Sociology and Criminology-Open Access
Open Access
ISSN: 2375-4435
ISSN: 2375-4435
Research Article - (2021)Volume 9, Issue 3
The present study aims to identify individuals' alcoholism in the society through qualitative method and thematic analysis. 18 people who were addicted to alcoholic beverages in Mashhad in 2020 were selected by purposeful sampling. Data was collected using narrative interview technique.
Contrary to other cultures in foreign countries, drinking alcohol, and due to the cultural and religious structure of the community, we cannot understand the dimensions of these social problems based on Western models. Because of religious and legal prohibitions on the drinking alcohol in the city, and even in the country, it distinguishes the country from other countries in the world. Hence, we are confronted with alcohol as a distraction, so it leads to drinking alcohol secretly, and therefore precise statistics are not available. We have only access to the statistics of Anonymous Alcoholics Association Unfortunately. Therefore, in order to plan for reducing this social problem, we must first accept drinking alcohol as a social problem, and then we can find a treatment.
Before quitting alcohol, alcoholics pin into a drinking cycle, and during this period they form an inconsistent and dispersed identity through alcohol, they join alcoholic networks and drowned into alcohol, and, therefore, they use alcohol as a tool to fill their past gaps; then after some time they start to quit when they enter the Anonymous Alcoholics Association with the help of their peers.
Alcoholism; Alcoholics subculture; Anonymous Alcoholics Association; Narrative interview; Thematic analysis
In this modern era, people who are using harmful poisonous things, such as drugs, psychotropic substances, and especially alcohol, want to be happy and to be relaxed for a moment, but they are unaware of the irreparable harm of these drugs affecting their souls and their bodies.
Doctors believe that alcohol consumption damages or eliminates liver cells, causing fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis and alcoholic cirrhosis and also leads to diabetes, stroke, anaemia, and many other diseases and finally it leads to death. The most common consequence of drinking alcohol is drunk drivers that endanger the lives of themselves and other people. Although alcohol may have many benefits to the body, its harms are ten times worst for the body, soul and society. Therefore, it should not be forgotten that drinking alcohol also has widespread social consequences; some people in their lives have alcohol directly or indirectly in their diet, and often suffer from moral and behavioural disorders. Many people understand that alcohol makes their habits changed, but they still continue to drink it and sometimes they recommend it to others and talk about its benefits. Some alcohol drinkers drink alcohol in their parties and thinks it brings them prestige.
Although in our law and our culture alcohol consumption is considered a crime and the majority of people are aware of its consequences, and on the other hand, unfortunately, there is no accurate statistics about the number of alcohol drinkers; there is, however, an increasing number of alcohol drinkers are going to the Anonymous Alcoholics Association to stop alcohol.
What exactly has happened? Why it is really enjoyable for some to find themselves in a situation that the most unreasonable behaviours’ and deeds are acceptable to them? Why do they drink something that has many physical and psychological side effects?
Since our people consider alcoholism as a social problem, it is addressed in the field of social pathology. According to Hirsch’s social bonding theory (1990), weak and lifeless interactions between the individual and his family members, dull emotions and feelings, the observation of alcohol consumption by the relatives lead to alcohol consumption and according to Bandura's social learning theory (1986), after alcohol consumption a stigma is attributed to the alcoholic person by the community, which create a new and deviant identity, and these people are usually rejected, which will have irreparable consequences for themselves and society.
Many researches in the country have focused on alcohol consumption and factors affecting it. A number of studies have been conducted to measure the tendency toward alcohol consumption (Pourfakari, Bairamnejad, Reza Aminlooye, Moyeri: 2004), some have studied the demographic and lifestyle of alcohol drinkers (GhajavandMozaffari: 2005; Ataei, Khorvash: 2010), and Some others have studied the trend or pattern of alcohol consumption (Qavidl, Samadi, KharmanBayz, Asadi, Feizi, Ahmadi, Abedini, Hosseini: 2008 ; Land, Asgari, Ma'tolian, RoyaSahebi, Rahimi, Chahar-e Avsian: 2009; Haghdoust, Imami, Esmaeili, SaberiNia, Nezhad-Qadari, Mehralhasani: 2009). Anumber of researches have examined negative patterns (Ahmadi, Karmbakhsh, Mehrzamy, Third, NajafiMansesh:2011), and others have also been affected by the prevalence of alcohol consumption (Hamdieh, Mahni, Asheri, Boroujerdi: 2002; Najafi, Awkh, Khalkhali, Nazifi, Farahi, Faqirpour : 2003; MortazaviMoghadam, Mother Shahiyan, Natural, Pejmanhkhah, Sadeghi: 2003; Zarrabi, Najafi, Shirazi, Borna, Sabahi, Nazifi: 2006). However, it can be said that the difference in domestic and international research on drinking alcohol is that drinking alcohol in country is investigated in terms of sociocultural aspect, but research out of country is often related to the amount of drinking, the quality of alcohol and its relationship with physical health, etc., and so far no research has been conducted on alcoholism in country; Therefore, considering psychological foundations, this research aimed to address sociological problem related to this issues.
