Chemotherapy: Open Access
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-7700
ISSN: 2167-7700
Short Communication - (2022)Volume 10, Issue 4
We performed in 1975, the first heterotransplantation of invertebrate A.O in nude mouse, then a double heterotransplantation of human tumor and axial organ next to this last one, always in nude mouse: The human tumor was rejected in 50% of observed cases. Some years later, we found that A.O cells exerted an induced and spontaneous cytotoxicity against SP2 and MBL2 mouse tumoral cells. Recently, we discovered a sea star Igkappa gene with immune properties. This gene was first, inserted in a CMV (cytomegalovirus) and finally in a plasmid called «young» plasmid second, in HeK human cells to produce the specific protein. The induced «young» protein exerted a spontaneous cytotoxicity against osteosarcom cells (U2oS cells) against A-375 melanome cells and Hela cells.
Invertebrates; Vertebrates; Cloning; CMV; HEK cells
In 1975, Leclerc transplanted with success an invertebrate organ: The sea star axial organ (a primitive lymphoïd organ) in nude mouse then risked a double hetero transplantation always in nude mouse: it was composed of a sea star axial organ one and a human tumor skin one besides the precedent one, under the skin of nude mouse, in back position [1]. In 1983, Luquet and Leclerc shown that the axial organ cells (AO cells), exerted a spontaneous and induced cytotoxicity against mouse SP2 myeloma cells and MBL2 cells [2]. The AO cells included essentially lymphocytes and phagocytes 40 years later, we discovered a sea star Igkappa gene, with immune properties [3,4]. 40 years later, we discovered a sea star Igkappa gene, with immune properties. We have studied the behaviour of the «young» protein secreted by the sea star Igkappa gene, in front of human malignant: A-375 melanome cells, human Osteosarcome cells (U2oS cells) and human malignant cells Hela, by the use of plasmids. In the present time we study the protein issued from HeK cells against mammal cancerous cells.
Animals
• Asterias rubens, a sea star was collected at Arcachon (France)/ the A.O (axial organ) was excised.
• With pinces and passed or not in antibiotics (penistreptomycin) according to the used method. • Nude mice were purchased by the CSEAL-CNRS Orléans-La source.
• Mouse SP2 and MBL2 cells were cultured in our laboratory. Gene cloning in a cytomegalovirus was done, from the sea star Igkappa gene. It constitutes the «promoter».
• Following steps as plasmid realization in correlation with the promoter, plasmid amplifications, transfections were performed [5].
• Gene cloning in HeK human cells was at last realized; the protein is actually studied against human mammal cancerous cells [6]. A control of cell viability was done with doxorubicine.
• Recalling of cloning in N-terminal pCMV (Figure 1).
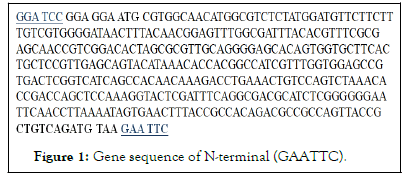
Figure 1: Gene sequence of N-terminal (GAATTC).
A-375 human melanome cells were used. They were transfected by plasmids, after electroporation, at time t=0. AMAXA process or by classical electroporation for U2oS cells and Hela cells. At time t=24 h, Cell suspensions were put on slides. Observations were realized with an optical microscope or by spectrophoto metry (Figure 2) [7].
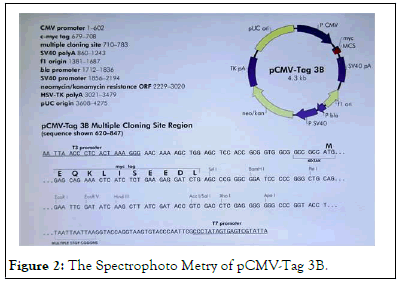
Figure 2: The Spectrophoto Metry of pCMV-Tag 3B.
• In 50% of observed cases, human skin cancer hetero transplantation was rejected by axial organ one in nude mouse: Extra-blood vessels were observed between the 2 hetero transplantations under the skin of the nude mouse. An antiserum (anti A.O cells) labelled many axial organ cells (mainly lymphocytes) which were surrounding cancerous human cells in the concerning hetero transplantation.
• In 30% of observed cases, A.O cells exert an induced and spontaneous cytotoxicity against Mouse SP2 cells.
• The protein «young», also named: Invertebrate primitive antibody exert a spontaneous cytotoxicity 24 hours after transfection against A-375 melanome cells, U2oS cells and Hela cells. Percentages are expressed in Figure 3.
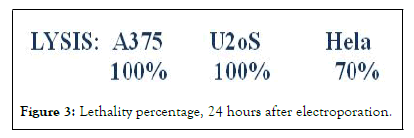
Figure 3: Lethality percentage, 24 hours after electroporation.
The young protein induces a lysis of mammal cancerous cells (unpublished results). First results show the activity of doxorubicine against these last ones (Table 1).
• Western blots do not confirm, the protein expression because of the high lethality of cancerous cells which is obtained (The peak of the protein in western blots would be situated at 12.000 daltons).
• Controls: A-375 cells, U2oS, Hela cells treated with alone electroporation show a weak lethality.
• Results with the young protein issued from HeK cells are promising.
In a general way these results are of particular importance and show undoubtly that axial organ cells from the Asterias rubens lymphoid organ exert a spontaneous cytotoxicity, and in certain cases, an induced cytotoxicity against Cancerous Vertebrate cells. Whatever the cloning it seems these results are reproducible.
[Crossref] [Google scholar] [Pubmed].
[Crossref] [Google scholar] [Pubmed].
[Crossref] [Google scholar] [Pubmed].
[Crossref] [Google scholar] [Pubmed].
[Crossref] [Google scholar].
[Crossref] [Google scholar] [Pubmed].
Citation: Leclerc M (2022) Xenografts and Genomic in Cancer Research from Invertebrates to Vertebrates with the Sea Star as a Model of Study. Chemo Open Access. 10:159.
Received: 30-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. CMT-22-17175; Editor assigned: 01-Apr-2022, Pre QC No. CMT-22-17175 (PQ); Reviewed: 13-Apr-2022, QC No. CMT-22-17175; Revised: 21-Apr-2022, Manuscript No. CMT-22-17175 (R); Published: 02-May-2022 , DOI: 10.4172/2167-7700.22.10.159
Copyright: © 2022 Leclerc M. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credit.