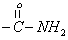 |
| 8.1 | s | 1 | 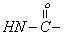 |
Table 3: 1H-NMR data of the compound N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone.
In vitro antimicrobial assay
The N-nitroso-2,6-diarylpiperidin-4-one and its semicarbazone derivative have being screened In vitro for its potency against bacterial strains such as, B. subtilis, S. aureus and Escherichia coli and fungal strains such as C. albicans and A. flavus. The In vitro activities of the test compound were studied using agar plates containing Sabourauds dextrose broth for fungi and in nutrient broth for bacteria. The test compound was tested against each microbial species [18]. The antibacterial and antifungal potencies of the test compound have being compared with ciprofloxacin (bacteria) and cetramazole (fungi). The antimicrobial inhibitions of test compound are expressed as the area of zone of inhibition and summarized in Table 4. The compound N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone display very good antifungal and moderate antibacterial activity. This marked antifungal and antibacterial activity may be due to the presence of high hydrophobic content of this family of compounds and the piperidine ring system. The compound containing the piperidin-4-one segment are more active against bacteria as compared to that of semicarbazone segment, presumptively due to the strong interaction of the later with the agar medium, which hinders their diffusion in agar medium.
| Compound | Zone of inhibition in mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial activity | Antifungal activity | |||
| E. coli | S. aureus | B.subtilis | C. albicans | |
| Test Compound | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 17 | 17 | 18 | NA |
| Cetramazole | NA | NA | NA | 17 |
Table 4: Antimicrobial activity of the synthesized compound.
The compound N-nitroso-2,6-diphenylpiperidin-4-one semicarbazone was synthesized and characterized by CHN analysis, IR and 1H NMR spectra. The spectral data supported and confirmed the formation of semicarbazone derivative. The compound was screened for its antimicrobial activity and they exhibited excellent activity against B. substilis, S. aureus and C. albicans.
Melting points were determined in open capillaries on a Thomas Hoover apparatus and are uncorrected. 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker WH 500 spectrometer using tetramethylsilane (TMS) as an internal standard. Chemical Shifts are given in parts per million (ppm). Splitting patterns are designated as follows: s-singlet, d doublet, t-triplet, quartet and m-multiplet. Mass spectra (MS) were recorded on Shimadzu LC-MS. The reactions were followed on precoated TLC plates (Silica gel 60 F254, Merck) visualizing the spots in iodine chamber.