In what families alcoholic people have grown up? What shortcomings they experience inside their families? Who are their relatives and friends? And why do they quit alcohol finally? In this research, we are going to give an answer to all of these questions in an appropriate and acceptable way.
Since the qualitative research is a type of research that its findings have not been obtained through statistical methods or other quantitative tools. This kind of research could include research on people's lives, their experiences, their behaviours’, their emotions and their feelings [1] therefore, in this research qualitative, collective case study [2] and narrative interview technique were used. First, the initial status was described (Where did the story begin), then narrative events were selected from a large number of experiences and presented as a set of coherent events (how events occurred one after another), and eventually at the end of the events, the situation is drawn [3] According to this definition and in this study, the life of alcoholic people has been told as a narrative. Anonymous Alcoholics Association in Mashhad was our target, we used purposeful sampling .In this sampling, and the participants are selected based on the researcher's judgment [4]
To theoretical saturation, data collection was stopped, so the number of interviewees was 8 women and 10 men, to analyse and interpret the data, thematic analysis was performed (Fielding & Fielding, 1986), and using the MAXDA 10 software, which investigated credibility, dependability, conformability and transferability [5]
Selection of alcoholic specifications
Introducing selected items
The number of interviewees of the Association are 8 women and 10 men and it is between 2 and 6 years that they quit drinking .The education of female alcoholics and men is between the secondary school and bachelor degree. The average age of women starting to quit is 32 years old and men are 38 years old (Tables 1 & 2).
| Column | Number | Stop drinking | Age | Education |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1st interviewee | 2.5 years | 35 | Civil Engineer |
| 2 | 2nd interviewee | 6 years | 51 | High school unfinished degree |
| 3 | 3rd interviewee | 5 years | 60 | High school unfinished degree |
| 4 | 4th interviewee | 4 years | 38 | B.A |
| 5 | 5th interviewee | 5 years | 40 | High school unfinished degree |
| 6 | 6th interviewee | 3 years | 37 | B.A |
| 7 | 7th interviewee | 6 years | 41 | B.A in political Science |
| 8 | 8th interviewee | 4 years | 35 | High school unfinished degree |
| 9 | 9th interviewee | 2 years | 33 | Secondary education |
| 10 | 10th interviewee | 4 years | 50 | B.A |
Table 1: Men addicted to alcohol.
| Column | Number | Stop drinking | Age | Education |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1st interviewee | 3 years | 26 | Secondary education |
| 2 | 2nd interviewee | 5 years | 41 | High school degree |
| 3 | 3rd interviewee | 6 years | 42 | High school degree |
| 4 | 4th interviewee | 4 years | 27 | High school Accountant degree |
| 5 | 5th interviewee | 4 years | 45 | Secondary education |
| 6 | 6th interviewee | 4 years | 39 | High school degree |
| 7 | 7th interviewee | 3.5 years | 25 | B.A |
| 8 | 8th interviewee | 5.5 years | 41 | High school degree |
Table 2: Women addicted to alcohol.
Findings
If we want to summarize and have an overview of people's alcoholism, each alcoholic person, when he/she starts alcohol and when he/she stops drinking in the Association of Alcoholics, follows this process:
Step one: The formation of identity crisis and cold interactions inside the family
Step two: Entering to community of alcoholic peers and drinking more alcohol
1- Joining the alcoholic communication network and start drinking alcohol by alcoholic relatives,
2- Drinking alcohol as a tool to fill past gaps;
3. Two much drinking alcohol and use of other alcohol supplements;
Step Three: Trying to stop drinking alcohol and get the message of the Association.
First, findings the research are discussed and then a brief description of interview are told in alcoholics’ point of view. In this study, we arrived at 20 axial categories [1] each of them was presented in brief, followed by the results of the research and a discussion of alcohol consumption in the community where alcoholics live.
In the following, to better understand the central axial, a part of the interviews is presented that provides a brief description of what participants expressed
Step one: The formation of identity crisis and cold interactions inside the family
Cool interaction category
The lack of intimate interactions between children and parents has led to frustrations; children suffer from shortcomings and gaps in the family leading to deprivation of empathy, emotional deprivation and deprivation of protection. “
This schema refers to the belief that one’s primary emotional needs will never be met by others.
“These needs can be described in three categories: Nurturance-needs for affection, closeness and love; Empathy-needs to be listened to and understood; Protection- needs for advice, guidance and direction. Generally parents
Are cold or Removed and don’t adequately care for the child in ways that would adequately meet the above needs [6].
Nima talks about the distance between himself and his father:
I had everything, but he brought us what he liked, for example, he went to pilgrimage trips for many times. At that time I wanted my dad bring me a toy, but he brought me a Messy T-shirt; I prefer to have toys at that time, I don’t know about t-shirts and clothes, and all these made me a huge gap between me and my father!
Arash says about leaving the school:
When I was a junior at high school, I tried to cheat. I got a zero point, and after that I never got back to school anymore.
Nima’s dream did not come true and also he had no companion:
I thought I could have been one of the top experts in the country, and I really had the ability to do that, I had a fantastic talent.
Sahar speaks about her marriage and the freedom she gained. She grew up in a family with dogmatic and religious parents:
When I got married I was so happy, I said, "oh, thanks God, I can polish my nails now, I can even have a make-up, I can cut my hair in different styles."
Maryam talks about her parent’s struggle and their separation:
My parents were separated, I have never seen my dad, but anyway, I lived with my mom.
Mohsen describes his excessive freedom in the family as follows:
I was living in the same place where I worked, so I went home very often, I had too much freedom, no one controlled me, I lived for myself, my father said nothing, my mother also was busy with my sister's children and nobody cares about me!
The category of identity crisis
To better understand the concept of reducing self-confidence in drinkers, first a definition of self-confidence is given and then some examples of self-confidence are presented according to interviews.
“A person with good self-confidence often has: a pleasant demeanors, a cheerful outlook on life, and a satisfaction with one’s personal life” [7] Therefore, it should be said that the people (potential drinkers) who have not yet tasted alcohol, have not believed in their abilities and talents in the process of socialization, and they see themselves as being humble or are scared to be rash with their words in front of others.
We bring here some interviews: Sanaz feels humiliation against her husband and tries to compensate it:
I got married, my husband did not like that people disobey him, he was a showy and pretentious person, and I felt I’m nothing, my husband said to me: "you are nothing, you don’t deserve me. One hundred girls want to marry with me!
Mehdi is a shy person and he is afraid of appearing in the society:
I am a conservative and a shy person, even hanging out with my friends, if I had no subject, I have nothing to say, I do not know what the reason is?
Gender Identity Crisis
In alcoholic families that gender is considered as a criterion of excellence, and masculinity has a special status and is formed as a social norm in such families, some alcoholic women who are still prone to alcoholism prefer to be male.
Alcoholic women also have a gender identity crisis and they wish they were born as a male!
Setare says:
In our families, boys are more respected, so we wanted to be a boy!
Marjan has also been trained like men:
My late grandfather always said: Marjan is a man. If it was the time to plow the garden, I was the first person to volunteer to help, I worked at the same time with the workers, but now if my husband asks me to put a glass there, if I do not want to, I won't! I do what I like. Now, I have a store with a masculine job, I work there, my husband is also there, but I do not accept his job so I go there, I like to interfere in masculine jobs.
The two categories of cold relationships and inconsistent identity formation between the individual in the family before becoming alcoholic will cause problems in the family over time. These issues are presented in the following categories Figure 1.
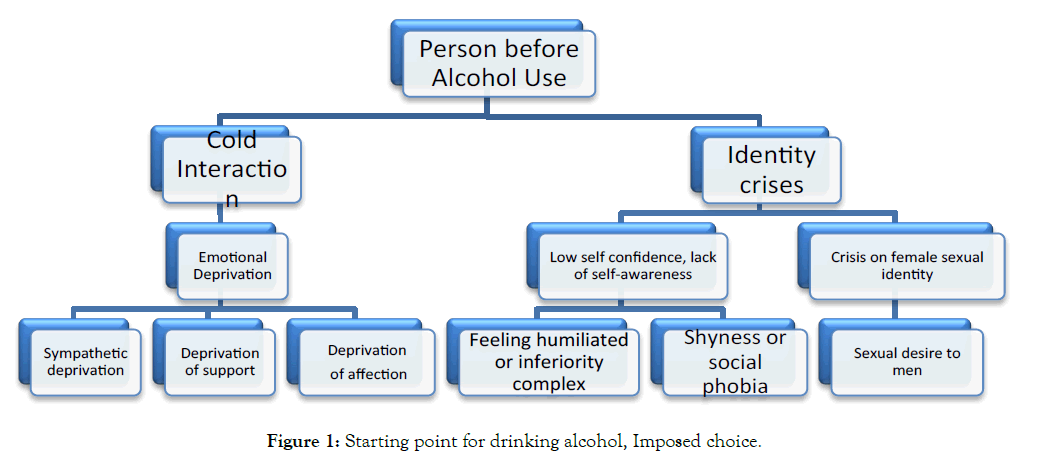
Figure 1: Starting point for drinking alcohol, Imposed choice.
The starting point for drinking alcohol, Imposed choice
This is when a person chooses to drink alcohol, but his choice is imposed because when he drinks alcohol for the first time he feels that his voids have been filled, but in the long run, given the irreparable effects of alcoholism, he becomes an alcoholic. Therefore, it should be said that as his choice is not conscious it will not be a rational choice (Coleman, 1990).
Saeed talks about his relatives and their habit of drinking alcohol and the time he started alcohol:
I was dealing with people who had a high social level, I saw them drinking, I did not think it was a bad habit, so I tried alcohol like them!
Drinking as an Instrument
After drinking alcohol for the first time, alcoholics use it as a tool for filling their voids in life:
Zohre speaks about her experience after drinking alcohol for the first time:
Drinking alcohol for the first time made me feels good, you are not in the real world anymore, you forget many things, for example, and who is your family? What is your location? You forget all these things.
Sara says about drinking alcohol and standing up against her husband:
There was a lot of physical conflict between us, my husband hit me, I tolerated it, but when I started drinking alcohol I used to stand in front of my husband. When he said something, I responded him, I was afraid of responding him before!
Mohsen drinks alcohol to relieve his humility:
But what I felt inside was a sense of tedium, I wanted to be something different, before I started to drink I wanted to say people that I am important, that I'm also important! Really I was nothing, because I had no education, and I was not an artist. But alcohol did it for me!
Arash says about his physical strength and his weakness, he says:
When I started to drink, my abilities went too high at work I worked three times more than usual, I earned 60 thousand to mans a day and drank alcohol 5 thousand to mans the same day.
Ehsan’s sexual desires also increase after drinking alcohol:
One reason that I used to drink alcohol was sex. It was sex that I continue drinking alcohol. Sex was so fantastic after drinking.
Nima is extremely curious about drinking alcohol:
I wanted to experience everything, it was in my gene, and I said to myself: Well, everybody drinks, why I shouldn’t drink? I drink alcohol to experience it.
Mahdi talks about drinking alcohol when he is with friends in leisure time:
Drinking alcohol was a fun for me, and I did not need to have fun anymore; we were sitting about 5 hours with my friends, watching movies, drinking, and it was the best moments in my life.
An alcoholic most important tools is “being happy”, or earning "selfconfidence" (sense of excellence, differentiation, and tolerance), along with other tools such as “disease elimination", "sexual needs", "Fun" and "arouse curiosity”. This period can be called the" golden age "of alcohol consumption. The following figure shows drinking alcohol as a primary and secondary tool.
An alcoholic after some time drinking alcohol, alcoholic person is matched with other people alcoholics and afterwards he/she is get used to drink alcohol continuously Figure 2.
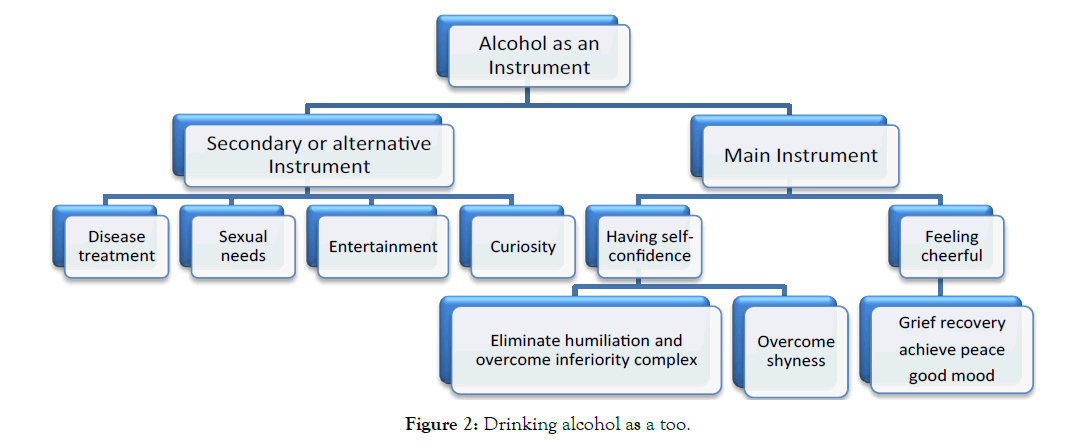
Figure 2: Drinking alcohol as a too.
Entering into the gatherings of alcoholics, people join the subculture of alcoholics and make excuses for their behaviour [8] and they gain power in this subculture, then, the process of alcoholism will speed up, in other words, this subculture will facilitate their path!
This alcohol sub culture uses certain terms such as matching, longing or compulsory consumption, time of drinking, using alcohol complementary, taking the message of the association for quitting, and so on.
Joining the subculture of alcoholics
Most alcoholics prefer to drink alcohol in groups such as Arash:
I didn’t drink alone at all, I drank when I was in groups, I could not even say no to my friends if they wanted to drink.
In the end, alcoholic women after alcoholism often drink alcohol when their spouses or their boyfriend drink alcohol.
Setare speaks:
In the gatherings of alcoholics, I liked my boyfriend as he was a good drinker. We drank together and enjoyed our time together. When I was alone I did not drink so much.
Times of drinking alcohol!
Alcoholics are more likely to drink alcohol at a particular time, such as when they are happy, angry, and sad and sometimes when couples start a quarrel or finish a quarrel.
Saeed: My wife and I were not emotionally involved anymore; our connection was just when we drank alcohol!
Zohre: It was full of joy, I was sad for almost always, I was bad, I was drinking, after sometime it changes to a pain killer, and it acts as a painkiller when you are in pain.
Addiction to Alcohol (Alcoholism)
Alcohol- drinking habit
Alcoholics arrive at a point where they can no longer leave alcohol. Sara says:
I quitted for many times, but I drank again, my children asked me: “Mom! Please don’t stop alcohol again, because you'll be angry afterwards”!
Forced drinking
It's not bad to hear Behzad's words about drinking excessive amount of alcohol.
When I was 19 years old, I told to myself what that alcohol is you are drinking? What are you doing with yourself? You’re not studying, you’re changed, you have to stop drinking alcohol and change yourself, but I could not do it anymore, it was a part of my soul.
Unwillingness to quit alcohol
Behzad also speaks about his unwillingness to quit alcohol:
I remember my parent's look, even their tears, I do care, but I could not stop drinking, alcohol was so powerful, I could not quit.
Need something more powerful than alcohol!
The alcoholic person never experience the first mood anymore after drinking for a long time, so he/she prefers to use drugs, and temporarily discards alcohol, so that she/he finds again the first experience of drinking alcohol.
Saeed:I was looking for something more powerful than alcohol to make me feel good, I used to drink opium, but, afterwards, I took heroin, crystal, glass and everything.
The negative effect of drinking alcohol
Now he is drunk, there is no longer a way to escape, and the consequences of alcohol addiction would be with him forever, now the alcoholic person is in "Black Period"!
Sanaz speaks ofhis abusive behaviors:
They said: "If somebody opposes you, don’t you upset?" I said: I kill them, I was bad tempered. Since I was drinking, I hit my husband a few times, now I get better.
Saeed says the effect of alcohol on his face:
I damaged my face, because I drank too much, once I stayed home about 15 days, I remember.
Zohreh says about her lack of spirituality in her life with alcohol."
On that time I never think about God! I would say: I can do everything, and besides, there's no God!
Reza tells us his friends left him only because he was a drunk:
Even those friends who did not drink left me, because every time we went go out together I started to drink!
These periods happen when alcohol is no longer meet the person’s needs, so he/she takes drugs to fulfill his/her needs. They twisted in the phenomenon of alcoholism so much that they are drowned in drinking alcohol and so they forced to drink it. Their need to drink makes them passive. Because of drinking too much alcohol and promiscuity, they are rejected from the non-alcoholic friends and relatives and the individual is spirituality deprived and turns away from God. In addition to the exclusion of the society and moral deprivation, there are other consequences of alcoholism, such as confusion, sleeping, and hallucination that are physical reactions and meaningless behaviors, aggression and disrespect that are behavioral reactions of drinking alcohol.
The effect of alcohol in the black period is as follows:
It's time to stop alcohol, there is no way around!
Something happens in her life that she stops alcohol forever; there is a strong will behind quitting drinking Figure 3. Maryam is scared to lose a worthy person in her life:
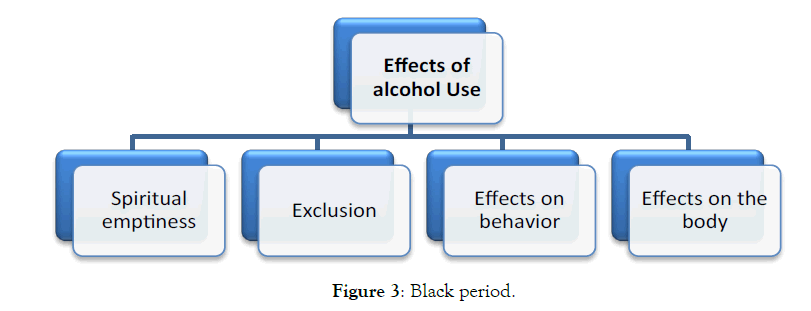
Figure 3: Black period.
My brother in law said: “go and quit alcohol, may be everything gets better”, I didn’t want to get divorce. I wanted husband.
When Set are quits alcohol there are no other alcoholic groups around her:
We decided, we repented, and we did not drink, since nobody comes to my husband's house.
Meyhan says her child never pays attention to her anymore:
My son once said to me, "Mom!" I do not want an addicted mom”, I always thought, "If my husband kicks me out, my son pays attention to me, but when he says so, I was worried!
Ehsan says of his illness because of alcohol:
I was drinking alcohol every day until I found I had digestive problems and the doctor told me: "You should not drink alcohol again, although I could not leave alcohol until I joined the Association!" The categories of quitting drinking are shown in the figure below:
Step Three: Trying to stop drinking alcohol and get the message of the Association
Anonymous alcoholics association
The alcoholic has already heard about the Association of Alcoholics
Anonymous, so when he decides to quit alcohol, according to the subculture of alcoholics, he receives a message from the association and decides seriously to quit alcohol with the help of the association Figure 4.
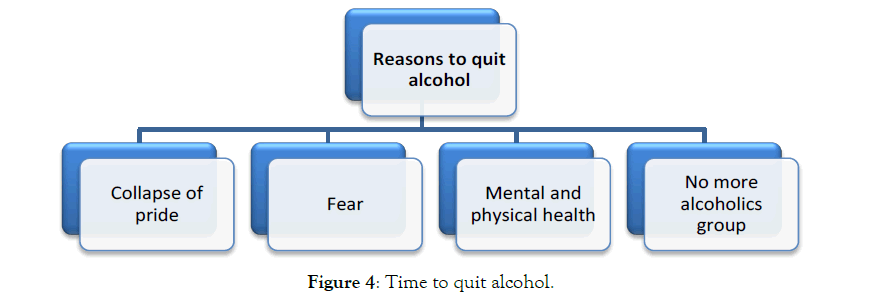
Figure 4: Time to quit alcohol.
After entering the Association, Setare felt God in a different way:
Before entering the Association, I thought God wants to torture me, just to take revenge on me!
Nima also finds no place better than the Association:
The only thing that makes me happy right now is just this Association!
Sahar talks about sympathy with the Association:
Only a person who takes part in the Association can understand us, yes, only a member in the Association can understand what our problem is.
Ehsan says that he will not be tempted after entering the Association:
Now I never want to drink alcohol and drugs, even sometimes my friends invite me to drink at the parties, I say no.
Maryam, after quitting alcohol, says about her power:
During these four years, I feel the power, the same power I had after the first drink, going to every session of the association, this feeling of power comes to me, and it calms me down!
An alcoholic will stop drinking alcohol when one of these four conditions happens:
Their alcoholic peers disappear; they suffer from physical and mental illness, their pride breaks down, and their fear of losing their spouse or child. Now the addicted person decides to quit, but how? When they get a message from their spouse or a friend to quit alcohol, then they take the first step to quit. When an alcoholic comes to the Anonymous Association, he/she starts to substitute old habits with the new ones, such as pleasure, sense of power; all are consistent with the cases in which a person used alcohol as a means to achieve his goals (Figure 5).
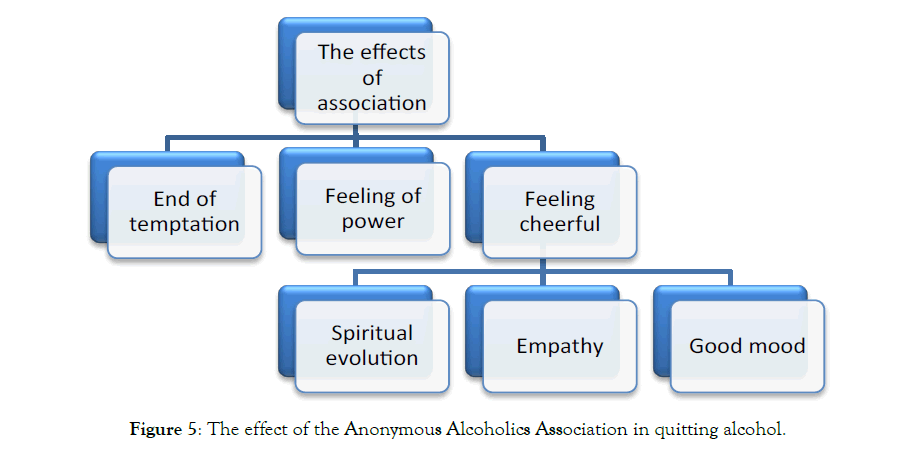
Figure 5: The effect of the Anonymous Alcoholics Association in quitting alcohol.
The person before starting alcohol in his/her childhood and adolescence faced with psychological problems. During this period some problems such as the existence of strict and authoritarian parents, lack of parental control, family conflict, lack of sympathy and lack of their support leads to a cold interaction in the family that causes identity crisis and low self-confidence. All these problems make the person shy (social phobia) and humiliated.
Teenagers who are in a state of dispersal and identity diffusion, often rejected and forgotten from their parents [9] In alcoholic women, the formation of identity crisis against their gender role will also lead to a gender identity crisis, in which they wish to be born as a male, therefore, they could not adapt themselves to the expectations of the community. The adolescent's biggest challenge is to solve the crisis of "his/her identity against his/her role" and that the teenager needs to organize his own needs and abilities to meet the society expectations [10].
A person, before alcoholization, first faces psychological problems inside the family, and after addiction to alcohol, he/she gradually involves in social problems, that is to say, the socialization and fixation of the personality that Parsons mentioned do not happen here (Ritzer et al., 2017). Regarding to Hirschi’s social bonding, Since alcoholics have psychological problems and they are not fully socialized, there is no strong moral bond between the individual and the society, so social participation is very low and there is no moral order in the society, However, the link between the individual and society and social and legal institutions is losing, and they do not believe in the laws so they start drinking alcohol and they drink alcohol with the help of alcoholic people around them.[11] Their Family life and their job positions affects by alcohol, and their failure to perform their duties in the family and business cause aggression and hatred in them.
If parents, close relatives and friends drink alcohol, it makes people around them to drink alcohol as well [12] Drinking alcohol changes to an instrument for achieving their main goals. These tools are good enough when a person is at the golden age of drinking alcohol, and in order to increase his/her pleasure, the person prefers to drink it among his alcoholic friends.
This subculture considers alcohol as a value and a norm. These norms are tools that alcoholic assemblies use to continue drinking. Lemert’s labeling theory confirms this fact [13].
The important issue is that alcoholism will have irreparable consequences. The community and even close relatives will show a severe reaction to this alcohol subculture due to the lack of common values and norms, and ultimately the alcoholics will alcohol by attending the Association of Alcoholics Anonymous, and the replacement is only done by being with alcohol-free friends .You can never truly extinguish a bad habit; you can just change it [14] be excluded so that it can be said that this separation goes up to the level [15] hence, observing the negative consequences of drinking alcohol and understanding the message of the association, the alcoholic chooses a replacement for alcohol by attending the Association of Alcoholics Anonymous, and the replacement is only done by being with alcohol-free friends .You can never truly extinguish a bad habit; you can just change it.
Drinking alcohol as a social problem!!!
In addition to mental and psychological damages, drinking alcohol has negative influence on family relationships. Besides the physical and psychological disorders that it produces, alcohol has negative social consequences. Negative individual consequences are losing job, unemployment and family problems and driving accidents. So alcoholism is considered as social problem.
Contrary to other cultures in foreign countries, drinking alcohol, and due to the cultural and religious structure of the community, we cannot understand the dimensions of these social problems based on Western models. Because of religious and legal prohibitions on the drinking alcohol in the city, and even in the country, it distinguishes the country from other countries in the world. Hence, we are confronted with alcohol as a distraction, so it leads to drinking alcohol secretly, and therefore precise statistics are not available. We have only access to the statistics of Anonymous Alcoholics Association Unfortunately. Therefore, in order to plan for reducing this social problem, we must first accept drinking alcohol as a social problem, and then we can find a treatment.
Since alcohol addicts have grown up in disorganized families, they show low self-confidence. Their behaviour is against social norms, alcohol as a fashion especially in parties. These alcoholic drinkers face a kind of social identity crisis, and to fill these gaps, as Bernard says: they do some unstable and irrational acts [16] to show their protest against the current situation. Their protest is not against ban on drinking, but against the loss of their rights, as social pressures such as the inability to achieve their rights in the family and, consequently, society, and many other issues that the person faces in life, and since one cannot widths and pressures, he/she consumes alcohol to compensate for this vacuum, therefore, social ties loose and existing social pressures strengthen the individual's tendency toward alcohol [17].
Another important point is that because drinking is forbidden by law, government has no control on alcohol beverages. So a significant percentage of alcohol beverages is handmade. If they meet the essential standards, they are too expensive. The government, therefore, cannot reduce the consumption of alcoholic beverages using factors such as high alcohol prices, less access and prohibition, and specific age restrictions. The government should so take other approach at the level of prevention and treatment.
1- Drinking alcohol should accept as a social problem.
2- Then families’ awareness through social institutions should be used to create warm and constructive interactions between parents and children to strength friendly environment under the control of parents.
3- And also to show physical, psychological and social consequences of alcohol, such as addiction.
4- In the field of rehabilitation of identity, more advertisement should be done about the Association of Anonymous Alcoholics, so that as soon as the individual leaves the Association, they never start drinking alcohol again.
5- We should note that there are people who do not still start drinking alcohol in the Association of Anonymous Alcoholics again, but they have a tendency to drink, so they should be treated as a patient, since it leads to more drinking alcohol.
Citation: Rezazadeh M, Afsari A, shadloo N (2019) The Cold Relationships inside Families, the warm Relationships among Alcoholic Drinkers: Research on Alcohol Addiction. Social and Crimonol 8: 206.
Received: 02-Feb-2021 Accepted: 03-Feb-2021 Published: 10-Feb-2021 , DOI: 10.35248/2375-4435.21.9.206
Copyright: © 2021 Rezazadeh M, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.